Abstract
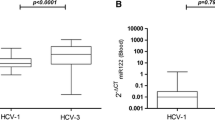
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA molecules, which have an important function in regulating RNA stability and gene expression. They also can circulate in a cell-free form in the blood thatmakes them potential disease markers. The liver contains various classes of miRNAs in which miR-122 accounts for about 70% of all miRNAs and it has been proved that its level increases in case of liver damage. Here, we investigated plasma levels of miR-122 as a useful disease parameter in patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC) infection. Thirty five hemophilia and thalassemia patients with CHC were studied. The total RNA was extracted from plasma samples, and miR-122 levels were measured by qPCR and then compared with the specific liver markers. The plasma levels of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase(AST) were correlated with plasma miR-122 level in CHC patients, and the level of circulating miR-122 in healthy individual groups were rarely lower than those of patients with CHC. In our study, miR-122 levels correlated well with markers of liver inflammatory activity. Plasma miR-122 can be assumed to be another marker in liver similar to the currently used specific markers such as ALT and AST for evaluation of liver damage in hepatitis C virus (HCV) infected patients. Moreover, the correlation between miR-122 and ALT was shown to be higher than between miR-122 and AST.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams A.E. 2008. Functional aspects of animal microRNAs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65, 545–562.
Bihrer V., Friedrich-Rust M., Kronenberge B., Forestie N., Haupentha J., Shi Y., Peveling-Oberha J., Radek H.H., Sarrazi C., Herrman E., Zeuze S., Waidman O., Piiper A. 2011. Serum miR-122 as a biomarker of necroinflammation in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 106, 1663–1669.
Iorio M.V., Croce C.M. 2009. MicroRNAs in cancer: Small molecules with a huge impact. J. Clin. Oncol. 27, 5848–5856.
Lee Y., Ahn C., Han J., Choi H., Kim J., Yim J., Lee J., Provost P., Radmark O., Kim S., Kim V.N. 2003. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature. 425, 415–419.
Ambros V. 2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 431, 350–355.
Cortez M.A., Bueso-Ramos C., Ferdin J., Lopez-Berestein G., Sood A.K., Calin G.A. 2011. MicroRNAs in body fluids: The mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 8, 467–477.
Wang G.K., Zhu J.Q., Zhang J.T., Li Q., Li Y., He J., Qin Y.W., Jing Q. 2010. Circulating microRNA: A novel potential biomarker for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in humans. Eur. Heart J. 31, 659–666.
Chen X., Ba Y., Ma L., Cai X., Yin Y., Wang K., Guo J., Zhang Y., Chen J., Guo X., Li Q., Li X., Wang W., Zhang Y., Wang J., et al. 2008. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 18, 997–1006.
Mitchell P.S., Parkin R.K., Kroh E.M., Fritz B.R., Wyman S.K., Pogosova-Agadjanyan E.L., Peterson A., Noteboom J., O’ Briant K.C., Allen A., Lin D.W., Urban N., Drescher C.W., Knudsen B.S., Stirewalt D.L., et al. 2008. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 10513–10518.
Laterza O.F., Lim L., Garrett-Engele P.W., Vlasakova K., Muniappa N., Tanaka W.K., Johnson J.M., Sina J.F., Fare T.L., Sistare F.D., Glaab W.E. 2009. Plasma microRNAs as sensitive and specific biomarkers of tissue injury. Clin. Chem. 55, 1977–1983.
Chang J., Nicolas E., Marks D., Sander C., Lerro A., Buendia M.A., Xu C., Mason W.S., Moloshok T., Bort R., Zaret K.S., Taylor J.M. 2004. miR-122, a mammalian liver-specific microRNA, is processed from hcr mRNA and may downregulate the high affinity cationic amino acid transporter CAT-1. RNA Biol. 1, 106–113.
Bihrer V., Friedrich-Rust M., Kronenberger B., Forestier N., Haupenthal J., Shi Y., Peveling-Oberhag J., Radeke H.H., Sarrazin C., Herrmann E. 2011. Serum miR-122 as a biomarker of necroinflammation in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 106, 1663–1669.
Sarasin-Filipowicz M., Krol J., Markiewicz I., Heim M.H., Filipowicz W. 2009. Decreased levels of microRNA miR-122 in individuals with hepatitis C responding poorly to interferon therapy. Nat. Med. 15, 31–33.
Wang Y., Tang N., Hui T., Wang S., Zeng X., Li H., Ma J. 2013. Identification of endogenous reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of plasma microRNAs levels in rats with acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. J. Appl. Toxicol. 33, 1330–1336.
Zhang J., Zhao H., Gao Y., Zhang W. 2012. Secretory miRNAs as novel cancer biomarkers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1826, 32–43.
Starkey Lewis P.J., Dear J., Platt V., Simpson K.J., Craig D.G., Antoine D.J., French N.S., Dhaun N., Webb D.J., Costello E.M. 2011. Circulating microRNAs as potential markers of human drug-induced liver injury. Hepatology. 54, 1767–1776.
Wang K., Zhang S., Marzolf B., Troisch P., Brightman A., Hu Z., Hood L.E., Galas D.J. 2009. Circulating microRNAs, potential biomarkers for drug-induced liver injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 4402–4407.
Zhang Y., Jia Y., Zheng R., Guo Y., Wang Y., Guo H., Fei M., Sun S. 2010. Plasma microRNA-122 as a biomarker for viral-, alcohol-, and chemical-related hepatic diseases. Clin. Chem. 56, 1830–1838.
Zhang X., Zhang Z., DaiF., Shi B., Chen L., Zhang X., Zang G., Zhang J., Chen X., Qian F. 2014. Comparison of circulating, hepatocyte specific messenger RNA and microRNA as biomarkers for chronic hepatitis B and C. PLoS ONE. 9, e92112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2016, Vol. 50, No. 2, pp. 279–283.
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gholami, M., Ravanshad, M., Alavian, SM. et al. Evaluation of miR-122 level in the plasma of chronically HCV infected patients. Mol Biol 50, 242–245 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893316020072
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893316020072