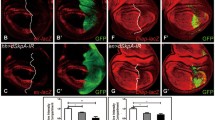
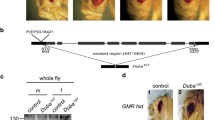
Abstract—
The ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS) is an important regulator of the main cellular processes. The components of the UPS are involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, signal transduction, the cell response to DNA damage, metabolism, and transcription control. E3 ubiquitin ligases (the enzymes that covalently attaches ubiquitin to target proteins) play a key role in the functioning of the UPS. The Drosophila tumor suppressor Hyd (hyperplastic discs) is one of the most interesting E3 ligases; it is required for the regulation of proliferation, growth, and cell differentiation. The study of hyd mutations in different tissues of Drosophila demonstrated that depending on the cellular context, Hyd can not only perform proteolytic functions associated with protein degradation, but can also, interacting with other proteins and/or nucleic acids, act as an important regulator of cellular processes.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Finley D. 2009. Recognition and processing of ubiquitin-protein conjugates by the proteasome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 78, 477–513.
Schnell J.D., Hicke L. 2003. Non-traditional functions of ubiquitin and ubiquitin binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 35857–35860.
Mukhopadhyay D., Riezman H. 2007. Proteasome-independent functions of ubiquitin in endocytosis and signaling. Science. 315, 201–205.
Hicke L. 2001. A new ticket for entry into budding vesicles – ubiquitin. Cell. 106, 527–530.
Kirisako T., Kamei K., Murata S., Kato M., Fukumoto H., Kanie M., Sano S., Tokunaga F., Tanaka K., Iwai K. 2006. A ubiquitin ligase complex assembles linear polyubiquitin chains. EMBO J. 25 (20), 4877–4887.
Pickart C.M., Fushman D. 2004. Polyubiquitin chains: polymeric protein signals. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 8, 610–616.
Bernassola F., Karin M., Aaron Ciechanover A., Melino G. 2008. The HECT family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: multiple players in cancer development. Cancer Cell. 14, 10–21.
Sun Y. 2006. E3 ubiquitin ligases as cancer targets and biomarkers. Neoplasia. 8, 645–654.
Deshaies R.J., Joazeiro C.A.P. 2009. RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 78, 399–434.
Yang Y., Fang S., Jensen J.P., Weissman A.M., Ashwell J.D. 2000. Ubiquitin protein ligase activity of IAPs and their degradation in proteasomes in response to apoptotic stimuli. Science. 288, 874–877.
Fang S., Jensen J.P., Ludwig R.L., Vousden K.H., Weissman A.M. 2000. Mdm2 is a RING finger-dependent ubiquitin protein ligase for itself and p53. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 8945–8951.
Deshaies R.J. 1999. SCF and cullin/RING H2-based ubiquitin ligases. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 15, 435–467.
Chang L., Barford D. 2014. Insights into the anaphase-promoting complex: A molecular machine that regulates mitosis. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 29, 1–9.
Scheffner M., Nuber U., Huibregtse J.M. 1995. Protein ubiquitination involving an E1–E2–E3 enzyme ubiquitin thioester cascade. Nature. 373, 81–83.
Wenzel D.M., Lissounov A., Brzovic P.S., Klevit R.E. 2011. UBCH7 reactivity profile reveals parkin and HHARI to be RING/HECT hybrids. Nature. 474, 105–108.
Martin P., Martin A., Shearn A. 1977. Studies of l(3)c43hs1 a polyphasic, temperature-sensitive mutant of Drosophila melanogaster with a variety of imaginal disc defects. Dev. Biol. 55, 213–232.
Mansfield E., Hersperger E., Biggs J., Shearn A. 1994. Genetic and molecular analysis of hyperplastic discs, a gene whose product is required for regulation of cell proliferation in Drosophila melanogaster imaginal discs and germ cells. Dev. Biol. 165, 507–526.
Kozlov G., Nguyen L., Lin T., De Crescenzo G., Park M., Gehring K. 2007. Structural basis of ubiquitin recognition by the ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domain of the ubiquitin ligase EDD. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 35787–35795.
Tasaki T., Mulder L.C., Iwamatsu A., Lee M.J., Davydov I.V., Varshavsky A., Muesing M., Kwon Y.T. 2005. A family of mammalian E3 ubiquitin ligases that contain the UBR box motif and recognize N-degrons. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 7120–7136.
Matta-Camacho E., Kozlov G., Menade M., Gehring K. 2012. Structure of the HECT C-lobe of the UBR5 E3 ubiquitin ligase. Acta Crystallogr. F: Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 68, 1158–1163.
Deo R.C., Sonenberg N., Burley S.K. 2001. X-ray structure of the human hyperplastic discs protein: An ortholog of the C-terminal domain of poly(A)-binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 4414–4419.
Lim N.S., Kozlov G., Chang T.C., Groover O., Siddiqui N., Volpon L., De Crescenzo G., Shyu A.B., Gehring K. 2006. Comparative peptide binding studies of the PABC domains from the ubiquitin-protein isopeptide ligase HYD and poly(A)-binding protein. Implications for HYD function. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 14376–14382.
Gateff E. 1994. Tumor suppressor and overgrowth suppressor genes of Drosophila melanogaster: Developmental aspects. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 38 (4), 565–590.
Lee J.D., Amanai K., Shearn A., Treisman J.E. 2002. The ubiquitin ligase hyperplastic discs negatively regulates hedgehog and decapentaplegic expression by independent mechanisms. Development. 129, 5697–5706.
Pertceva J.A., Dorogova N.V., Bolobolova E.U., Nerusheva O.O., Fedorova S.A., Omelyanchuk L.V. 2010. The role of Drosophila hyperplastic discs gene in spermatogenesis. Cell Biol. Int. 34, 991–996.
Flack J. E., Mieszczanek J., Novcic N., Bienz M. 2017. Wnt-dependent inactivation of the Groucho/TLE corepressor by the HECT E3 ubiquitin ligase Hyd/UBR5. Mol. Cell. 67, 181–193.
Shearer R.F., Iconomou M., Watts C.K., Saunders D.N. 2015. Functional roles of the E3 ubiquitin ligase UBR5 in cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 13, 1523–1532.
Scheffner M., Kumar S. 2014. Mammalian HECT ubiquitin-protein ligases: Biological and pathophysiological aspects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1843 (1), 61–74.
Muñoz-Escobar J., Matta-Camacho E., Kozlov G., Gehring K. 2015. The MLLE domain of the ubiquitin ligase UBR5 binds to its catalytic domain to regulate substrate binding. J. Biol. Chem. 290 (37), 22841–22850.
Qiao X., Liu Y., Prada M.L., Mohan A.K., Gupta A., Jaiswal A., Sharma M., Merisaari J., Haikala H.M., Talvinen K., Yetukuri L., Pylvänäinen J.W., Klefström J., Kronqvist P., Meinander A., et al. 2020. UBR5 is coamplified with MYC in breast tumors and encodes an ubiquitin ligase that limits MYC-dependent apoptosis. Cancer Res. 80 (7), 1414–1427.
Gupta I., Singh K., Varshney N.K., Khan S. 2018. Delineating crosstalk mechanisms of the ubiquitin proteasome system that regulate apoptosis. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 6, 11.
Matsuura K., Huang N.J., Cocce K., Zhang L., Kornbluth S. 2017. Downregulation of the proapoptotic protein MOAP-1 by the UBR5 ubiquitin ligase and its role in ovarian cancer resistance to cisplatin. Oncogene. 36 (12), 1698–1706.
Wang D., Xu Q., Yuan Q., Jia M., Niu H., Liu X., Zhang J, Young C.Y., Yuan H. 2019. Proteasome inhibition boosts autophagic degradation of ubiquitinated-AGR2 and enhances the antitumor efficiency of bevacizumab. Oncogene. 38, 3458–3474.
Wang G., Tang X., Chen Y., Cao J., Huang Q., Ling X., Ren W., Liu S., Wu Y., Ray L., Lin X. 2014. Hyperplastic discs differentially regulates the transcriptional outputs of Hedgehog signaling. Mech. Dev. 133, 117–125.
Cammarata-Mouchtouris A., Nguyen X.H., Acker A., Bonnay F., Goto A., Orian A., Fauvarque M.O., Boutros M., Reichhart J.M., Matt N. 2020. Hyd ubiquitinates the NF-κB co-factor Akirin to operate an effective immune response in Drosophila. PLoS Pathog. 16 (4), e1008458.
Su H., Meng S., Lu Y., Trombly M.I., Chen J., Lin C., Turk A., Wang X. 2011. Mammalian hyperplastic discs homolog EDD regulates miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Mol. Cell. 43 (1), 97–109.
Callaghan M.J., Russell A.J., Woollatt E., Sutherland G.R., Sutherland R.L., Watts C.K. 1998. Identification of a human HECT family protein with homology to the Drosophila tumor suppressor gene hyperplastic discs. Oncogene. 17, 3479–3491.
Clancy J.L., Henderson M.J., Russell A.J., Anderson D.W., Bova R.J., Campbell I.G., Choong D.Y., Macdonald G.A., Mann G.J., Nolan T., Brady G., Olopade O.I., Woollatt E., Davies M.J., Segara D., et al. EDD, the human orthologue of the hyperplastic discs tumour suppressor gene, is amplified and overexpressed in cancer. Oncogene. 22, 5070–5081.
Meissner B., Kridel R., Lim R.S., Rogic S., Tse K., Scott D.W., Moore R., Mungall A.J., Marra M.A., Connors J.M., Steidl C., Gascoyne R.D. 2013. The E3 ubiquitin ligase UBR5 is recurrently mutated in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood. 121, 3161–3164.
Forbes S.A., Bhamra G., Bamford S., Dawson E., Kok C., Clements J., Menzies A., Teague J.W., Futreal P.A., Stratton M.R (2008. The catalogue of somatic mutations in cancer (COSMIC). Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. Ch. 10, Unit 10–11.
O’Brien P.M., Davies M.J., Scurry J.P., Smith A.N., Barton C.A., Henderson M.J., Saunders D.N., Gloss B.S., Patterson K.I., Clancy J.L., Heinzelmann-Schwarz V.A., Scolyer R.A., Zeng Y., Williams E.D., Scurr L., et al. 2008. The E3 ubiquitin ligase EDD is an adverse prognostic factor for serous epithelial ovarian cancer and modulates cisplatin resistance in vitro. Br. J. Cancer. 98 (6), 1085–1093.
Funding
This work was supported by the Program of Fundamental Studies on the topics 0310-2019-0005 (I.A. Galimova) and 0324-2019-0042-C-01 (N.V. Dorogova and S.A. Fedorova).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by A. Barkhash
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galimova, I.A., Dorogova, N.V. & Fedorova, S.A. Functions of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Hyd in Drosophila Tissues. Mol Biol 55, 305–310 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893321020205
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893321020205