Abstract
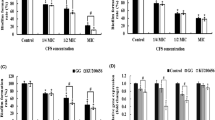
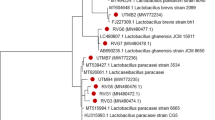
Manufacture of fermented foods/products, which, apart from basic nutrition, have health-promoting effects, is flourishing. Within the field of fermented foods, rapidly expanding is the area of probiotics. Probiotic bacteria are gaining growing attention in the last two decades as a result of the constantly increasing scientific evidence of their beneficial effects on human health. In the current study, the isolate Lactobacillus plantarum MYS84 was identified by morphological, biochemical, physiological, and genetic methods. The standard in vitro techniques revealed that the isolated strain possessed good probiotic attributes. The cell-free supernatant (CFS) was active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTCC 7903, probably due to its proteinaceous nature, and it retained activity after treatment with catalase, lysozyme, and papain. It was also heat-resistant and acid-stable. Moreover, the CFS exhibited strong biofilm inhibition (78%).




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Amin, R.A., Effect of biopreservation as a modern technology on quality aspects and microbial safety of minced beef, Global J. Biotechnol. Biochem., 2012, vol. 7, pp. 38–49.
Anju, K.M., Archana, M.M., Mohandas, C., and Nambisan, B., Purification and identification of an antibacterial protein from the symbiotic bacteria associated with novel entomopathogenic nematode, Rhabditis (Oscheius) sp., World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2015, vol. 31, pp. 621–632.
Argyri, A.A., Zoumpopoulou, G., Karatzas, K.A.G., Tsakalidou, E., Nychas, G.J.E., Panagou, E.Z., and Tassou, C.C., Selection of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria from fermented olives by in vitro tests, Food Microbiol., 2013, vol. 33, pp. 282–291.
Barbosa, M.S., Todorov, S.D., Ivanova, I.V., Belguesmia, Y., Choiset, Y., Rabesona, H., and Franco, B.D.G.D.M., Characterization of a two-peptide plantaricin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum MBSa4 isolated from Brazilian salami, Food Control, 2016, vol. 60, pp. 103–112.
Barnes, L.M., Lo, M.F., Adams, M.R., and Chamberlain, A.H., Effect of milk proteins on adhesion of bacteria to stainless steel surfaces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1999, vol. 65, pp. 4543–4548.
Batdorj, B., Dalgalarrondo, M., Choiset, Y., Pedroche, J., Metro, F., Prevost, H., and Haertlé., T., Purification and characterization of two bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria isolated from Mongolian airag, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 101, pp. 837–848.
Ben Slama, R., Kouidhi, B., Zmantar, T., Chaieb, K., Bakhrouf, A., Anti-listerial and anti-biofilm activities of potential probiotic Lactobacillus strains isolated from Tunisian traditional fermented food, J. Food Safety, 2013, vol. 33, pp. 8–16.
Bjarnsholt, T., The role of bacterial biofilms in chronic infections, APMIS Suppl., 2013, vol. 136, pp. 1–51.
Cappuccino, J.G. and Sherman, N., Microbiology: A Laboratory Manual, Singapore: Pearson Education, 2004.
Cegelski, L., Marshall, G., Eldridge, G.R., and Hultgren, S., The biology and future prospects of antivirulence therapies. Nature Rev. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 6, pp. 17–27.
Charteris, W.P., Kelly, P.M., Morelli, L., and Collins, J.K., Antibiotic susceptibility of potentially probiotic Lactobacillus species, J. Food Protect., 1998, vol. 61, pp. 1636–1643.
Chen, H., Temperature-assisted pressure inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes in turkey breast meat, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 2007, vol. 117, pp. 55–60.
Cortes-Zavaleta, O., López-Malo, A., Hernandez-Mendoza, A., and Garcia, H.S., Antifungal activity of Lactobacilli and its relationship with 3-phenyllactic acid production, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 2014, vol. 173, pp. 30–35.
Cotter, P.D., Hill, C., and Ross, R.P., Bacteriocins: developing innate immunity for food, Nature Rev. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 3, pp. 777–788.
Deepthi, B.V., Somashekaraiah, R., Poornachandra Rao K., Deepa, N., Dharanesha, N.K., Girish, K., and Sreenivasa, M.Y., Lactobacillus plantarum MYS6 ameliorates fumonisin B1-induced hepatorenal damage in broilers, Front Microbial., 2017, vol. 8, p. 2317.
Ge, J., Sun, Y., Xin, X., Wang, Y., and Ping, W., Purification and partial characterization of a novel bacteriocin synthesized by Lactobacillus paracasei HD1-7 isolated from Chinese sauerkraut juice, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 19366.
Ghafoor, A., Hay, I.D., and Rehm, B.H., Role of exopolysaccharides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and architecture, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 15, pp. 5238–5246.
Gloag, E.S., Turnbull, L., Huang, A., Vallotton, P., Wang, H., Nolan, L.M., Mililli, L., Hunt, C., Lu, J. Osvath, S.R., Monahan, L.G., Cavaliere, R., Charles, I.G., Wand, M.P., Gee M.L., et al., Self-organization of bacterial biofilms is facilitated by extracellular DNA, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2013, vol. 110, pp. 11541–11546.
Jaffar, N., Ishikawa, Y., Mizuno, K., Okinaga, T., and Maeda, T., Mature biofilm degradation by potential probiotics: Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans versus Lactobacillus spp., PLoS One, 2016, vol. 11, no. 7, p. e0159466.
Joint FAO, WHO Working Group Report on Drafting Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food, London, Ontario, Canada, 2002.
Kalyaraung, S., Viernstein, H., Sirithunyalug, J., and Okonogi, S., Probiotic properties of Lactobacilli isolated from thai traditional food, Sci. Pharm., 2008, vol. 76, pp. 485–503.
Kraft, A.A., Psychotropic Bacteria in Foods: Disease and Spoilage, Boca Raton: CRC, 1992.
Kumar, S., Bansal, A., Chakrabarti, A., and Singhi, S., Evaluation of efficacy of probiotics in prevention of Candida colonization in a PICU-a randomized controlled trial, Crit. Care Med., 2013, vol. 41, pp. 565–572.
Laemmli, U.K., Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4, Nature, 1970, vol. 227, pp. 680–685.
Lalitha, M.K., Manual on antimicrobial susceptibility testing. performance standards for antimicrobial testing, Twelfth Informational Supplement., 2004, vol. 56238, pp. 454–456.
Liu, M., Lu, J., Muller, P., Turnbull, L., Burke, C.M., Schlothauer, R.C., Carter, D.A., Whitchurch, C.B., and Harry, E.J., Antibiotic-specific differences in the response of Staphylococcus aureus to treatment with antimicrobials combined with manuka honey, Front. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 2014, p. 5.
Lopez, N., Puertolas, E., Condon, S., Alvarez, I., and Raso, J., Effects of pulsed electric fields on the extraction of phenolic compounds during the fermentation of must of Tempranillo grapes, Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol., 2008, vol. 9, pp. 477–482.
Ma, L., Wang, J., Wang, S., Anderson, E.M., Lam, J.S., Parsek, M.R., and Wozniak, D.J., Synthesis of multiple Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm matrix exopolysaccharides is post transcriptionally regulated, Environ. Microbiol., 2012, vol. 14, no. 8, pp. 1995–2005.
Mahdhi, A., Leban, N., Chakroun, I., Bayar, S., Mahdouani, K., Majdoub, H., and Kouidhi, B., Use of extracellular polysaccharides, secreted by Lactobacillus plantarum and Bacillus spp., as reducing indole production agents to control biofilm formation and efflux pumps inhibitor in Escherichia coli, Microb. Pathog., 2018, vol. 125, pp. 448–453.
Marianelli, C., Cifani, N., and Pasquali, P., Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of probiotic bacteria against Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar typhimurium 1344 in a common medium under different environmental conditions, Res. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 161, pp. 673–680.
Meliani, A. and Bensoltane, A., Review of Pseudomonas attachment and biofilm formation in food industry, Poult. Fish Wildl Sci., 2015, vol. 3, p. 126.
Nagpal, R., Kumar, A., Kumar, M., Behare, P.V., Jain, S., and Yadav, H., Probiotics, their health benefits and applications for developing healthier foods: a review, FEMS Microbiol .Lett., 2012, vol. 334, pp. 1–15.
Neal-McKinney, J.M., Lu, X., Duong, T., Larson, C.L., Call, D.R., Shah, D.H., and Konkel, M.E., Production of organic acids by probiotic Lactobacilli can be used to reduce pathogen load in poultry, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, p. e43928.
Onbas, T., Osmanagaoglu, O., and Kiran, F., Potential properties of Lactobacillus plantarum F-10 as a bio-control strategy for wound infections, Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins, 2018, vol. 11, pp. 1110–1123.
Percival, S.L., Suleman, L., Vuotto, C., and Donelli, G., Healthcare-associated infections, medical devices and biofilms: risk, tolerance and control, J. Med. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 64, pp. 323–334.
Rao, K.P., Chennappa, G., Suraj, U., Nagaraja, H., Raj, A.C., and Sreenivasa, M.Y., Probiotic potential of Lactobacillus strains isolated from sorghum-based traditional fermented food, Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins., 2015, vol. 7, pp. 146–156.
Rao, K.P., Hemanth Kumar, N.K., and Sreenivasa, M.Y., Therapeutic potential of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum MYS94 against Campylobacter jejuni, Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci., 2016, vol. 5, pp. 869–883.
Rao, K.P., Kumar, N.K., and Sreenivasa, M.Y., Characterization of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum MYS14 isolated from Sannas, a traditional fermented food for its therapeutic potential, Curr. Nutr. Food Sci., 2017, vol. 13, pp. 110–120.
Rojo-Bezares, B., Saenz, Y., Navarro, L., Zarazaga, M., Ruiz-Larrea, F., and Torres, C., Coculture-inducible bacteriocin activity of Lactobacillus plantarum strain J23 isolated from grape must, Food Microbiol., 2007, vol. 24, pp. 482–491.
Rossoni, R.D., Velloso, M.D.S., de Barros, P.P., de Alvarenga, J. A., dos Santos, J.D., dos Santos Prado, A.C.C., de Camargo Ribeiro, F., Lia, A.A., and Junqueira, J.C., Inhibitory effect of probiotic Lactobacillus supernatants from the oral cavity on Streptococcus mutans biofilms, Microb. Pathog., 2018, vol. 123, pp. 361–367.
Russotto, V., Cortegiani, A., Raineri, S.M., and Giarratano, A., Bacterial contamination of inanimate surfaces and equipment in the intensive care unit, J. Intensive Care, 2015, vol. 3, p. 54.
Sahadeva, R.P.K., Leong, S.F., Chua, K.H., Tan, C.H., Chan, H.Y., Tong, E.V., Wong, S.Y., and Chan, H.K., Survival of commercial probiotic strains to pH and bile, Int. Food Res. J., 2011, vol. 18, pp. 1515–1522.
Sharma, V., Harjai, K., and Shukla, G., Effect of bacteriocin and exopoly- saccharides isolated from probiotic on P. aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm, Folia Microbiol. (Praha), 2018, vol. 63, pp. 181–190.
Sure, K.P., Kotnis, P.V., Bhagwat, P.K., Ranveer, R.C., Dandge, P.B., and Sahoo, A.K., Production and characterization of bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus viridescence (NICM 2167), Brazilian Arch. Biol. Technol., 2016, vol. 59.
Sutherland, I.W., The biofilm matrix an immobilized but dynamic microbial environment, Trends Microbiol., 2011, vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 222–227.
Tan, Y., Leonhard, M., Moser, D., and Schneider-Stickler, B., Inhibition activity of Lactobacilli supernatant against fungal-bacterial multispecies bio- films on silicone, Microb. Pathog., 2017, vol. 113, pp. 197–201.
Turchi, B., Mancni, S., Fratini, F., Pedonese, F., Nuvoloni, R., Bertelloni, F., Ebani, V.V., and Cerri, D., Preliminary evaluation of probiotic potential of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from Italian food products, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2013, vol. 29, pp. 1913–1922.
US Food and Drug Administration, Draft Guidance for Industry: Hazard Analysis and Risk-Based Preventive Controls for Human Food, 2016.
Zhu, X., Zhao, Y., Sun, Y., and Gu, Q., Purification and characterization of plantaricin ZJ008, a novel bacteriocin against Staphylococcus spp. from Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ008, Food Chem., 2014, vol. 165, pp. 216–223.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao K, P., Kumar N, H., Somashekaraiah, R. et al. Probiotic Attributes and Inhibitory Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum MYS84 against the Growth and Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Microbiology 90, 361–369 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261721030103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261721030103