Abstract
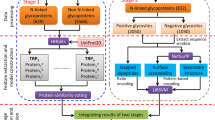
A new program, PSI Protein Classifier, generalizing the results of both successive and independent iterations of the PSI-BLAST program was developed. The technical opportunities of the program are described and illustrated by two examples. An iterative screening of the amino acid sequence database detected potential evolutionary relationships between GH5, GH13, GH27, GH31, GH36, GH66, GH101 and GH114 families of glycoside hydrolases. Analysis of the statistically significant sequence similarity (E-value analysis) allowed us to divide the family GH31 into 38 subfamilies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liolios K., Mavromatis K., Tavernarakis N., Kyrpides N.C. 2008. The Genomes On Line Database (GOLD) in 2007: Status of genomic and metagenomic projects and their associated metadata. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D475–D479.
Heger A., Holm L. 2003. Exhaustive enumeration of protein domain families. J. Mol. Biol. 328, 749–767.
Yeats C., Lees J., Reid A., Kellam P., Martin N., Liu X., Orengo C. 2008. Gene3D: Comprehensive structural and functional annotation of genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D414–D418.
Marsden R.L., Lee D., Maibaum M., Yeats C., Orengo C.A. 2006. Comprehensive genome analysis of 203 genomes provides structural genomics with new insights into protein family space. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, 1066–1080.
Mulder N.J., Apweiler R., Attwood T.K., Bairoch A., Bateman A., Binns D., Bork P., Buillard V., Cerutti L., Copley R., Courcelle E., Das U., Daugherty L., Dibley M., Finn R., Fleischmann W., Gough J., Haft D., Hulo N., Hunter S., Kahn D., Kanapin A., Kejariwal A., Labarga A., Langendijk-Genevaux P.S., Lonsdale D., Lopez R., Letunic I., Madera M., Maslen J., McAnulla C., McDowall J., Mistry J., Mitchell A., Nikolskaya A.N., Orchard S., Orengo C., Petryszak R., Selengut J.D., Sigrist C.J., Thomas P.D., Valentin F., Wilson D., Wu C.H., Yeats C. 2007. New developments in the InterPro database. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, D224–D228.
CluSTr database. 2009. Release 14.2. (http://www. ebi.ac.uk/clustr).
The Pfam database. 2008. Pfam 23.0. Release 1.6.1. (http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk).
Wallqvist A., Fukunishi Y., Murphy L.R., Fadel A., Levy R.M. 2000. Iterative sequence/secondary structure search for protein homologs: Comparison with amino acid sequence alignments and application to fold recognition in genome databases. Bioinformatics. 16, 988–1002.
Meinel T., Krause A., Luz H., Vingron M., Staub E. 2005. The SYSTERS Protein Family Database in 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, D226–D229.
Wilson D., Madera M., Vogel C., Chothia C., Gough J. 2007. The SUPERFAMILY database in 2007: Families and functions. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, D308–D313.
Holm L. 1998. Unification of protein families. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 8, 372–379.
Mi H., Lazareva-Ulitsky B., Loo R., Kejariwal A., Vandergriff J., Rabkin S., Guo N., Muruganujan A., Doremieux O., Campbell M.J., Kitano H., Thomas P.D. 2005. The PANTHER database of protein families, subfamilies, functions and pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, D284–D288.
Gough J. 2006. Genomic scale sub-family assignment of protein domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, 3625–3633.
Petryszak R., Kretschmann E., Wieser D., Apweiler R. 2005. The predictive power of the CluSTr database. Bioinformatics. 21, 3604–3609.
Heger A., Holm L., Wilton C. 2006. ADDA: Automatic Domain Decomposition Algorithm. Version V4. (http://ekhidna.biocenter.helsinki.fi/sqgraph/pairsdb).
Heger A., Wilton C.A., Sivakumar A., Holm L. 2005. ADDA: A domain database with global coverage of the protein universe. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, D188–D191.
Bru C., Courcelle E., Carrère S., Beausse Y., Dalmar S., Kahn D. 2005. The ProDom database of protein domain families: More emphasis on 3D. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, D212–D215.
Park J., Teichmann S.A. 1998. DIVCLUS: An automatic method in the GEANFAMMER package that finds homologous domains in single- and multi-domain proteins. Bioinformatics. 14, 144–150.
Enright A.J., Ouzounis C.A. 2000. GeneRAGE: A robust algorithm for sequence clustering and domain detection. Bioinformatics. 16, 451–457.
Tatusov R.L., Fedorova N.D., Jackson J.D., Jacobs A.R., Kiryutin B., Koonin E.V., Krylov D.M., Mazumder R., Mekhedov S.L., Nikolskaya A.N., Rao B.S., Smirnov S., Sverdlov A.V., Vasudevan S., Wolf Y.I., Yin J.J., Natale D.A. 2003. The COG database: An updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinformatics. 4, Art. 41.
Greene L.H., Lewis T.E., Addou S., Cuff A., Dallman T., Dibley M., Redfern O., Pearl F., Nambudiry R., Reid A., Sillitoe I., Yeats C., Thornton J.M., Orengo C.A. 2007. The CATH domain structure database: New protocols and classification levels give a more comprehensive resource for exploring evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, D291–D297.
Finn R.D., Mistry J., Schuster-Böckler B., Griffiths-Jones S., Hollich V., Lassmann T., Moxon S., Marshall M., Khanna A., Durbin R., Eddy S.R., Sonnhammer E.L., Bateman A. 2006. Pfam: Clans, web tools and services. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, D247–D251.
Finn R.D., Tate J., Mistry J., Coggill P.C., Sammut S.J., Hotz H.R., Ceric G., Forslund K., Eddy S.R., Sonnhammer E.L., Bateman A. 2008. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D281–D288.
Sadreyev R., Grishin N. 2003. COMPASS: A tool for comparison of multiple protein alignments with assessment of statistical significance. J. Mol. Biol. 326, 317–336.
Sadreyev R.I., Baker D., Grishin N.V. 2003. Profile-profile comparisons by COMPASS predict intricate homologies between protein families. Protein Sci. 12, 2262–2272.
Kaplan N., Sasson O., Inbar U., Friedlich M., Fromer M., Fleischer H., Portugaly E., Linial N., Linial M. 2005. ProtoNet 4.0: A hierarchical classification of one million protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, D216–D218.
Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes server. 2009. (http://www.cazy.org).
Naumoff D.G. 2001. β-Fructosidase superfamily: homology with some α-L-arabinases and β-D-xylosidases. Prot. Struct. Funct. Genet. 42, 66–76.
Naumoff D.G. 2006. Development of a hierarchical classification of the TIM-barrel type glycoside hydrolases. Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Bioinformatics of Genome Regulation and Structure, July 16–22, 2006, Novosibirsk, Russia, vol. 1, pp. 294–298 (http://www.bionet.nsc.ru/meeting/bgrs2006/BGRS_ 2006_V1.pdf).
Kuznetsova A.Y., Naumoff D.G. 2006. Phylogenetic analysis of COG1649, a new family of predicted glycosyl hydrolases. Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Bioinformatics of Genome Regulation and Structure, July 16–22, 2006, Novosibirsk, Russia, vol. 3, pp. 179–182 (http://www.bionet.nsc.ru/meeting/bgrs2006/BGRS_2006_V3.pdf).
Naumoff D.G. 2005. GH97 is a new family of glycoside hydrolases, which is related to the α-galactosidase superfamily. BMC Genomics. 6, Art. 112.
Ernst H.A., Leggio L.L., Willemoes M., Leonard G., Blum P., Larsen S. 2006. Structure of the Sulfolobus solfataricus α-glucosidase: implications for domain conservation and substrate recognition in GH31. J. Mol. Biol. 358, 1106–1124.
Henrissat B. 1998. Glycosidase families. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 26, 153–156.
Naumoff D.G. 2001. Sequence analysis of glycosylhydrolases: β-Fructosidase and α-galactosidase superfamilies. Glycoconjugate J. 18, 109.
Rigden D.J. 2002. Iterative database searches demonstrate that glycoside hydrolase families 27, 31, 36 and 66 share a common evolutionary origin with family 13. FEBS Lett. 523, 17–22.
Ernst H.A., Leggio L.L., Yu S., Finnie C., Svensson B., Larsen S. 2005. Probing the structure of glucan lyases by sequence analysis, circular dichroism and proteolysis. Biologia (Bratislava). 60(Suppl. 16), 149–159.
Janeček Š., Svensson B., Macgregor E.A. 2007. A remote but significant sequence homology between glycoside hydrolase clan GH-H and family GH31. FEBS Lett. 581, 1261–1268.
Nagano N., Porter C.T., Thornton J.M. 2001. The (β/α)8 glycosidases: Sequence and structure analyses suggest distant evolutionary relationships. Protein Eng. 14, 845–855.
MacGregor E.A. 2005. An overview of clan GH-H and distantly related families. Biologia (Bratislava). 60(Suppl. 16), 5–12.
Rigden D.J., Franco O.L. 2002. β-Helical catalytic domains in glycoside hydrolase families 49, 55 and 87: Domain architecture, modelling and assignment of catalytic residues. FEBS Lett. 530, 225–232.
Rigden D.J., Jedrzejas M.J., de Mello L.V. 2003. Identification and analysis of catalytic TIM barrel domains in seven further glycoside hydrolase families. FEBS Lett. 544, 103–111.
Mian I.S. 1998. Sequence, structural, functional, and phylogenetic analyses of three glycosidase families. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 24, 83–100.
Holm L., Sander C. 1994. Structural similarity of plant chitinase and lysozymes from animals and phage. An evolutionary connection. FEBS Lett. 340, 129–132.
Monzingo A.F., Marcotte E.M., Hart P.J., Robertus J.D. 1996. Chitinases, chitosanases, and lysozymes can be divided into procaryotic and eucaryotic families sharing a conserved core. Nature Struct. Biol. 3, 133–140.
MacGregor E.A, Janeček Š., Svensson B. 2001. Relationship of sequence and structure to specificity in the α-amylase family of enzymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1546, 1–20.
Pei J., Grishin N.V. 2005. COG3926 and COG5526: A tale of two new lysozyme-like protein families. Protein Sci. 14, 2574–2581.
Stam M.R., Danchin E.G., Rancurel C., Coutinho P.M., Henrissat B. 2006. Dividing the large glycoside hydrolase family 13 into subfamilies: Towards improved functional annotations of α-amylase-related proteins. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 19, 555–562.
Kuenne C.T., Ghai R., Chakraborty T., Hain T. 2007. GECO-linear visualization for comparative genomics. Bioinformatics. 23, 125–126.
Altschul S.F., Madden T.L., Schäffer A.A., Zhang J., Zhang Z., Miller W., Lipman D.J. 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 3389–3402.
Carreras M. 2009. Blast Parser: The Excel style viewer (http://geneproject.altervista.org).
Naumoff D.G. 2008. The GH31 family of glycoside hydrolases: subfamily structure and evolutionary connections. Abstracts of the Sixth International Conference on Bioinformatics of Genome Regulation and Structure, June 22–28, 2008, Novosibirsk, Russia, p. 169 (http://www.bionet.nsc.ru/meeting/bgrs2008/BGRS2008_Proceedings.pdf).
Lovering A.L., Lee S.S., Kim Y.W., Withers S.G., Strynadka N.C. 2005. Mechanistic and structural analy sis of a family 31 α-glycosidase and its glycosyl-enzyme intermediate. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 2105–2115.
Sim L., Quezada-Calvillo R., Sterchi E.E., Nichols B.L., Rose D.R. 2008. Human intestinal maltase-glucoamylase: crystal structure of the N-terminal catalytic subunit and basis of inhibition and substrate specificity. J. Mol. Biol. 375, 782–792.
Naumoff D.G. 2008. Hierarchical classification of glycosyl hydrolases. Proceedings of the Second International Sci.-Pract. Conf. “The Postgenomic Era in Biology and Problems of Biotechnology,” September 15–16, 2008, Kazan, Russia, pp. 94–95 (http://www.ksu.ru/bio2008/tez_18_09.pdf).
Naumoff D.G. 2004. Phylogenetic analysis of α-galactosidases of the GH27 family. Mol. Biol. (Engl. Tr.) 38, 388–399.
Naumoff D.G. 2007. Structure and evolution of the mammalian maltase-glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase genes. Mol. Biol. (Engl. Tr.) 41, 962–973.
Caines M.E., Zhu H., Vuckovic M., Willis L.M., Withers S.G., Wakarchuk W.W., Strynadka N.C. 2008. The structural basis for T-antigen hydrolysis by Streptococcus pneumoniae: A target for structure-based vaccine design. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 31279–31283.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.G. Naumoff, M. Carreras, 2009, published in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2009, Vol. 43, No. 4, pp. 709–721.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naumoff, D.G., Carreras, M. PSI protein classifier: A new program automating PSI-BLAST search results. Mol Biol 43, 652–664 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893309040189
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893309040189