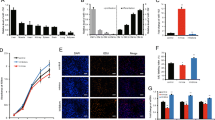
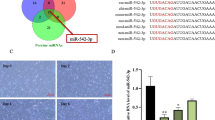
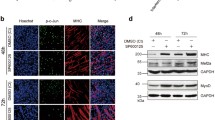
Abstract
MiR-222-3p has been implicated in tumor cell proliferation and has an important role in the differentiation and maturation of myogenic cells. However, its role in skeletal myoblast proliferation is still unclear. In this study, we found that miR-222-3p expression increases initially and then decreases during C2C12 myoblast proliferation. Using synthetic miRNA mimics and inhibitors in gain- or loss-of-function experiments, we showed that miR-222-3p overexpression in C2C12 cells promotes myoblast proliferation and represses myofiber formation, while miR-222-3p downregulation has the opposite effect. Using a prediction program, BTG2 was identified as a possible target gene of miR-222-3p. During myogenesis, miR-222-3p mimics repress BTG2 expression, while miR-222-3p inhibitors promote BTG2 expression. Using dual-luciferase reporter assay, we further demonstrated that miR-222-3p specifically targets BTG2. Additionally, we show that siRNA-mediated downregulation of BTG2 expression in C2C12 myoblasts promotes the proliferation and suppresses differentiation. In conclusion, we provide a novel insight into the mechanism by which miR-222-3p regulates the proliferation and differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts by targeting BTG2. This information contributes to our understanding of the role of miRNAs in skeletal muscle development.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ambros V. 2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 7006, 350‒355.
Berkes C.A., Tapscott S.J. 2005. MyoD and the transcriptional control of myogenesis. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 16, 585‒595.
Cardinali B., Cappella M., Provenzano C., Garcia-Manteiga J.M., Lazarevic D., Cittaro D., Martelli F., Falcone G. 2016. MicroRNA-222 regulates muscle alternative splicing through Rbm24 during differentiation of skeletal muscle cells. Cell Death Dis. 7, e2086.
Cardinali B., Castellani L., Fasanaro P., Basso A., Alemà S., Martelli F., Falcone G. 2009. MicroRNA-221 and microRNA-222 modulate differentiation and maturation of skeletal muscle cells. PLos One. 4, e7607.
Chen J.F., Mandel E.M., Thomson J.M., Wu Q.L., Callis T.E., Hammond S.M., Conlon F.L., Wang D.Z. 2006. The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation. Nat. Genet. 38, 228‒233.
Chen J.F., Tao Y., Li J., Deng Z.L., Yan Z., Xiao X., Wang D.Z. 2010. microRNA-1 and microRNA-206 regulate skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by repressing Pax7. J. Cell Biol. 190, 867‒879.
De F.M., De L.A. 2006. Involvement of cdks and cyclins in muscle differentiation. Eur. J. Histochem. 62, 19‒23.
Elghissassi F., Valsesiawittmann S., Falette N., Duriez C., Walden P. D., Puisieux A. 2002. BTG2 (TIS21/PC3) induces neuronal differentiation and prevents apoptosis of terminally differentiated PC12 cells. Oncogene. 21, 6772.
Evangelisti C., Astolfi A., Gaboardi G.C., Tazzari P., Pession A., Goto K., Alberto M. 2009. TIS21/BTG2/ PC3 and cyclin D1 are key determinants of nuclear diacylglycerol kinase-zeta-dependent cell cycle arrest. Cell. Signal. 21, 801‒809.
Feng Z., Tang Z. L., Li K., Liu B., Yu M., Zhao S.H. 2007. Molecular characterization of the BTG2 and BTG3 genes in fetal muscle development of pigs. Gene. 403, 170‒177.
Galardi S., Mercatelli N., Giorda E., Massalini S., Frajese G.V., Ciafrè S.A. 2007. miR-221 and miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27Kip1. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 23716‒23724.
Ge Y., Chen J. 2011. MicroRNAs in skeletal myogenesis. Cell Cycle. 10, 441‒448.
Huang W.W., Yang J.S., Pai S.J., Wu P.P., Chang S.J., Chu F.S., Fan M.J., Chiou S.M., Kuo H.M., Yeh C.C., Chen P.Y., Tsuzuki M., Chung J.G. 2012. Bufalin induces G0/G1 phase arrest through inhibiting the levels of cyclin D, cyclin E, CDK2 and CDK4, and triggers apoptosis via mitochondrial signaling pathway in T24 human bladder cancer cells. Mutat. Res. 732, 26‒33.
Livak K.J., Schmittgen T.D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(–Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25, 402‒408.
Montarras D., Chelly J., Bober E., Arnold H., Ott M.O., Gros F., Pinset C. 1991. Developmental patterns in the expression of Myf5, MyoD, myogenin, and MRF4 during myogenesis. New Biol. 3, 592‒600.
Reiter R.J., Tan D.X., Galano A. 2014. Melatonin reduces lipid peroxidation and membrane viscosity. Front. Physiol. 5, 377.
Roy R., Taourit S., Zaragoza P., Eggen A., Rodellar C. 2005. Genomic structure and alternative transcript of bovine fatty acid synthase gene (FASN): Comparative analysis of the FASN gene between monogastric and ruminant species. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 111, 65‒73.
Sabourin L.A., Rudnicki M.A. 2000. The molecular regulation of myogenesis. Clin. Genetics. 57, 16‒25.
Tan S.B., Li J.B., Chen X., Zhang W., Zhang D., Zhang C., Li D., Zhang Y. 2014. Small molecule inhibitor of myogenic microRNAs leads to a discovery of miR-221/222–myoD–myomiRs regulatory pathway. Chem. Biol. 21, 1265‒1270.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, D.L., Gan, M.L., Tan, Y. et al. MiR-222-3p Regulates the Proliferation and Differentiation of C2C12 Myoblasts by Targeting BTG2. Mol Biol 53, 38–44 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893319010187
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893319010187