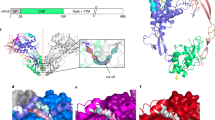
Abstract
Dikkoppf-1 (DKK1) is an antagonist of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. The importance of DKK1 as a diagnostic and therapeutic agent in a wide range of diseases along with its significance in a variety of biological processes accentuate the necessity to decipher its 3D structure that would pave the way towards the development of relevant selective inhibitors. A DKK1 structure model predicted by the Robetta server with structural refinements including a 10 ns molecular dynamics run was subjected to functional and docking analyses. We hypothesize that the N-terminal region of the DKK1 molecule could be functionally important for both canonical and noncanonical Wnt pathways. Moreover, it seems that DKK1 could be involved in interactions with the Frizzled receptors, leading to the activation of the Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) pathway (activation of Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) Pathway) and Wnt/Ca2+ pathway (activation of CamKII).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cadigan K.M., Nusse R. 1997. Wnt signaling: A common theme in animal development. Gen. Develop. 11, 3286–3305.
Huelsken J., Birchmeier W. 2001. New aspects of Wnt signaling pathways in higher vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Gen. Develop. 11, 547–553.
Kikuchi A. 2000. Regulation of ß-catenin signaling in the Wnt pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 268, 243–248.
Lee D.K., Grantham R.N., Trachte A.L., Mannion J.D., Wilson C.L. 2006. Activation of the canonical Wnt/ß-catenin pathway enhances monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 347, 109–116.
Masckauchán T.N.H., Shawber C.J., Funahashi Y., Li C.-M., Kitajewski J. 2005. Wnt/ß-catenin signaling induces proliferation, survival and interleukin-8 in human endothelial cells. Angiogenesis. 8, 43–51.
Pandur P., Maurus D., Kühl M. 2002. Increasingly complex: New players enter the Wnt signaling network. Bioessays. 24, 881–884.
Ueland T., Otterdal K., Lekva T., Halvorsen B., Gabrielsen A., Sandberg W.J. Paulsson-Berne G., Pedersen T.M., Folkersen L., Gullestad L. 2009. Dickkopf-1 enhances inflammatory interaction between platelets and endothelial cells and shows increased expression in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 29, 1228–1234.
Zerlin M., Julius M.A., Kitajewski J. 2008. Wnt/Frizzled signaling in angiogenesis. Angiogenesis. 11, 63–69.
Bafico A., Liu G., Yaniv A., Gazit A., Aaronson S.A. 2001. Novel mechanism of Wnt signalling inhibition mediated by Dickkopf-1 interaction with LRP6/Arrow. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 683–686.
González-Sancho J.M., Aguilera O., García J.M., Pendás-Franco N., Peña C., Cal S., de Herreros A.G., Bonilla F., Muñoz A. 2005. The Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-1 gene is a downstream target of ß-catenin/TCF and is downregulated in human colon cancer. Oncogene. 24, 1098–10103.
Mao B., Wu W., Davidson G., Marhold J., Li M., Mechler B.M., Delius H., Hoppe D., Stannek P., Walter C. 2002. Kremen proteins are Dickkopf receptors that regulate Wnt/ß-catenin signalling. Nature. 417 (6889), 664–667.
Willert K., Jones K.A. 2006. Wnt signaling: Is the party in the nucleus? Gen. Develop. 20, 1394–1404.
Marvin M.J., Di Rocco G., Gardiner A., Bush S.M., Lassar A.B. 2001. Inhibition of Wnt activity induces heart formation from posterior mesoderm. Gen. Develop. 15, 316–327.
Niehrs C. 2006. Function and biological roles of the Dickkopf family of Wnt modulators. Oncogene. 25, 7469–7481.
Krupnik V.E., Sharp J.D., Jiang C., Robison K., Chickering T.W, Amaravadi L., Brown D.E., Guyot D., Mays G., Leiby K. 1999. Functional and structural diversity of the human Dickkopf gene family. Gene. 238, 301–313.
Kuphal S., Lodermeyer S., Bataille F., Schuierer M., Hoang B., Bosserhoff A. 2006. Expression of Dickkopf genes is strongly reduced in malignant melanoma. Oncogene. 25, 5027–5036.
Vibhakar R., Foltz G., Yoon J.-G., Field L., Lee H., Ryu G.-Y., Pierson J., Davidson B., Madan A. 2007. Dickkopf-1 is an epigenetically silenced candidate tumor suppressor gene in medulloblastoma. Neurooncology. 9 (2), 135–144.
Mikesch J., Steffen B., Berdel W., Serve H., Müller- Tidow C. 2007. The emerging role of Wnt signaling in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 21, 1638–1647.
Thompson M.D., Monga S.P. 2007. WNT/ß-catenin signaling in liver health and disease. Hepatology. 45, 1298–1305.
Turashvili G., Bouchal J., Burkadze G., Kolar Z. 2006. Wnt signaling pathway in mammary gland development and carcinogenesis. Pathobiology. 73 (5), 213–223.
Yamabuki T., Takano A., Hayama S., Ishikawa N., Kato T., Miyamoto M., Ito T., Ito H., Miyagi Y., Nakayama H. 2007. Dikkopf-1 as a novel serologic and prognostic biomarker for lung and esophageal carcinomas. Cancer Res. 67, 2517–2525.
Yardy G., Brewster S. 2005. Wnt signalling and prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 8 (2), 119–226.
Gomceli I., Bostanci E., Ozer I., Kemik A., Turhan N., Tez M., Kilic S., Demiriz B., Akoglu M. 2012. A novel screening biomarker in gastric cancer: Serum Dickkopf-1. Hepatogastroenterology. 59, 1661–1664.
Forget M., Turcotte S., Beauseigle D., Godin-Ethier J., Pelletier S., Martin J., Tanguay S., Lapointe R. 2007. The Wnt pathway regulator DKK1 is preferentially expressed in hormone-resistant breast tumours and in some common cancer types. Br. J. Cancer. 96, 646–653.
Granchi D., Corrias M.V., Garaventa A., Baglìo S.R., Cangemi G., Carlini B., Paolucci P., Giunti A., Baldini N. 2011. Neuroblastoma and bone metastases: Clinical significance and prognostic value of Dickkopf 1 plasma levels. Bone. 48, 152–159.
Kaiser M., Mieth M., Liebisch P., Oberländer R., Rademacher J., Jakob C., Kleeberg L., Fleissner C., Braendle E., Peters M. 2008. Serum concentrations of DKK-1 correlate with the extent of bone disease in patients with multiple myeloma. Eur. J. Hematol. 80 (6), 490–494.
Kemik O., Kemik A.S., Sumer A., Begenik H., Purisa S., Tuzun S., Kotan C. 2011. Relationship between clinicopathologic variables and serum and tissue levels of dickkopf-1 in patients with rectal cancer. J. Invest. Med. 59 (6), 947–950.
Le Sheng S., Huang G., Yu B., Qin W.X. 2009. Clinical significance and prognostic value of serum Dickkopf-1 concentrations in patients with lung cancer. Clin. Chem. 55 (9), 1656–1664.
Lee H.S., Lee H.E., Park D.J., Kim H.-H., Kim W.H., Park K.U. 2012. Clinical significance of serum and tissue Dickkopf-1 levels in patients with gastric cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta. 413 (21), 1753–1760.
Lee N., Smolarz A., Olson S., David O., Reiser J., Kutner R., Daw N., Prockop D., Horwitz E., Gregory C. 2007. A potential role for Dkk-1 in the pathogenesis of osteosarcoma predicts novel diagnostic and treatment strategies. Br. J. Cancer. 97, 1552–1559.
Politou M.C., Heath D.J., Rahemtulla A., Szydlo R., Anagnostopoulos A., Dimopoulos M.A., Croucher P.I., Terpos E. 2006. Serum concentrations of Dickkopf-1 protein are increased in patients with multiple myeloma and reduced after autologous stem cell transplantation. Int. J. Cancer. 119, 1728–1731.
Shen C.-H., Hsieh H.-Y., Wang Y.-H., Chen S.-Y., Tung C.-L., Wu J.-D., Lin C.-T., Chan M.W.-Y., Hsu C.-D., Chang D. 2010. High Dickkopf-1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma. Exp. Therap. Medicine. 1, 893–898.
Shen Q., Fan J., Yang X.-R., Tan Y., Zhao W., Xu Y., Wang N., Niu Y., Wu Z., Zhou J. 2012. Serum DKK1 as a protein biomarker for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A large-scale, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 13, 817–826.
Tung E.K.K., Mak C.K.M., Fatima S., Lo R.C.L., Zhao H., Zhang C., Dai H., Poon R.T., Yuen M.F., Lai C.L., Li J.J., Luk J.M., Ng I.O. 2011. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of serum and tissue Dickkopf-1 levels in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 31, 1494–1504.
Voorzanger-Rousselot N., Journe F., Doriath V., Body J.-J., Garnero P. 2009. Assessment of circulating Dickkopf-1 with a new two-site immunoassay in healthy subjects and women with breast cancer and bone metastases. Calcif. Tissue Int. 84, 348–354.
Fulciniti M., Tassone P., Hideshima T., Vallet S., Nanjappa P., Ettenberg S.A., Shen Z., Patel N., Tai Y.-T., Chauhan D. 2009. Anti-DKK1 mAb (BHQ880) as a potential therapeutic agent for multiple myeloma. Blood. 114, 371–379.
Sato N., Yamabuki T., Takano A., Koinuma J., Aragaki M., Masuda K., Ishikawa N., Kohno N., Ito H., Miyamoto M. 2010. Wnt inhibitor Dickkopf-1 as a target for passive cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 70, 5326–5336.
Boyden L.M., Mao J., Belsky J., Mitzner L., Farhi A., Mitnick M.A., Wu D., Insogna K., Lifton R.P. 2002. High bone density due to a mutation in LDL-receptorrelated protein 5. New Engl. J. Medicine. 346, 1513–1521.
Patel M.S., Karsenty G. 2002. Regulation of bone formation and vision by LRP5. New Engl. J. Med. 346, 1572–1574.
Khalili S., Jahangiri A., Borna H., Ahmadi Zanoos K., Amani J. 2014. Computational vaccinology and epitope vaccine design by immunoinformatics. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 61, 285–307.
Mihasan M. 2010. Basic protein structure prediction for the biologist: A review. Arch. Biol. Sci. 62, 857–871.
Rahbar M.R., Rasooli I., Gargari S.L.M., Sandstrom G., Amani J., Fattahian Y., Jahangiri A., Jalali M. 2012. A potential in silico antibody–antigen based diagnostic test for precise identification of Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Theor. Biol. 294, 29–39.
Sefid F., Rasooli I., Jahangiri A. 2013. In silico determination and validation of baumannii acinetobactin utilization a structure and ligand binding site. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 1–14.
Mohammadpour H., Khalili S., Hashemi Z.S. 2015. Kremen is beyond a subsidiary co-receptor of Wnt signaling: An in silico validation: 2. Turk. J. Biol. 39, 501–511.
Ahn V.E., Chu M.L.-H., Choi H.-J., Tran D., Abo A., Weis W.I. 2011. Structural basis of Wnt signaling inhibition by Dickkopf binding to LRP5/6. Dev. Cell. 21, 862–873.
Cheng Z., Biechele T., Wei Z., Morrone S., Moon R.T., Wang L., Xu W. 2011. Crystal structures of the extracellular domain of LRP6 and its complex with DKK1. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 18, 1204–1210.
Xie H., Vucetic S., Iakoucheva L.M., Oldfield C.J., Dunker A.K., Uversky V.N., Obradovic Z. 2007. Functional anthology of intrinsic disorder: 1. Biological processes and functions of proteins with long disordered regions. J. Proteome Res. 6, 1882–1898.
Ferreiro D.U., Hegler J.A., Komives E.A., Wolynes P.G. 2007. Localizing frustration in native proteins and protein assemblies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104, 19819–19824.
Bourhis E., Wang W., Tam C., Hwang J., Zhang Y., Spittler D., Huang O.W., Gong Y., Estevez A., Zilberleyb I., Rouge L., Chiu C., Wu Y., Costa M., Hannoush R.N., et al. 2011. Wnt antagonists bind through a short peptide to the first ß-propeller domain of LRP5/6. Structure. 19, 1433–1442.
Wang K., Zhang Y., Li X., Chen L., Wang H., Wu J., Zheng J., Wu D. 2008. Characterization of the Kremen-binding site on Dkk1 and elucidation of the role of Kremen in Dkk-mediated Wnt antagonism. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 23371–23375.
Menezes M.E., Devine D.J., Shevde L.A., Samant R.S. 2012. Dickkopf1: A tumor suppressor or metastasis promoter? Int. J. Cancer. 130, 1477–1483.
Janda C.Y., Waghray D., Levin A.M., Thomas C., Garcia K.C. 2012. Structural basis of Wnt recognition by Frizzled. Science. 337 (6090), 59–64.
Jessen J.R. 2009. Noncanonical Wnt signaling in tumor progression and metastasis. Zebrafish. 6, 21–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Published in Russian in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2017, Vol. 51, No. 1, pp. 180–192.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalili, S., Rasaee, M.J. & Bamdad, T. 3D structure of DKK1 indicates its involvement in both canonical and non-canonical Wnt pathways. Mol Biol 51, 155–166 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893317010095
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893317010095