Abstract—
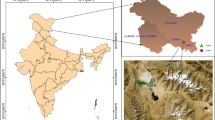
Groundwater, which appears on the surface in the form of springs, is an important ecologically significant component of the aquatic ecosystem, sensitive to changes in environmental conditions. The anthropogenic impact associated with urbanization leads to a change in the characteristics of groundwater, which, in turn, affects the composition of microbial communities in spring waters. Using high-throughput sequencing of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene fragments, we characterized the composition of microbial communities in five natural springs in the city of Moscow in the spring, summer, and winter seasons. The microbial communities of each spring in different seasons were similar to each other and clearly differed from the microbiomes of the other springs. Among the Archaea, which averaged about 20% of the microbial communities, ammonium-oxidizing Crenarchaeota predominated, as well as Nanoarchaeota. Most of the Bacteria belonged to the phyla Proteobacteria, Patescibacteria, Verrucomicrobiota, Chloroflexi, and Bacteroidota. Autotrophic bacteria, including iron-oxidizing bacteria of the family Gallionellaceae and nitrifiers, as well as methanotrophs, accounted for significant proportions in the microbial communities of the springs with a presumably deeper water source. Chemical and molecular analyses did not reveal contamination of spring waters with toxic substances and oil-derived products, as well as the presence of pathogenic microorganisms and indicators of fecal pollution. However, during the spring season, the proportions of halophilic and hydrocarbon-oxidizing bacteria increased in water microbiomes, which may reflect the entry into groundwater after snow thawing of deicing reagents and hydrocarbons, which are successfully biodegraded in the soil.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Akbari, A., David, C., Rahim, A.A., and Ghoshal, S., Salt selected for hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria and enhanced hydrocarbon biodegradation in slurry bioreactors, Water. Res., 2021, vol. 202, p. 117424.
Bärenstrauch, M., Vanhove, A.S., Allégra, S., Peuble, S., Gallice, F., Paran, F., Lavastre, V., and Girardot, F., Microbial diversity and geochemistry of groundwater impacted by steel slag leachates, Sci. Total. Environ., 2022, vol. 843, pp. 156987.
Beam, J.P., Becraft, E.D., Brown, J.M., Schulz, F., Jarett, J.K., Bezuidt, O., Poulton, N., Clark, K., Dunfield, P., Ravin, N., Spear, J., Hedlund, B., Kormas, K., Sievert, S., Elshahed, M., et al., Ancestral absence of electron transport chains in Patescibacteria and DPANN, Front. Microbiol., 2020, vol. 11, p. 1848.
Brown, C.T., Hug, L.A., Thomas, B.C., Sharon, I., Castelle, C.J., Singh, A., Wilkins, M., Wrighton, K., Williams, K., and Banfield, J.F., Unusual biology across a group comprising more than 15% of domain Bacteria, Nature, 2015, vol. 523, pp. 208‒211.
Cao, H., Auguet, J.C., and Gu, J.D., Global ecological pattern of ammonia-oxidizing archaea, PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, p. e52853.
Chistoserdova, L., Methylotrophy in a lake: from metagenomics to single-organism physiology, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 77, pp. 4705‒4711.
David, G.M., López-García, P., Moreira, D., Alric, B., Deschamps, P., Bertolino, P., Restoux, G., Rochelle-Newall, E., Thébault, E., Simon, M., and Jardillier, L., Small freshwater ecosystems with dissimilar microbial communities exhibit similar temporal patterns, Mol. Ecol., 2021, vol. 30, pp. 2162‒2177.
Dombrowski, N., Lee, J.H., Williams, T.A., Offre, P., and Spang, A., Genomic diversity, lifestyles and evolutionary origins of DPANN archaea, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2019, vol. 366, p. fnz008.
Edgar, R.C., Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST, Bioinformatics, 2010, vol. 26, pp. 2460–2461.
Emerson, D., Fleming, E.J., and McBeth, J.M., Iron-oxidizing bacteria: an environmental and genomic perspective, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 64, pp. 561‒583.
Emerson, D., Field, E.K., Chertkov, O., Davenport, K.W., Goodwin, L., Munk, C., Nolan, M., and Woyke, T., Comparative genomics of freshwater Fe-oxidizing bacteria: implications for physiology, ecology, and systematics, Front. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 4, p. 254.
Ettwig, K.F., Butler, M.K., Le Paslier, D., Pelletier, E., Mangenot, S., Kuypers, M.M., Schreiber, F., Dutilh, B.E., Zedelius, J., de Beer, D., Gloerich, J., Wessels, H.J.C.T., van Alen, T., Luesken, F., Wu, M.L., et al., Nitrite-driven anaerobic methane oxidation by oxygenic bacteria, Nature, 2010, vol. 464, pp. 543‒548.
Fakhrzadegan, I., Hassanshahian, M., Askari Hesni, M., and Saadatfar, A., A study of crude oil-degrading bacteria from mangrove forests in the Persian Gulf, Mar. Ecol., 2019, vol. 40, p. e12544.
Finneran, K.T., Johnsen, C.V., and Lovley, D.R., Rhodoferax ferrireducens sp. nov., a psychrotolerant, facultatively anaerobic bacterium that oxidizes acetate with the reduction of Fe(III), Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 53, pp. 669‒673.
Frey, B., Rime, T., Phillips, M., Stierli, B., Hajdas, I., Widmer, F., and Hartmann, M., Microbial diversity in European alpine permafrost and active layers, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2016, vol. 92, p. fiw018.
Govarthanan, M., Khalifa, A.Y., Kamala-Kannan, S., Srinivasan, P., Selvankumar, T., Selvam, K., and Kim, W., Significance of allochthonous brackish water Halomonas sp. on biodegradation of low and high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, Chemosphere, 2020, vol. 243, p. 125389.
Grimm, N.B., Foster, D., Groffman, P., Grove, J.M., Hopkinson, C.S., Nadelhoffer, K.J., Pataki, D.E., and Peters, D.P., The changing landscape: ecosystem responses to urbanization and pollution across climatic and societal gradients, Front. Ecol. Environ., 2008, vol. 6, pp. 264‒272.
Harayama, S., Kasai, Y., and Hara, A., Microbial communities in oil-contaminated seawater, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2004, vol. 15, pp. 205‒214.
Haroon, M.F., Hu, S., Shi, Y., Imelfort, M., Keller, J., Hugenholtz, P., Yuan, Z., and Tyson, G.W., Anaerobic oxidation of methane coupled to nitrate reduction in a novel archaeal lineage, Nature, 2013, vol. 500, pp. 567‒570.
Herrmann, M., Wegner, C.E., Taubert, M., Geesink, P., Lehmann, K., Yan, L., Lehmann, R., Totsche, K.U., and Küsel, K., Predominance of Cand. Patescibacteria in groundwater is caused by their preferential mobilization from soils and flourishing under oligotrophic conditions, Front. Microbiol., 2019, vol. 10, p. 1407.
Huang, G., Liu, C., Zhang, Y., and Chen, Z., Groundwater is important for the geochemical cycling of phosphorus in rapidly urbanized areas: a case study in the Pearl River Delta, Environ. Pollut., 2020, vol. 260, p. 114079.
Huu, N.B., Nga, V.H., and Ha, D.T.C., Survey of the petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading capacity of three bacteria strains isolated from the oil sludge in Vietnam, Academia J. Biol., 2003, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 62‒68.
Il’inskii, V.V., Shadrina, N.A., and Komarova, T.I., Heterotrophic bacteria of urban springs: Krylatskie Kholmy Nature Reserve, Moscow, Water Resour., 2010, vol. 37, pp. 494‒501.
Ivanova, A.A., Oshkin, I.Y., Danilova, O.V., Philippov, D.A., Ravin, N.V., and Dedysh, S.N., Rokubacteria in northern peatlands: habitat preferences and diversity patterns, Microorganisms, 2021, vol. 10, p. 11.
Kato, S., Krepski, S., Chan, C., Itoh, T., and Ohkuma, M., Ferriphaselus amnicola gen. nov., sp. nov., a neutrophilic, stalk-forming, iron-oxidizing bacterium isolated from an iron-rich groundwater seep, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2014, vol. 64, pp. 921‒925.
Kato, S., Ohkuma, M., Powell, D.H., Krepski, S.T., Oshima, K., Hattori, M., Shapiro, N., Woyke, T., and Chan, C.S., Comparative genomic insights into ecophysiology of neutrophilic, microaerophilic iron oxidizing bacteria, Front. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 6, p. 1265.
Kløve, B., Allan, A., Bertrand, G., Druzynska, E., Ertürk, A., Goldscheider, N., Henry, S., Karakaya, N., Karjalainen, T.P., Koundouri, P., Kupfersberger, H., Kvœrner, J., Lundberg, A., Muotka, T., Preda, E., et al., Groundwater dependent ecosystems. Part II. Ecosystem services and management in Europe under risk of climate change and land use intensification, Environ. Sci. Policy, 2011, vol. 14, pp. 782‒793.
Kolinko, S., Richter, M., Glöckner, F.O., Brachmann, A., and Schüler, D., Single-cell genomics of uncultivated deep-branching magnetotactic bacteria reveals a conserved set of magnetosome genes, Environ. Microbiol., 2016, vol. 18, pp. 21‒37.
Kuroda, K. and Fukushi, T., Groundwater contamination in urban areas, in Groundwater Management in Asian Cities, Takizawa, S., Ed., Tokyo: Springer, 2008, vol. 2, p. 125‒149.
Kuroda, K., Yamamoto, K., Nakai, R., Hirakata, Y., Kubota, K., Nobu, M.K., and Narihiro, T., Symbiosis between Candidatus Patescibacteria and Archaea discovered in wastewater-treating bioreactors, mBio, 2022, p. e01711-22.
Lerner, D.N., Groundwater recharge in urban areas, Atmos. Environ., 1990, vol. 24, pp. 29‒33.
Leu, A.O., Cai, C., McIlroy, S.J., Southam, G., Orphan, V.J., Yuan, Z., Hu, S., and Tyson, G.W., Anaerobic methane oxidation coupled to manganese reduction by members of the Methanoperedenaceae, ISME J., 2020, vol. 14, pp. 1030‒1041.
Li, F., Liu, X., Zhang, X., Zhao, D., Liu, H., Zhou, C., and Wang, R., Urban ecological infrastructure: an integrated network for ecosystem services and sustainable urban systems, J. Clean. Prod., 2017, vol. 163, pp. S12‒S18.
Magoč, T. and Salzberg, S.L., FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies, Bioinformatics, 2011, vol. 27, pp. 2957‒2963.
Martín, S., Márquez, M.C., Sánchez-Porro, C., Mellado, E., Arahal, D.R., and Ventosa, A., Marinobacter lipolyticus sp. nov., a novel moderate halophile with lipolytic activity, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 53, pp. 1383‒1387.
McPhearson, T., Pickett, S.T., Grimm, N.B., Niemelä, J., Alberti, M., Elmqvist, T., Weber, C., Haase, D., Breuste, J., and Qureshi, S., Advancing urban ecology toward a science of cities, Bioscience, 2016, vol. 66, pp. 198‒212.
Mehrshad, M., Rodriguez-Valera, F., Amoozegar, M.A., López-García, P., and Ghai, R., The enigmatic SAR202 cluster up close: shedding light on a globally distributed dark ocean lineage involved in sulfur cycling, ISME J., 2018, vol. 12, pp. 655‒668.
Nelson, W.C. and Stegen, J.C., The reduced genomes of Parcubacteria (OD1) contain signatures of a symbiotic lifestyle, Front. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 6, p. 713.
Orata, F.D., Meier-Kolthoff, J.P., Sauvageau, D., and Stein, L.Y., Phylogenomic analysis of the gammaproteobacterial methanotrophs (order Methylococcales) calls for the reclassification of members at the genus and species levels, Front. Microbiol., 2018, vol. 9, p. 3162.
Paul, M., Wolf, L., Fund, K., Held, I., Winter, J., Eiswirth, M., Gallert, C., and Hoetzl, H., Microbiological condition of urban groundwater in the vicinity of leaky sewer systems, Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol., 2004, vol. 32, pp. 351‒360.
Plummer, J.D. and Long, S.C., Identifying sources of surface water pollution: a toolbox approach, J. Am. Water. Works. Assoc., 2009, vol. 101, no. 9, pp. 75‒88.
Powell, K.L., Taylor, R.G., Cronin, A.A., Barrett, M.H., Pedley, S., Sellwood, J., Trowsdale, S.A., and Lerner, D.N., Microbial contamination of two urban sandstone aquifers in the UK, Water. Res., 2003, vol. 37, pp. 339‒352.
Quast, C., Pruesse, E., Yilmaz, P., Gerken, J., Schweer, T., Yarza, P., Peplies, J., and Glöckner, F.O., The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools, Nucleic Acids Res., 2013, vol. 41 (Database issue), pp. D590‒D596.
Rezaei Somee, M., Shavandi, M., Dastgheib, S.M.M., and Amoozegar, M.A., Bioremediation of oil-based drill cuttings by a halophilic consortium isolated from oil-contaminated saline soil, 3 Biotech., 2018, vol. 8, p. 229.
Rognes, T., Flouri, T., Nichols, B., Quince, C., and Mahé, F., VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics, PeerJ, 2016, vol. 4, p. e2584.
Scharping, R.J. and Garey, J.R., Relationship between aquifer biofilms and unattached microbial indicators of urban groundwater contamination, Mol. Ecol., 2021, vol. 30, pp. 324‒342.
Sharp, J.M., The impacts of urbanization on groundwater systems and recharge, Aqua Mundi, 2010, pp. 51‒56. https://doi.org/10.4409/Am-004-10-0008
Singer, E., Webb, E.A., Nelson, W.C., Heidelberg, J.F., Ivanova, N., Pati, A., and Edwards, K.J., Genomic potential of Marinobacter aquaeolei, a biogeochemical “opportunitroph,” Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 77, pp. 2763‒2771.
Sonthiphand, P., Ruangroengkulrith, S., Mhuantong, W., Charoensawan, V., Chotpantarat, S., and Boonkaew-wan, S., Metagenomic insights into microbial diversity in a groundwater basin impacted by a variety of anthropogenic activities, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int., 2019, vol. 26, pp. 26765‒26781.
Stahl, D.A. and de la Torre, J.R., Physiology and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 2012, vol. 66, pp. 83‒101.
Szekeres, E., Chiriac, C.M., Baricz, A., Szőke-Nagy, T., Lung, I., Soran, M.L., Rudi, K., Dragos, N., and Coman, C., Investigating antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes, and microbial contaminants in groundwater in relation to the proximity of urban areas, Environ. Pollut., 2018, vol. 236, pp. 734‒744.
van Kessel, M.A., Speth, D.R., Albertsen, M., Niel-sen, P.H., Op den Camp, H.J., Kartal, B., Jetten, M.S.M., and Lücker, S., Complete nitrification by a single microorganism, Nature, 2015, vol. 528, pp. 555‒559.
Yakimov, M.M., Denaro, R., Genovese, M., Cappello, S., D’Auria, G., Chernikova, T.N., Timmis, K.N., and Giluliano, L., Natural microbial diversity in superficial sediments of Milazzo Harbor (Sicily) and community successions during microcosm enrichment with various hydrocarbons, Environ. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 7, pp. 1426‒1441.
Yakimov, M.M., Timmis, K.N., and Golyshin, P.N., Obligate oil-degrading marine bacteria, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2007, vol. 18, pp. 257‒266.
Yin, J., Chen, J.C., Wu, Q., and Chen, G.Q., Halophiles, coming stars for industrial biotechnology, Biotechnol. Adv., 2015, vol. 33, pp. 1433‒1442.
Zanini, A., Petrella, E., Sanangelantoni, A.M., Angelo, L., Ventosi, B., Viani, L., Rizzo, P., Remelli, S., Bartoli, M., Bolpagni, R., Chelli, A., Feo, A., Francese, R., Iacumin, P., Menta, C., et al., Groundwater characterization from an ecological and human perspective: an interdisciplinary approach in the Functional Urban Area of Parma, Italy, Rend. Lincei. Sci. Fis. Nat., 2019, vol. 30, pp. 93‒108.
Zare, N., Bonakdarpour, B., Amoozegar, M.A., Sha-vandi, M., Fallah, N., Darabi, S., and Taromsary, N.B., Using enriched water and soil-based indigenous halophilic consortia of an oilfield for the biological removal of organic pollutants in hypersaline produced water generated in the same oilfield, Process. Saf. Environ. Prot., 2019, vol. 127, pp. 151‒161.
Zhou, N., Keffer, J.L., Polson, S.W., and Chan, C.S., Unraveling Fe(II)-oxidizing mechanisms in a facultative Fe(II) oxidizer, Sideroxydans lithotrophicus strain ES-1, via culturing, transcriptomics, and reverse transcription-quantitative PCR, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2022, vol. 88, p. e01595-21.
Zhu, W.Y., Yang, L., Zhang, Z.T.L., Mu, C.G., Wang, Y., Kou, Y.R., Jiang, G.Q., Yin, M., and Tang S.K., Oceanobacillus salinisoli sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from saline soil of Turpan city in Xinjiang province, north–west China, Arch. Microbiol., 2021, vol. 203, pp. 2919‒2924.
Funding
The study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research and the Government of Moscow, project no. 21-34-70027, and the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Collection of water samples and their physicochemical characterization, as well as isolation of metagenomic DNA, were carried out by E.V. Gruzdev and V.V. Kadnikov. 16S rRNA gene libraries were sequenced by A.V. Mardanov. Analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequencing results was performed by Sh.A. Begmatov and A.V. Beletsky. Data were analyzed and the article was prepared by E.V. Gruzdev, V.V. Kadnikov, and N.V. Ravin. The project was managed by V.V. Kadnikov. All authors participated in the discussion of the results.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by E. Babchenko
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gruzdev, E.V., Begmatov, S.A., Beletsky, A.V. et al. Structure and Seasonal Variability of Microbial Communities of Groundwater in the City of Moscow. Microbiology 92, 192–203 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261722603293
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261722603293