Abstract
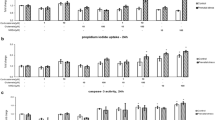
The ratio of the expression levels of the immediate early genes c-jun and c-fos that encode components of the AP-1 transcription complex determines the direction of changes in the expression of genes controlled by the complex, including changes induced by glucocorticoids. The aim of the present work was to assess the levels of mRNA encoded by genes c-jun and c-fos and the ratio of expression levels of these genes in various regions of the neonatal rat brain after the administration of dexamethasone, a selective ligand of the glucocorticoid receptor. The level of mRNA encoded by the immediate early gene c-fos in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of 3-day-old rat pups was elevated at 30, 60, and 120 min after dexamethasone administration. The basal level of c-fos gene expression in the brainstem was higher than in the cortex and hippocampus, and administration of the hormone was followed by a reduction in the amount of transcript detectable in the brainstem after 2 h. As a result, the ratio of c-jun to c-fos transcript levels in the brainstem of neonatal rats was doubled after dexamethasone administration. The dexamethasone-induced shift of the ratio of c-jun to c-fos transcript levels in the brainstem of neonatal rats towards a predominance of c-jun reported for the first time in the present work may induce the expression of genes that contain AP-1 response elements in the promoters, since the glucocorticoid receptor can be involved in protein–protein interactions with the Jun/Jun homodimer of the AP-1 complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GR:
-
glucocorticoid receptor
References
Turpaev K.T. 2006. Role of transcription factor AP-1 in integration of cell signaling systems. Mol. Biol. (Moscow). 40 (6), 851–866.
Kassel O., Herrlich P. 2007. Crosstalk between the glucocorticoid receptor and other transcription factors: molecular aspects. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 275, 13–29.
Rani C.S., Elango N., Wang S.S., Kobayashi K., Strong R. 2009. Identification of an activator protein-1-like sequence as the glucocorticoid response element in the rat tyrosine hydroxylase gene. Mol. Pharmacol. 75, 589–598.
Kalinina T.S., Shishkina G.T., Dygalo N.N. 2012. Induction of tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression by glucocorticoids in the perinatal rat brain is age-dependent. Neurochem. Res. 37, 811–818.
Teurich S., Angel P. 1995. The glucocorticoid receptor synergizes with Jun homodimers to activate AP-1-regulated promoters lacking GR binding sites. Chem. Senses. 20, 251–255.
Hoffman G.E., Smith M.S., Verbalis J.G. 1993. c-Fos and related immediate early gene products as markers of activity in neuroendocrine systems. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 14, 173–213.
Healy S., Khan P., Davie J.R. 2013. Immediate early response genes and cell transformation. Pharmacol. Ther. 137, 64–77.
Kalinina T.S., Bannova A.V., Dygalo N.N. 2001. Content of apoptotic enzyme caspase-3 mRNA in brain stem and cortex in rats during postnatal ontogeny. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 132, 748–750.
Bannova A.V., Menshanov P.N., Ilinykh F.A., Kalinina T.S., Dygalo N.N. 2005. Bax and Bcl-XL apoptosis protein mRNA in rat brain stem and cortex during ontogeny. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 139, 700–702.
Buss R.R., Sun W., Oppenheim R.W. 2006. Adaptive roles of programmed cell death during nervous system development. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 29, 1–35.
Moisiadis V.G., Matthews S.G. 2014. Glucocorticoids and fetal programming: 1. Outcomes. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 10, 391–402.
Slotkin T.A., Kreider M.L., Tate C.A., Seidler F.J. 2006. Critical prenatal and postnatal periods for persistent effects of dexamethasone on serotonergic and dopaminergic systems. Neuropsychopharmacology. 31, 904–911.
Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. 1987. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanatephenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162, 156–159.
Parma D.L., Benasayag S.J., Szijan I. 1991. Expression of c-myc and c-fos oncogenes in different rat brain regions during postnatal development. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 9, 613–619.
Salehi M., Barron M., Merry B.J., Goyns M.H. 1999. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of the fos/jun ratio in the ageing brain. Mech. Ageing Dev. 107, 61–71.
Olesen K.M., Auger A.P. 2005. Sex differences in Fos protein expression in the neonatal rat brain. J. Neuroendocrinol. 17, 255–261.
Dygalo N.N, Kalinina T.S, Shishkina G.T. 2008. Neonatal programming of rat behavior by downregulation of alpha2A-adrenoreceptor gene expression in the brain. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1148, 409–414.
O’Donnell A., Odrowaz Z., Sharrocks A.D. 2012. Immediate-early gene activation by the MAPK pathways: What do and don’t we know? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 40, 58–66.
Slotkin T.A., Zhang J., McCook E.C., Seidler F.J. 1998. Glucocorticoid administration alters nuclear transcription factors in fetal rat brain: Implications for the use of antenatal steroids. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 111, 11–24.
Szakács R., Fazekas I., Mihály A., Krisztin-Péva B., Juhász A., Janka Z. 2010. Single-dose and chronic corticosterone treatment alters c-Fos or FosB immunoreactivity in the rat cerebral cortex. Acta. Histochem. 112, 147–160.
Brown E.R., Sawchenko P.E. 1997. Hypophysiotropic CRF neurons display a sustained immediate-early gene response to chronic stress but not to adrenalectomy. J. Neuroendocrinol. 9, 307–316.
Hansson A.C., Fuxe K. 2008. Time-course of immediate early gene expression in hippocampal subregions of adrenalectomized rats after acute corticosterone challenge. Brain Res. 1215, 1–10.
Skórzewska A., Bidzinski A., Lehner M., Turzynska D., Wislowska-Stanek A., Sobolewska A., Szyndler J., Maciejak P., Taracha E., Plaznik A. 2006. The effects of acute and chronic administration of corticosterone on rat behavior in two models of fear responses, plasma corticosterone concentration, and c-Fos expression in the brain structures. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 85, 522–534.
Karst H., Joëls M. 2005. Corticosterone slowly enhances miniature excitatory postsynaptic current amplitude in mice CA1 hippocampal cells. J. Neurophysiol. 94, 3479–3486.
van Hasselt F.N., de Visser L., Tieskens J.M., Cornelisse S., Baars A.M., Lavrijsen M., Krugers H.J., van den Bos R., Joëls M. 2012. Individual variations in maternal care early in life correlate with later life decision-making and c-fos expression in prefrontal subregions of rats. PLoS ONE. 7, e37820.
Kassel O., Sancono A., Kratzschmar J., Kreft B., Stassen M., Cato A.C. 2001. Glucocorticoids inhibit MAP kinase via increased expression and decreased degradation of MKP-1. EMBO J. 20, 7108–7116.
Biddie S.C, John S., Sabo P.J., Thurman R.E., Johnson T.A., Schiltz R.L., Miranda T.B., Sung M.H., Trump S., Lightman S.L., Vinson C., Stamatoyannopoulos J.A., Hager G.L. 2011. Transcription factor AP1 potentiates chromatin accessibility and glucocorticoid receptor binding. Mol. Cell. 43, 145–155.
Wei P., Inamdar N., Vedeckis W.V. 1998. Transrepression of c-jun gene expression by the glucocorticoid receptor requires both AP-1 sites in the c-jun promoter. Mol. Endocrinol. 12, 1322–1333.
Speksnijder N., Christensen K.V., Didriksen M., De Kloet E.R., Datson N.A. 2012. Glucocorticoid receptor and myocyte enhancer factor 2 cooperate to regulate the expression of c-JUN in a neuronal context. J. Mol. Neurosci. 48, 209–218.
Briski K.P., DiPasquale B.M., Gillen E. 1997. Induction of immediate-early gene expression in preoptic and hypothalamic neurons by the glucocorticoid receptor agonist, dexamethasone. Brain Res. 768, 185–196.
Kovács K.J. 2008. Measurement of immediate-early gene activation: c-fos and beyond. J. Neuroendocrinol. 20, 665–672.
Shah K., Tyagi S. 2013. Barriers to transmission of transcriptional noise in a c-fos c-jun pathway. Mol. Syst. Biol. 9, 687.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.V. Sukhareva, N.N. Dygalo, T.S. Kalinina, 2016, published in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2016, Vol. 50, No. 2, pp. 266–271.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sukhareva, E.V., Dygalo, N.N. & Kalinina, T.S. Effect of dexamethasone on the expression of immediate early genes c-fos and c-jun in different regions of the neonatal brain. Mol Biol 50, 230–235 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893316020254
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893316020254