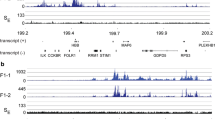
Abstract
Using native chromatin imunoprecipitation (N-ChIP) followed by TaqMan RT-PCR quantitative analysis, we have determined the profiles of histone acetylation and histone methylation within the α-globin gene domain before and after switching of embryonic globin gene expression. The results obtained do not support a supposition that the inactivation of the embryonic α-type globin gene π in the erythroid cells of the adult lineage is mediated via formation of an inactive chromatin domain. On the other hand, we have demonstrated that suppression of the gene π activity in erythroid cells of adult lineage correlates with decrease of the histone acetylation level within the embryonic subdomain of the α-globin gene domain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peterson K.R. 2003. Hemoglobin switching: New insights. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 10, 123–129.
Orkin S.H. 1995. Regulation of globin gene expression in erythroid cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 231, 271–281.
Yin W., Barkess G., Fang X., Xiang P., Cao H., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Li Q. 2007. Histone acetylation at the human beta-globin locus changes with developmental age. Blood. 110, 4101–4107.
Stamatoyannopoulos G. 2005. Control of globin gene expression during development and erythroid differentiation. Exp. Hematol. 33, 259–271.
Li Q., Peterson K.R., Stamatoyannopoulos G. 1998. Developmental control of epsilon- and gamma-globin genes. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 850, 10–17.
Mabaera R., Richardson C.A., Johnson K., Hsu M., Fiering S., Lowrey C.H. 2007. Developmental- and differentiation-specific patterns of human gamma- and beta-globin promoter DNA methylation. Blood. 110, 1343–1352.
Palstra R.J., de Laat W., Grosveld F. 2008. Beta-globin regulation and long-range interactions. Adv. Genet. 61, 107–142.
Palstra R.J., Tolhuis B., Splinter E., Nijmeijer R., Grosveld F., de Laat W. 2003. The beta-globin nuclear compartment in development and erythroid differentiation. Nature Genet. 35, 190–194.
de Laat W., Klous P., Kooren J., Noordermeer D., Palstra R.J., Simonis M., Splinter E., Grosveld F. 2008. Three-dimensional organization of gene expression in erythroid cells. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 82, 117–139.
Higgs D.R., Wood W.G., Jarman A.P., Sharpe J., Lida J., Pretorius I.-M., Ayyub H. 1990. A major positive regulatory region located far upstream of the human α-globin gene locus. Genes Dev. 4, 1588–1601.
Jarman A.P., Wood W.G., Sharpe J.A., Gourdon G., Ayyub H., Higgs D.R. 1991. Characterization of the major regulatory element upstream of the human α-globin gene cluster. Mol. Cell. Biol. 11, 4679–4689.
Sharpe J.A., Chan-Thomas P.S., Lida J., Ayyub H., Wood W.G., Higgs D.R. 1992. Analysis of the human alpha globin upstream regulatory element (HS-40) in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 11, 4565–4572.
Flint J., Tufarelli C., Peden J., Clark K., Daniels R.J., Hardison R., Miller W., Philipsen S., Tan-Un K.C., McMorrow T., Frampton J., Alter B.P., Frischauf A.M., Higgs D.R. 2001. Comparative genome analysis delimits a chromosomal domain and identifies key regulatory elements in the alpha globin cluster. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, 371–382.
Dillon N., Sabbatini P. 2000. Functional gene expression domains: Defining the functional units of eukaryotic gene regulation. BioEssays. 22, 657–665.
Razin S.V., Farrell C.M., Recillas-Targa F. 2003. Genomic domains and regulatory elements operating at the domain level. Int. Rev. Cytol. 226, 63–125.
Razin S.V., Ioudinkova E.S. 2007. Mechanisms controlling activation of the alpha-globin gene domain in chicken erythroid cells. Biochemistry (Moscow). 72, 467–470.
Recillas-Targa F., Razin S.V. 2001. Chromatin domains and regulation of gene expression: Familiar and enigmatic clusters of chicken globin genes. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 11, 227–242.
Bruns G.A., Ingram V.M. 1973. Erythropoiesis in the developing chick embryo. Dev. Biol. 30, 455–459.
Knezetic J., Felsenfeld G. 1989. Identification and characterization of a chicken α-globin enhancer. Mol. Cell. Biol. 9, 893–901.
Chapman B.S., Tobin A.J. 1979. Distribution of developmentally regulated hemoglobins in embryonic erythroid populations. Dev. Biol. 69, 375–387.
Weintraub H., Larsen A., Groudine M. 1981. Alphaglobin gene switching during the development of chicken embryos: Expression and chromosome structure. Cell. 24, 333–344.
Landes G.M., Villeponteau B., Pribyl T.M., Martinson H.G. 1982. Hemoglobin switching in chickens. Is the switch initiated post-transcriptionally? J. Biol. Chem. 257, 11008–11014.
Rincon-Arano H., Guerrero G., Valdes-Quezada C., Recillas-Targa F. 2009. Chicken alpha-globin switching depends on autonomous silencing of the embryonic pi globin gene by epigenetics mechanisms. J. Cell Biochem. 108, 675–687.
Klochkov D., Rincon-Arano H., Ioudinkova E.S., Valadez-Graham V., Gavrilov A., Recillas-Targa F., Razin S.V. 2006. A CTCF-dependent silencer located in the differentially methylated area may regulate expression of a housekeeping gene overlapping a tissue-specific gene domain. Mol. Cell Biol. 26, 1589–1597.
Bernstein E., Hake S.B. 2006. The nucleosome: A little variation goes a long way. Biochem. Cell Biol. 84, 505–517.
Wang Y., Fischle W., Cheung W., Jacobs S., Khorasanizadeh S., Allis C.D. 2004. Beyond the double helix: Writing and reading the histone code. Novartis Found Symp. 259, 3–17; discussion 17–21, 163–169.
Cosgrove M.S., Wolberger C. 2005. How does the histone code work? Biochem. Cell Biol. 83, 468–476.
Nakayama J., Rice J.C., Strahl B.D., Allis C.D., Grewal S.I. 2001. Role of histone H3 lysine 9 methylation in epigenetic control of heterochromatin assembly. Science. 292, 110–113.
Prioleau M.N., Nony P., Simpson M., Felsenfeld G. 1999. An insulator element and condensed chromatin region separate the chicken beta-globin locus from an independently regulated erythroid-specific folate receptor gene. EMBO J. 18, 4035–4048.
Ghirlando R., Litt M.D., Prioleau M.N., Recillas-Targa F., Felsenfeld G. 2004. Physical properties of a genomic condensed chromatin fragment. J. Mol. Biol. 336, 597–605.
Litt M.D., Simpson M., Gaszner M., Allis C.D., Felsenfeld G. 2001. Correlation between histone lysine methylation and developmental changes at the chicken beta-globin locus. Science. 293, 2453–2455.
Litt M.D., Simpson M., Recillas-Targa F., Prioleau M.N., Felsenfeld G. 2001. Transitions in histone acetylation reveal boundaries of three separately regulated neighboring loci. EMBO J. 20, 2224–2235.
Haigh L.S., Owens B.B., Hellewel O.S., Ingram V.M. 1982. DNA methylation in chicken alpha-globin gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 79, 5332–5336.
Singal R., vanWert J.M., Ferdinand L., Jr. 2002. Methylation of alpha-type embryonic globin gene alpha pi represses transcription in primary erythroid cells. Blood. 100, 4217–4222.
Ballestar E., Wolffe A.P. 2001. Methyl-CpG-binding proteins: Targeting specific gene repression. Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 1–6.
Wade P.A. 2001. Methyl CpG-binding proteins and transcriptional repression. Bioessays. 23, 1131–1137.
Gavrilov A.A., Razin S.V. 2008. Spatial configuration of the chicken α-globin gene domain: immature and active chromatin hubs. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, 4629–4640.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.S. Yudinkova, D.A. Bunina, S.V. Ulyanov, A.A. Gavrilov, S.V. Razin, 2011, published in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2011, Vol. 45, No. 4, pp. 662–667.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yudinkova, E.S., Bunina, D.A., Ulyanov, S.V. et al. Patterns of histone modifications across the chicken alfa-globin genes’ domain. Mol Biol 45, 608–613 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893311030216
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893311030216