Abstract
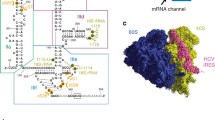
Ribosomal protein p40 is a structural component of the eukaryotic 40S ribosomal subunit, is partly homologous to prokaryotic ribosomal protein S2, and has a long eukaryote-specific C-terminal region. The internal ribosome entry site (IRES) of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA was tested for the binding to 40S ribosomal subunits deficient in p40, saturated with recombinant p40, or pretreated with monoclonal antibody (MAB) 4F6 against p40. The apparent association constant of HCV IRES binding to 40S subunits was shown to directly depend on the p40 content in the subunits. MAB 4F6 prevented HCV IRES binding to 40S subunits and blocked translation of IRES-containing RNA in a cell-free translation system. The results implicate p40 in the binding of the HCV IRES to the ribosome and, therefore, in translation initiation on HCV RNA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Merrick W.C. 1992. Mechanism and regulation of eukaryotic protein synthesis. Microbiol. Rev. 56, 291–315.
Pestova T.V., Kolupaeva V.G., Lomakin I.B., Pilipenko E.V., Shatsky I.N., Agol V.I., Hellen C.U. 2001. Molecular mechanisms of translation initiation in eukaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 98, 7029–7036
Skulachev M.V. 2005. Internal initiation of translation: Diversity of mechanisms and probable role in cell life activities. Usp. Biol. Khim. 45, 123–172.
Pisarev A.V., Shirokikh N.E., Hellen C.U. 2005. Translation initiation by factor-independent binding of eukaryotic ribosomes to internal ribosomal entry sites. C. R. Biol. 328, 589–605.
Lancaster A.M., Jan E., Sarnow P. 2006. Initiation factor-independent translation mediated by the hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site. RNA. 12, 894–902.
Fraser C.S., Doudna J.A. 2007. Structural and mechanistic insights into hepatitis C viral translation initiation. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 5, 29–38.
Pestova T.V., Shatsky I.N., Fletcher S.P., Jackson R.J., Hellen C.U. 1998. A prokaryotic-like mode of cytoplasmic eukaryotic ribosome binding to the initiation codon during internal translation initiation of hepatitis C and classical swine fever virus RNAs. Genes Dev. 12, 67–83.
Spahn C.M., Kieft J.S., Grassucci R.A., Penczek P.A., Zhou K., Doudna J.A., Frank J. 2001. Hepatitis C virus IRES RNA-induced changes in the conformation of the 40S ribosomal subunit. Science. 291, 1959–1962.
Boehringer D., Thermann R., Ostareck-Lederer A., Lewis J.D., Stark H. 2005. Structure of the hepatitis C virus IRES bound to the human 80S ribosome: Remodeling of the HCV IRES. Structure. 13, 1695–1706.
Fukushi S., Okada M., Stahl J., Kageyama T., Hoshino F.B., Katayama K. 2001. Ribosomal protein S5 interacts with the internal ribosomal entry site of hepatitis C virus. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 20824–20826.
Otto G.A., Lukavsky P.J., Lancaster A.M., Sarnow P., Puglisi J.D. 2002. Ribosomal proteins mediate the hepatitis C virus IRES-HeLa 40S interaction. RNA. 8, 913–923.
Lu H., Li W., Noble W.S., Payan D., Anderson D.C. 2004. Riboproteomics of the hepatitis C virus internal ribosomal entry site. J. Proteome Res. 3, 949–957.
Laletina E., Graifer D., Malygin A., Ivanov A., Shatsky I., Karpova G. 2006. Proteins surrounding hairpin IIIe of the hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site on the human 40S ribosomal subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, 2027–2036.
Babaylova E., Graifer D., Malygin A., Stahl J., Shatsky I., Karpova G. 2009. Positioning of subdomain IIId and apical loop of domain II of the hepatitis C IRES on the human 40S ribosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 1141–1151.
Varaklioti A., Georgopoulou U., Kakkanas A., Psaridi L., Serwe M., Caselmann W.H., Mavromara P. 1998. Mutational analysis of two unstructured domains of the 5′ untranslated region of HCV RNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 253, 678–685.
Malygin A.A., Graifer D.M., Laletina E.S., Shatsky I.N., Karpova G.G. 2003. An approach to identifying the functionally important RNA sites by complementary addressed modification. Mol. Biol. 37, 873–879.
Lukavsky P.J., Otto G.A., Lancaster A.M., Sarnow P., Puglisi J.D. 2000. Structures of two RNA domains essential for hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site function. Nature Struct. Biol. 7, 1105–1110.
Kosinova O.A., Malygin A.A., Babailova E.S., Karpova G.G. 2008. Binding of human ribosomal protein p40 and its truncated mutants to the small ribosomal subunit. Mol. Biol. 42, 911–916.
Bondarenko E.I., Protopopova E.B., Nekrasov V.M., Loktev V.B. 2004. Monoclonal antibodies to recombinant human laminin-binding protein: Isolation and immunochemical characterization. Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk. 8, 31–34.
Matasova N.B., Myltseva S.V., Zenkova M.A., Graifer D.M., Vladimirov S.N., Karpova G.G. 1991. Isolation of ribosomal subunits containing intact rRNA from human placenta: Estimation of functional activity of 80S ribosomes. Anal. Biochem. 198, 219–223.
Graifer D.M., Malygin A.A., Matasova N.B., Mundus D.A., Zenkova M.A., Karpova G.G. 1997. Studying functional significance of the sequence 980–1061 in the central domain of human 18S rRNA using complementary DNA probes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1350, 335–344.
Ardini E., Pesole G., Tagliabue E., Magnifico A., Castronovo V., Sobel M.E., Colnaghi M.I., Menard S. 1998. The 67-kDa laminin receptor originated from a ribosomal protein that acquired a dual function during evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 15, 1017–1025.
Jamieson K.V., Wu J., Hubbard S.R., Meruelo D. 2008. Crystal structure of the human laminin receptor precursor. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 3002–3005.
Spahn C.M., Beckmann R., Eswar N., Penczek P.A., Sali A., Blobel G., Frank J. 2001. Structure of the 80S ribosome from Saccharomyces cerevisiae tRNA-ribosome and subunit-subunit interactions. Cell. 107, 373–386.
Brodersen D.E., Clemons W.M., Jr., Carter A.P., Wimberly B.T., Ramakrishnan V. 2002. Crystal structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit from Thermus thermophilus: Structure of the proteins and their interactions with 16S RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 316, 725–768.
Chandramouli P., Topf M., Menetret J.F., Eswar N., Cannone J.J., Gutell R.R., Sali A., Akey C.W. 2008. Structure of the mammalian 80S ribosome at 8.7 Å resolution. Structure. 16, 535–548.
Demeshkina N.A., Laletina E.S., Meshchaninova M.I., Repkova M.N., Ven’iaminova A.G., Graifer D.M., Karpova G.G. 2003. The mRNA codon environment at the P and E sites of human ribosomes deduced from photo crosslinking with pUUUGUU derivatives. Mol. Biol. 37, 132–139.
Graifer D., Molotkov M., Styazhkina V., Demeshkina N., Bulygin K., Eremina A., Ivanov A., Laletina E., Ven’yaminova A., Karpova G. 2004. Variable and conserved elements of human ribosomes surrounding the mRNA at the decoding and upstream sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 3282–3293.
Molotkov M.V., Graifer D.M., Popugaeva E.A., Bulygin K.N., Meschaninova M.I., Ven’yaminova A.G., Karpova G.G. 2006. mRNA 3′ of the A site bound codon is located close to protein S3 on the human 80S ribosome. RNA Biol. 3, 122–129.
Masek T., Vopalensky V., Horvath O., Vortelova L., Feketova Z., Pospisek M. 2007. Hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site initiates protein synthesis at the authentic initiation codon in yeast. J. Gen. Virol. 88, 1992–2002.
Sizova D.V., Kolupaeva V.G., Pestova T.V., Shatsky I.N., Hellen C.U. 1998. Specific interaction of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 with the 5′ nontranslated regions of hepatitis C virus and classical swine fever virus RNAs. J. Virol. 72, 4775–4782.
Valasek L., Mathew A.A., Shin B.S., Nielsen K.H., Szamecz B., Hinnebusch A.G. 2003. The yeast eIF3 subunits TIF32/a, NIP1/c, and eIF5 make critical connections with the 40S ribosome in vivo. Genes Dev. 17, 786–799.
Auth D., Brawerman G. 1992. A 33-kDa polypeptide with homology to the laminin receptor: Component of translation machinery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 89, 4368–4372.
Garcia-Hernandez M., Davies E., Baskin T.I., Staswick P.E. 1996. Association of plant p40 protein with ribosomes is enhanced when polyribosomes form during periods of active tissue growth. Plant Physiol. 111, 559–568.
Siridechadilok B., Fraser C.S., Hall R.J., Doudna J.A., Nogales E. 2005. Structural roles for human translation factor eIF3 in initiation of protein synthesis. Science. 310, 1513–1515.
Otto G.A., Puglisi J.D. 2004. The pathway of HCV IRES-mediated translation initiation. Cell. 119, 369–380.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.A. Malygin, Z.V. Bochkaeva, E.I. Bondarenko, O.A. Kossinova, V.B. Loktev, I.N. Shatsky, G.G. Karpova, 2009, published in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2009, Vol. 43, No. 6, pp. 1070–1076.
Presented for publication by O.A. Dontsova
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malygin, A.A., Bochkaeva, Z.V., Bondarenko, E.I. et al. Binding of the IRES of hepatitis C virus RNA to the 40S ribosomal subunit: Role of p40. Mol Biol 43, 997–1003 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893309060120
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893309060120