Abstract—
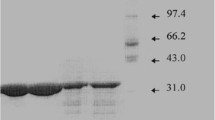
The chemical structure of the extracellular reactivating factor (RF) from Luteococcus japonicus subsp. casei was determined; this factor promotes survival of a small subpopulation of the producer cells under lethal stress impact. For the isolation and purification of this RF, the previously developed method for RF isolation from Saccharomyces cerevisiae was optimized. A total of 15 fractions were obtained from the culture liquid of Luteococcus casei, two of which (I and IV) exhibited reactivation activity against the cells subjected to a lethal stress impact (UV irradiation). The method included solid-phase extraction of the peptides on a hydrophobic sorbent with the C8 phase and subsequent multistage separation using RP-HPLC. Mass spectral analysis (MALDI-TOF) was used to determine the molecular characteristics of fraction IV. Efficient ionization was not achieved for fraction I. Mass charges for fraction IV were 773.394 and 788.102 Da. Edman automatic sequencing was used to identify these components as peptides: Ala-Pro-Asn-Glu-Asn-Gln-Gly and Ala-Pro-Asn-Glu-Glu-Gln-Gly. No similarity to any known full-size functional peptide molecules in the databases on polypeptide primary structures was revealed. Formation of biologically active peptides by L. casei may be associated with non-template synthesis and probably involves proteolysis of a large protein.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Collins, M.D., Hitson, R.A., Nikolaitchouk, N., Nyberg, A., and Folsen, E. Luteococcus sanguinis sp. nov., isolated from human blood, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 53, pp. 1889–1891.
Fan, X., Zhang, Z., and Zhang, X.H., Luteococcus sediminum sp. nov., isolated from subseafloor sediment of the South Pacific Gyre, Int. J. Evol. Microbiol., 2014, vol. 64, pp. 2522–2527.
Loiko, N.G., Vorob’eva, L.I., Khodzhaev, E.Yu., Kozlova, A.N., Gal’chenko, V.F., and El’ Registan, G.I., Effect of the reactivating factor of Luteococcus japonicus subsp. casei on the expression of SOS response genes, Microbiology (Moscow), 2013, vol. 82, pp. 126–132.
Tamura, T., Takaechi, M., and Yokota, A., Luteococcus japonicus gen. nov., sp., nov., a new gram-positive coccus with LL-diaminopimelic acid in the cell wall, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., vol. 44, pp. 348–356.
Thorenoor, N., Kim, Y., Lee, C., Yu, M.H., and Engesser, K.H., A previously uncultured papermill Propionibacteria is able to degrade O-aryl alkyl ethers and various aromatic hydrocarbons, Chemosphere, 2009, vol. 75, pp. 1287–1293.
Van Niewholtz, J.A., A taxonomic re-evaluation of Propionibacterium coccoides, Ph.D. Thesis, Dep. Microbiol. Biochem. Univ. Orange Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 1998.
Vorob’eva, L.I., Turova, T.P., Kraeva, N.I., and Alekseeva, A.A., Propionic acid cocci and their systematic position, Microbiology (Moscow), 1983, vol. 52, pp. 368–374.
Vorobjeva, L.I., Propionibacteria, Kluwer Academic, 1999.
Vorob’eva, L.I., Khodjaev, E.Yu., and Ponomareva, G.M., The extracellular protein of Luteococcus japonicus subsp. reactivates cells inactivated by UV-irradiation or heat shock, Microbiology (Moscow), 2003, vol. 72, pp. 428–433.
Vorob’eva, L.I., Khodzhaev, E.Yu., Mulyukin, A.L., and Toropygin, I.Yu., The mechanism of action of reactivating factor from Luteococcus japonicus subsp. casei, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 45, pp. 489–493.
Vorob’eva, L.I. and Khodzhaev, E.Yu., Protective and reactivating effect of the protein exometabolite on yeast cells inactivated by the ultraviolet irradiation, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 46, pp. 177–183.
Vorob’yova, L.I., Fedotova, A.V., and Khodzhaev, E.Yu., Protective action of reactivating factor of Luteococcus japonicus subsp. casei toward cells of Escherichia coli reparation mutants inactivated with UV-light, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 46, pp. 567–573.
Vorob’eva, L.I., Khodzhaev, E.Yu., and Vustin, M.M., Extracellular protein metabolite of Luteococcus japonicus subsp. casei reactivates cells subjected to oxidative stress, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 47, pp. 264–269.
Vorob’eva, L.I., Khodzhaev, E.Yu., Novikova, T.M., Mulyukin, A.L., Chudinova, E.M., Kozlova, A.N., and El’-Registan, G.I., Stress-protective and cross action of the extracellular reactivating factor of the microorganisms of the domains bacteria, archaea, and eukaryota, Microbiology (Moscow), 2013, vol. 82, pp. 594–599.
Vorob’eva, L.I., Khodzhaev, E.Yu., Rogozhin, E.A., Samoilenko, V.A., and Kharchenko, N.V., Structural characterization of the extracellular peptide metabolites of Luteococcus japonicus subsp. casei and their protective effect on probiotic bacteria, Microbiology (Moscow), 2015, vol. 84, pp. 502–511.
Vorob’eva, L.I., Rogozhin, E.A., Khodzhaev, E.Yu., Nikolaev, I.V., and Turova T.P., Reactivating factor of Luteococcus japonicus subsp. casei: isolation and characterization, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 51, pp. 44–51.
Vorob’eva, L.I., Khodzhaev, E.Yu., Rogozhin, E.A., Cherdyntseva, T.A., and Netrusov, A.I., Characterization of extracellular yeast peptide factors and their stress-protective effect on probiotic lactic acid bacteria, Microbiology (Moscow), 2016, vol. 85, pp. 411–419.
Vorob’eva, L.I., Rogozhin, E.A., Khodzhaev, E.Yu., Volodyazhkin, R.A., and Samoilenko, V.A., Characterization and stress-protective action of Saccharomyces cerevisiae extracellular peptide factors on propionic acid bacteria, Microbiology (Moscow), 2017, vol. 86, pp. 698–707. Translated by Е. Makeeva
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rogozhin, E.A., Vorob’eva, L.I., Khodzhaev, E.Y. et al. Optimized Fractioning and Structure Analysis of the Reactivating Factor from Luteococcus japonicus subsp. casei. Microbiology 88, 132–136 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261719020097
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261719020097