Abstract
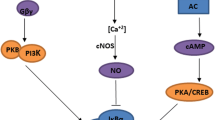
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) regulate proteolysis of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and as a consequence are involved in a number of physiological and pathological states, including cancer. A crucial feature of cancer progression and metastasis is the disruption of the ECM and spreading of proliferating cancer cells. Over-expression of MMPs and uPA is common for most types of cancers and correlates well with the adverse prognosis. Compounds able to modulate the activity of these proteolytic enzymes may become important agents in cancer therapy. In the present study, we examined the effect of the μ-opioid receptor selective peptide, morphiceptin, and its two synthetic analogs on mRNA and protein levels of MMP-9 and uPA in three human cancer cell lines: MCF-7, HT-29, and SHSY5Y. Our findings indicate that in all three cell lines morphiceptin and its analogs attenuated MMP-9 expression and secretion and that this effect is not mediated by opioid receptors but is under control of the nitric oxide system. On the other hand, tested opioids up-regulated uPA levels through a mechanism that involved opioid-receptors. Different pathways by which opioid peptides exert their action in cancer cells can explain their contradictory influence on the level of cancer markers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- eNOS:
-
endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- GAPDH:
-
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- MMPs:
-
matrix metalloproteinases
- MMP-2:
-
gelatinase A
- MMP-9:
-
gelatinase B
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffered saline
- uPA:
-
urokinase plasminogen activator
References
Geiger T.R., Peeper D.S. 2009. Metastasis mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1796, 293–308.
Engbring J.A., Kleinman H.K. 2003. The basement membrane matrix in malignancy. J. Pathol. 200, 465–470.
Widel M.S., Widel M. 2006. Mechanisms of metastasis and molecular markers of malignant tumor progression: 1. Colorectal cancer. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. (Online) 60, 453–470.
Das S., Banerji A., Frei E., Chatterjee A. 2008. Rapid expression and activation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 upon exposure of human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) to fibronectin in serum free medium. Life Sci. 82, 467–476.
Zhang W., Yang H.C., Wang Q., Yang Z.J., Chen H., Wang S.M., Pan Z.M., Tang B.J., Li Q.Q., Li L. 2011. Clinical value of combined detection of serum matrix metalloproteinase-9, heparanase, and cathepsin for determining ovarian cancer invasion and metastasis. Anticancer Res. 31, 3423–3428.
Duffy M.J. 2004. The urokinase plasminogen activator system: Role in malignancy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 10, 39–49.
Duffy M.J., Duggan C. 2004. The urokinase plasminogen activator system: A rich source of tumour markers for the individualised management of patients with cancer. Clin. Biochem. 37, 541–548.
Holst-Hansen C., Johannessen B., Hoyer-Hansen G., Romer J., Ellis V., Brunner N. 1996. Urokinase-type plasminogen activation in three human breast cancer cell lines correlates with their in vitro invasiveness. Clin. Exp. Metastasis. 14, 297–307.
Morgan H., Hill P.A. 2005. Human breast cancer cellmediated bone collagen degradation requires plasminogen activation and matrix metalloproteinase activity. Cancer Cell. Int. 5, 1.
Harbeck N., Kates R.E., Gauger K., Willems A., Kiechle M., Magdolen V., Schmitt M. 2004. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and its inhibitor PAI-I: Novel tumor-derived factors with a high prognostic and predictive impact in breast cancer. Thromb. Haemost. 91, 450–456.
Dano K., Behrendt N., Hoyer-Hansen G., Johnsen M., Lund L.R., Ploug M., Römer J. 2005. Plasminogen activation and cancer. Thromb. Haemost. 93, 676–681.
Han B., Nakamura M., Mori I., Nakamura Y., Kakudo K. 2005 Urokinase-type plasminogen activator system and breast cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 14, 105–112.
Strek M., Gorlach S., Podsedek A., Sosnowska D., Koziolkiewicz M., Hrabec Z, Hrabec, E. 2007. Procyanidin oligomers from Japanese quince (Chaenomeles japonica) fruit inhibit activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 metalloproteinases. J. Agric. Food Chem. 55, 6447–6452.
Wyrębska A., Gach K., Szemraj J., Szewczyk K., Hrabem E., Koszuk J., Janecki T., Janecka, A. 2012. Comparison of anti-invasive activity of parthenolide and 3-isopropyl-2-methyl-4-methyleneisoxazolidin-5-one (MZ-6), a new compound with alpha-methylene-gamma-lactone motif, on two breast cancer cell lines. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 79, 112–120.
Wang X.Y., Wang Y., Liu H.C. 2011. Tamoxifen lowers the MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio and inhibits the invasion capacity of ER-positive non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 65, 525–528.
Gach K., do-Rego J.C., Fichna J., Storr M., Delbro D., Toth G., Janecka A. 2010. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel peripherally active morphiceptin analogs. Peptides. 31, 1617–1624.
Pfeilschifter J., Eberhardt W., Huwiler A. 2001. Nitric oxide and mechanisms of redox signalling: Matrix and matrix-metabolizing enzymes as prime nitric oxide targets. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 429, 279–286.
Shariftabrizi A., Nifli A.P., Ansari M., Saadat F., Ebrahimkhani M.R., Alizadeh N., Nasseh A., Alexaki V.I., Dehpour A.R., Castanas E., Khorramizadeh M.R. 2006. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 secretion in WEHI 164 fibrosarcoma cells is nitric oxide-related and modified by morphine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 530, 33–39.
Gach K., Wyr bska A., Fichna J., Janecka A. 2011. The role of morphine in regulation of cancer cell growth. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 384, 221–230.
Tegeder I., Geisslinger G. 2004. Opioids as modulators of cell death and survival: Unraveling mechanisms and revealing new indications. Pharmacol. Rev. 56, 351–369.
Mathew B., Lennon F., Siegler J., Gerhold L., Mambetsariev N., Moreno-Vinasco L., Garcia J., Salgia R., Moss J., Singleton P. 2009. The mu-opioid receptor regulates Lewis lung carcinoma tumor growth and metastasis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 8, C79–79C.
Kawase M., Sakagami H., Furuya K., Kikuchi H., Nishikawa H., Motohashi N., Morimoto Y., Varga, A., Molnár J. 2002. Cell death-inducing activity of opiates in human oral tumor cell lines. Anticancer Res. 22, 211–214.
Koodie L., Ramakrishnan S., Roy S. 2010. Morphine suppresses tumor angiogenesis through a HIF-1alpha/p38MAPK pathway. Am. J. Pathol. 177, 984–997.
Harimaya Y., Koizumi K., Andoh T., Nojima H., Kuraishi Y., Saiki I. 2002. Potential ability of morphine to inhibit the adhesion, invasion and metastasis of metastatic colon 26-L5 carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 187, 121–127.
Moss J., Rosow C.E. 2008. Development of peripheral opioid antagonists: New insights into opioid effects. Mayo Clin. Proc. 83, 1116–1130.
Wang C.Z., Li X.L., Sun S., Xie J.T., Aung H.H., Tong R., McEntee E., Yuan C.S. 2009. Methylnaltrexone, a peripherally acting opioid receptor antagonist, enhances tumoricidal effects of 5-Fu on human carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 29, 2927–2932.
Singleton P.A., Moss J. 2010. Effect of perioperative opioids on cancer recurrence: A hypothesis. Future Oncol. 6, 1237–1242.
Gach K., Szemraj J., Wyrbska A., Janecka A. 2011. The influence of opioids on matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 secretion and mRNA levels in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Mol. Biol. Rep. 38, 1231–1236.
Nylund G., Pettersson A., Bengtsson C., Khorram-Manesh A., Nordgren S., Delbro D.S. 2008. Functional expression of mu-opioid receptors in the human colon cancer cell line, HT-29, and their localization in human colon. Dig. Dis. Sci. 53, 461–466.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gach, K., Wyrębska, A., Szemraj, J. et al. The influence of opioid peptides on matrix metalloproteinase-9 and urokinase plasminogen activator expression in three cancer cell lines. Mol Biol 46, 796–801 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893312060052
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893312060052