Abstract
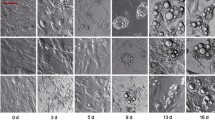
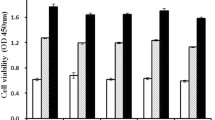
Obesity is a major disease that causes significant complications. Inhibition of preadipocyte proliferation has the potential to prevent obesity and metabolic diseases. Melatonin is a pineal gland hormone that has various effects on cells and tissues. In this research, we investigated whether melatonin induces apoptosis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. 3T3-L1 preadipocytes were cultured until confluence and then treated with 0, 10, 100, and 1000 μM melatonin for 1, 3, and 5 days. A cell viability assay kit was used for determining cell viability. Cell death marker proteins were assessed by Western blot analysis using GAPDH for control. Apoptotic morphological changes with nuclei fragmentation were observed using DAPI staining. Melatonin treatment decreased the phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases (p-ERK) activation while increasing the activation of caspase-3, 8, and 9. Furthermore, melatonin not only increased Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) but decreased B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) expression as dose increases from 0 to 1000 µM. The melatonin treatment also suppressed the growth of preadipocytes with increasing concentration. These effects were attenuated by luzindole, a melatonin receptor antagonist and U0126, an inhibitor of p-ERK activation. In conclusion, melatonin can induce apoptosis of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes via p-ERK decrease.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Devlin M.J., Yanovski S.Z., Wilson G.T. 2000. Obesity: What mental health professionals need to know. Am. J. Psychiatry. 157, 854‒866.
Janssen I., Katzmarzyk P.T., Ross R. 2002. Body mass index, waist circumference, and health risk: Evidence in support of current National Institutes of Health guidelines. Arch. Intern. Med. 162, 2074‒2079.
Mokdad A.H., Ford E.S., Bowman B.A., Dietz W.H., Vinicor F., Bales V.S., Marks J.S. 2003. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 289, 76‒79.
Barrett P., Bolborea M. 2012. Molecular pathways involved in seasonal body weight and reproductive responses governed by melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 52, 376‒388.
Stolk R.P., Meijer R., Mali W.P., Grobbee D.E., Graaf Y. 2003. Ultrasound measurements of intraabdominal fat estimate the metabolic syndrome better than do measurements of waist circumference. Am. J. Clin. Nutr.77, 857‒860.
Lefterova M.I., Lazar M.A. 2009. New developments in adipogenesis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 20, 107‒114.
Seale P., Kajimura S., Spiegelman B.M. 2009. Transcriptional control of brown adipocyte development and physiological function—of mice and men. Genes Dev. 23, 788‒797.
Green H., Meuth M. 1974. An established pre-adipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. Cell. 3, 127‒133.
Ailhaud G., Grimaldi P., Negrel R. 1994. Hormonal regulation of adipose differentiation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 5, 132‒136.
Li H., Lee J.H., Kim S.Y., Yun H.Y., Baek K.J., Kwon N.S., Yoon Y., Jeong J.H., Kim D.S. 2011. Phosphatidylcholine induces apoptosis of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Biomed. Sci. 18, 91.
Xiao Y., Yuan T., Yao W., Liao K. 2010. 3T3-L1 adipocyte apoptosis induced by thiazolidinediones is peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma-dependent and mediated by the caspase-3-dependent apoptotic pathway. FEBS J.277, 687‒696.
Wang N., Wang X., Shi M., Shi H., Yan X., Li H., Wang S., Wang Y. 2013. LMO4 modulates proliferation and differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. FEBS Lett. 587, 3032‒3037.
Birk R.Z., Rubinstein M. 2006. IFN-alpha induces apoptosis of adipose tissue cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 345, 669‒674.
Perdomo J., Cabrera J., Estevez F., Loro J., Reiter R.J., Quintana J. 2013. Melatonin induces apoptosis through a caspase-dependent but reactive oxygen species-independent mechanism in human leukemia Molt-3 cells. J. Pineal Res. 55, 195‒206.
Pacchierotti C., Iapichino S., Bossini L., Pieraccini F., Castrogiovanni P. 2001. Melatonin in psychiatric disorders: A review on the melatonin involvement in psychiatry. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 22, 18‒32.
Prunet-Marcassus B., Desbazeille M., Bros A., Louche K., Delagrange P., Renard P., Casteilla L., Penicaud L. 2003. Melatonin reduces body weight gain in Sprague Dawley rats with diet-induced obesity. Endocrinology. 144, 5347‒5352.
Wolden-Hanson T., Mitton D.R., McCants R.L., Yellon S.M., Wilkinson C.W., Matsumoto A.M., Rasmussen D.D. 2000. Daily melatonin administration to middle-aged male rats suppresses body weight, intraabdominal adiposity, and plasma leptin and insulin independent of food intake and total body fat. Endocrinology. 141, 487‒497.
Barrenetxe J., Delagrange P., Martinez J.A. 2004. Physiological and metabolic functions of melatonin. J. Physiol. Biochem. 60, 61‒72.
Brzezinski A. 1997. Melatonin in humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 336, 186‒195.
Reiter R.J., Tan D.X., Korkmaz A., Ma S. 2012. Obesity and metabolic syndrome: Association with chronodisruption, sleep deprivation, and melatonin suppression. Ann. Med. 44, 564‒577.
Spiegel K., Leproult R., Van Cauter E. 1999. Impact of sleep debt on metabolic and endocrine function. Lancet. 354, 1435‒1439.
Cipolla-Neto J., Amaral F.G., Afeche S.C., Tan D.X., Reiter R.J. 2014. Melatonin, energy metabolism, and obesity: A review. J. Pineal Res. 56, 371‒381.
Heslop P., Smith G.D., Metcalfe C., Macleod J., Hart C. 2002. Sleep duration and mortality: The effect of short or long sleep duration on cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in working men and women. Sleep Med. 3, 305‒314.
Sun F.Y., Lin X., Mao L.Z., Ge W.H., Zhang L.M., Huang Y.L., Gu J. 2002. Neuroprotection by melatonin against ischemic neuronal injury associated with modulation of DNA damage and repair in the rat following a transient cerebral ischemia. J. Pineal Res. 33, 48‒56.
Bułdak R.J., Pilc‑Gumuła K., Bułdak Ł., Witkowska D., Kukla M., Polaniak R., Zwirska‑Korczala K. 2015. Effects of ghrelin, leptin and melatonin on the levels of reactive oxygen species, antioxidant enzyme activity and viability of the HCT 116 human colorectal carcinoma cell line. Mol. Med. Rep. 12, 2275‒2282.
Joo S.S., Yoo Y.M. 2009. Melatonin induces apoptotic death in LNCaP cells via p38 and JNK pathways: Therapeutic implications for prostate cancer. J. Pineal Res. 47, 8‒14.
Martin V., Herrera F., Carrera-Gonzalez P., Garcia-Santos G., Antolin I., Rodriguez-Blanco J., Rodriguez C. 2006. Intracellular signaling pathways involved in the cell growth inhibition of glioma cells by melatonin. Cancer Res. 66, 1081‒1088.
Jung-Hynes B., Reiter R.J., Ahmad N. 2010. Sirtuins, melatonin and circadian rhythms: Building a bridge between aging and cancer. J. Pineal Res. 48, 9‒19.
Martin-Renedo J., Mauriz J.L., Jorquera F., Ruiz-Andres O., Gonzalez P., Gonzalez-Gallego J. 2008. Melatonin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cell line. J. Pineal Res. 45, 532‒540.
Haslam D.W., James W.P. 2005. Obesity. Lancet. 366, 1197‒1209.
Kntayya S., Ibrahim M., Mohd Ain N., Iori R., Ioannides C., Abdull Razis A. 2018. Induction of apoptosis and cytotoxicity by isothiocyanate sulforaphene in human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells. Nutrients. 10, 718.
Brydon L., Petit L., Delagrange P., Strosberg A.D., Jockers R. 2001. Functional expression of MT2 (Mel1b) melatonin receptors in human PAZ6 adipocytes. Endocrinology. 142, 4264‒4271.
Claustrat B., Brun J., Chazot G. 2005. The basic physiology and pathophysiology of melatonin. Sleep Med. Rev. 9, 11‒24.
Dubocovich M.L. 2007. Melatonin receptors: Role on sleep and circadian rhythm regulation. Sleep Med. 3, 34‒42.
Alonso-Vale M.I.C., Peres S.B., Vernochet C., Farmer S.R., Lima F.M. 2009. Adipocyte differentiation is inhibited by melatonin through the regulation of C/EBPb transcriptional activity. J. Pineal Res. 47, 221‒227.
Zhang L., Su P., Xu C., Chen C., Liang A., Du K., Peng Y., Huang D. 2010. Melatonin inhibits adipogenesis and enhances osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells by suppressing PPARgamma expression and enhancing Runx2 expression. J. Pineal Res. 49, 364‒372.
Hong Y., Won J., Lee Y., Lee S., Park K., Chang K.T., Hong Y. 2014. Melatonin treatment induces interplay of apoptosis, autophagy, and senescence in human colorectal cancer cells. J. Pineal Res. 56, 264‒274.
Brauchle E., Thude S., Brucker S.Y., Schenke-Layland K. 2014. Cell death stages in single apoptotic and necrotic cells monitored by Raman microspectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 4, 4698.
Elmore S. 2007. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 35, 495‒516.
Arya R., White K. 2015. Cell death in development: signaling pathways and core mechanisms. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 39, 12‒19.
Cohen G.M. 1997. Caspases: The executioners of apoptosis. Biochem. J.326, 1‒16.
Fan T.J., Han L.H., Cong R.S., Liang J. 2005. Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 37, 719‒727.
Kroemer G., Reed J.C. 2000. Mitochondrial control of cell death. Nat. Med. 6, 513‒519.
Sun X., Zemel M.B. 2004. Role of uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2) expression and 1alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in modulating adipocyte apoptosis. FASEB J.18, 1430‒1432.
Antonsson B., Martinou J.C. 2000. The Bcl-2 protein family. Exp. Cell Res. 256, 50‒57.
Adamczyk-Sowa M., Sowa P., Zwirska-Korczala K., Pierzchala K., Bartosz G., Sadowska-Bartosz I. 2013. Role of melatonin receptor MT 2 and quinone reductase II in the regulation of the redox status of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes in vitro.Cell Biol. Int.37, 835‒842.
Kokkola T., Vaittinen M., Laitinen J.T. 2007. Inverse agonist exposure enhances ligand binding and G protein activation of the human MT1 melatonin receptor, but leads to receptor down-regulation. J. Pineal Res.43, 255‒262.
Johnson G.L., Lapadat R. 2002. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science. 298, 1911‒1912.
Robinson M.J., Cobb M.H. 1997. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 180‒186.
Xia Z., Dickens M., Raingeaud J., Davis R.J., Greenberg M.E. 1995. Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis. Science. 270, 1326‒1331.
Prusty D., Park B.H., Davis K.E., Farmer S.R. 2002. Activation of MEK/ERK signaling promotes adipogenesis by enhancing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor(PPAR) and C/EBP gene expression during the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 46226‒46232.
Almeida R.D., Manadas B.J., Melo C.V., Gomes J.R., Mendes C.S., Graos M.M., Carvalho R.F., Carvalho A.P., Duarte C.B. 2005. Neuroprotection by BDNF against glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death is mediated by ERK and PI3-kinase pathways. Cell Death Differ. 12, 1329‒1343.
Cheung A., Newland P.L., Zaben M., Attard G.S., Gray W.P. 2012. Intracellular nitric oxide mediates neuroproliferative effect of neuropeptide Y on postnatal hippocampal precursor cells. J. Biol. Chem.287, 20187‒20196.
Rubio S., Estevez F., Cabrera J., Reiter R.J., Loro J., Quintana J. 2007. Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis by melatonin in human myeloid HL-60 cells. J. Pineal Res. 42, 131‒138.
Funding
This study was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2015R1D1A1A01060699).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
Ethical approval. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Coflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
The text was submitted by the author(s) in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Yoo, YM., Lee, Y.H. et al. Melatonin Induces Apoptotic Cell Death in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes. Mol Biol 54, 204–212 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320020120
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320020120