Abstract
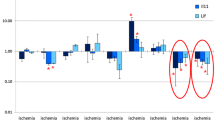
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A) is hypoxia-inducible signal glycoprotein. VEGF-A induces vascular endothelial cell proliferation, which leads to the reconstitution of the vascular network in brain regions damaged by ischemia. However, this protein is also involved in the processes of inflammation and edema in early stages of ischemia. The synthetic peptide Semax has neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties and is actively used in the treatment of cerebral ischemia. We have previously shown that Semax reduces vascular injury and activates the mRNA synthesis of neurotrophins and their receptors during global cerebral ischemia in rats. In this work, we studied the effect of Semax and its C-terminal Pro-Gly-Pro tripeptide on Vegfa mRNA expression in different regions of the rat brain after 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 24 h, which is the irreversible occlusion of the common carotid arteries. It was shown that ischemia increases the levels of Vegfa mRNA in rat brains (4 h after occlusion in cerebellum, cerebral cortex, and hippocampus; 8 h after occlusion in the cortex and hippocampus; and 24 h after occlusion in the cortex). Treatment with Semax reduces the levels of Vegfa mRNA in the frontal cortex (4, 8 and 12 h after occlusion) and the hippocampus (2 and 4 h after occlusion). The effect of PGP on the Vegfa gene expression was almost negligible. It was shown that Semax prevents the activating effect of hypoxia on the expression of the Vegfa gene at early stages of global cerebral ischemia. In turn, an increase in the level of Vegfa mRNA in the hippocampus 24 h after occlusion and Semax administration apparently reflects the neuroprotective properties of the drug.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- RT:
-
reverse transcription
- GADPH:
-
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
References
Zachary I. 2005. Neuroprotective role of vascular endothelial growth factor: signalling mechanisms, biological function, and therapeutic potential. Neurosignals. 14(5), 207–221.
Madan A., Curtin P.T. 1993. A 24-base-pair sequence 3’ to the human erythropoietin gene contains a hypoxiaresponsive transcriptional enhancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90(9), 3928–3932.
Ma Y., Qu Y., Fei Z. 2011. Vascular endothelial growth factor in cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 89(7), 969–978.
Zhang Z.G., Zhang L., Jiang Q., Zhang R., Davies K., Powers C., Bruggen N., Chopp M. 2000. VEGF enhances angiogenesis and promotes blood-brain barrier leakage in the ischemic brain. J. Clin. Invest. 106(7), 829–838.
Ribatti D. 2005. The crucial role of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor in angiogenesis: a historical review. Br. J. Haematol. 128(3), 303–309.
Guan W., Somanath P.R., Kozak A., Goc A., El-Remessy A.B., Ergul A., Johnson M.H., Alhusban A., Soliman S., Fagan S.C. 2011. Vascular protection by angiotensin receptor antagonism involves differential VEGF expression in both hemispheres after experimental stroke. PLoS ONE. 6(9), e24551.
Sebentsova E.A., Denisenko A.V., Levitskaia N.G., Andreeva L.A., Kamenskii A.A., Myasoedov N.F. 2005. Long-lasting behavioral effects of chronic neonatal treatment with ACTH (4-10) analogue semax in white rat pups. Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat. im. I.P. Pavlova. 55(2), 213–220.)
Storozhevykh T.P., Tukhbatova G.R., Senilova Y.E., Pinelis V.G., Andreeva L.A., Myasoyedov N.F. 2007. Effects of semax and its Pro-Gly-Pro fragment on calcium homeostasis of neurons and their survival under conditions of glutamate toxicity. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 143(5), 601–604.
Astashkin E.I., Bespalova Yu.B., Grivennikov I.A., Smirnov O.N., Glezer M.G., Myasoedov N.F. 2000. Analysis of the effect of Semax on Ca2+ responsees of human neutophils. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. 374(3), 401–403.
Bashkatova V.G., Koshelev V.B., Fadyukova O.E., Alexeev A.A., Vanin A.F., Rayevsky K.S., Ashmarin I.P., Armstrong D.M. 2001. Novel synthetic analogue of ACTH 4-10 (Semax) but not glycine prevents the enhanced nitric oxide generation in cerebral cortex of rats with incomplete global ischemia. Brain. Res. 894, 145–149.
Ashmarin I.P., Nezavibat’ko V.N., Levitskaya N.G., Kamensky A.A. 1995. Design and investigation of ACTH(4-10) analog deprived of D-amino acids and hydrophobic radicals. Neurosci. Res. Commun. 16, 105–112.
Martynova K.V., Andreeva L.A., Klimova P.A., Kirillova Yu.G., Shevchenko V.P., Nagaev I.Yu., Shram S.I., Shvets V.I., Myasoedov N.F. 2009. Structural-functional study of glycine-and-proline-containing peptides (glyprolines) as potential neuroprotectors. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 35(2), 150–156.
Storozhevykh T.P., Tukhbatova G.R., Senilova Ya.E., Pinelis V.G., Andreeva L.A., Myasoedov N.F. 2007. Effects of semax and its Pro-Gly-Pro fragment on calcium homeostasis of neurons and their survival under conditions of glutamate toxicity. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 143(5), 601–604.
Dmitrieva V.G., Dergunova L.V., Povarova O.V., Skvortsova V.I., Limborska S.A., Myasoedov N.F. 2008. The effect of Semax and the C-terminal peptide PGP on expression of growth factor genes and receptors in rats under conditions of experimental cerebral ischemia. Doklady Buiochem. Biophys. 422, 261–266.
Stavchansky V.V., Tvorogova T.V., Botsina A.Yu., Skvortsova V.I., Limborska S.A., Myasoedov N.F., Dergunova L.V. 2011. Effect of Semax and its C-terminal peptide PGP on expression of neurotrophins and their receptors in rat brain during incomplete global ischemia. Mol. Biol. (Moscow). 45, 941–949.
Stavchansky V.V., Yuzhakov V.V., Botsina A.Y., Skvortsova V.I., Bondurko L.N., Tsyganova M.G., Limborska S.A., Myasoedov N.F., Dergunova L.V. 2011. The effect of Semax and its C-end peptide PGP on the morphology and proliferative activity of rat brain cells during experimental ischemia: a pilot study. J. Mol. Neurosci. 45, 177–185.
Pfaffl M.W. 2001. A new mathematical model for ralative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 29(9), 2002–2007.
Pfaffl M.W., Horgan G.W., Dempfle L. 2002. Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 30(9), e36.
Jin K.L., Mao X.O., Greenberg D.A. 2000.Vascular endothelial growth factor: direct neuroprotective effect in in vitro ischemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97, 10242–10247.
Marti H.J., Bernaudin M., Bellail A., Schoch H., Euler M., Petit E., Risau W. 2000. Hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression precedes neovascularization after cerebral ischemia. Am. J. Pathol. 156(3), 965–976.
Khugaeva V.K., Aleksandrin V.V. 1997. Relationship between the therapeutic effect of the peptide preparation semax and the severity of brain ischemia. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 124(7), 39–42.
Bertolini A., Tacchi R., Vergoni A.V. 2009. Brain effects of melanocortins. Pharmacol. Res. 59(1), 13–47.
Plate K.H., Beck H., Danner S., Allegrini P.R., Wiessner C. 1999. Cell type specific upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in an MCA-occlusion model of cerebral infarct. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 58(6), 654–666.
Gusev E.I., Skvorthsova V.I. 2001. Ishemiya golovnogo mozga (Brain Ischemia). Moscow: Meditsina, pp. 260–270.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.V. Stavchanskii, T.V. Tvorogova, A.Yu. Botsina, S.A. Limborska, V.I. Skvortsova, N.F. Myasoedov, L.V. Dergunova, 2013, published in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2013, Vol. 47, No. 3, pp. 461–466.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stavchanskii, V.V., Tvorogova, T.V., Botsina, A.Y. et al. Effect of peptide Semax and its C-terminal fragment PGP on Vegfa gene expression during incomplete global cerebral ischemia in rats. Mol Biol 47, 406–410 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893313030151
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893313030151