Abstract
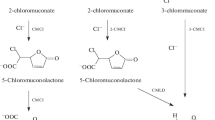
The strain Rhodococcus ruber P25 utilizes 4-chlorobiphenyl (4CB) and 4-chlorobenzoic acid (4CBA) as sole carbon and energy sources. 4CB degradation by washed cells of strain P25 was accompanied by transient formation of 4CBA, followed by its utilization and release of equimolar amounts of chloride ions into the medium. The strain R. ruber P25 possessed active enzyme systems providing 4CBA degradation via the stages of formation of intermediates, para-hydroxybenzoate (PHBA) and protocatechuic acid (PCA), to compounds of the basic metabolism. The involvement of protocatechuate 4,5-dioxygenase in 4CBA degradation by rhodococci was revealed. It was established that the initial stage of 4CBA degradation (dehalogenation) in the strain R. ruber P25 was controlled by the fcbA and fcbB genes encoding 4-CBA-CoA ligase and 4-CBA-CoA dehalogenase, respectively. The genes encoding 4CBA dehalogenase components have not been previously detected and characterized in bacteria of the genus Rhodococcus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seo, J.-S., Keum, Y.-S., and Li, Q.X., Bacterial Degradation of Aromatic Compounds, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health, 2009, vol. 6, pp. 278–309.
Quensen, J.F., III and Tiedje, J.M., Evolution of PCB Dechlorination in Sediments, in Methods in Biotechnology, vol. 2. Bioremediation Protocol, Sheehan, D., Ed., Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 1998, pp. 257–273.
Pieper, D.H., Aerobic Degradation of Polychlorinated Biphenyls, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2005, vol. 67, no. 2, pp. 170–191.
Maltseva, O.V., Tsoi, T.V., Quensen, J.F., III, Fucuda, M., and Tiedje, J.M., Degradation of Anaerobic Reductive Dechlorination Products of Aroclor 1242 by Four Aerobic Bacteria, Biodegradation, 1999, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 363–371
Kim, S. and Picardal, F.W., A Novel Bacterium that Utilizes Monochlorobiphenyls and 4-Chlorobenzoate as a Growth Substrates, FEMS Microb. Lett., 2000, vol. 185, pp. 225–229.
Rybkina, D.O., Plotnikova, E.G., Dorofeeva, L.V., Mironenko, Yu.L., and Demakov, V.A., A New Aerobic Gram-Positive Bacterium with a Unique Ability to Degrade ortho- and para-Chlorinated Biphenyls, Microbiology, 2003, vol. 72, no. 6, pp. 672–677.
Adebusoye, S.A., Picardal, F.W., Ilori, M.O., Amund, O.O., and Fugua, C., Characterization of Multiple Novel Aerobic Polychlorinated Biphenyl (PCB)-Utilizing Bacterial Strains Indigenous to Contaminated Tropical African Soil, Biodegradation, 2008, vol. 19, pp. 145–159.
Chae, J.C., Kim, E., Park, S.H., and Kim, C.K., Catabolic Degradation of 4-Chlorobiphenyl by Pseudomonas sp. DJ-12 via Consecutive Reaction of Meta-Cleavage and Hydrolytic Dechlorination, Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng., 2000, vol. 5, pp. 449–455.
Arensdorf, J.J. and Focht, D.D., A meta Cleavage Pathway for 4-Chlorobenzoate, an Intermediate in the Metabolism of 4-Chlorobiphenyl by Pseudomonas cepacia P166, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1995, vol. 61, pp. 443–447.
Egorova, D.O., Shumkova, E.S., Demakov, V.A., and Plotnikova, E.G., Degradation of Chlorinated Biphenyls and Products of Their Bioconversion by Rhodococcus sp. B7a Strain, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 46, no. 6, pp. 592–598.
Plotnikova, E.G., Rybkina, D.O., and Demakov, V.A., RF Patent No. 2262531 (2005).
Plotnikova, E.G., Rybkina, D.O., Anan’ina, L.N., Yastrebova, O.V., and Demakov, V.A., Characteristics of Microorganisms Isolated from Technogenic Soils of the Kama Region, Russ. J. Ecol., 2006, no. 4, pp. 233–240.
Tsoi, T.V., Zaitsev, G.M., Plotnikova, E.G., Kosheleva, I.A., and Boronin, A.M., Cloning and Expression of the Arthrobacter globiformis KZT-1 fcb Gene Encoding Dehalogenase (4-Chlorobenzoate-Hydroxylase) in E. coli, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1991, vol. 81, no. 2, pp. 165–170.
Ausbel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., and Struhl, K., Short Protocols in Molecular Biology. Third Edition, New York: Wiley, 1995.
Suvorova, M.M., Solyanikova, I.P., and Golovleva, L.A., Specificity of Catechol ortho-Cleavage during para-Toluate Degradation by Rhodococcus opacus 1cp, Biochemistry (Moscow), 2006, vol. 71, no. 12, pp. 1316–1323.
Jadan, A.P., Moonen, M.J.H., Golovleva, L.A., Rietjens, I.M.C.M., and van Berkel, W.J.H., Biocatalytic Potential of p-Hydroxybenzoate Hydroxylase from Rhodococcus rhodnii 135 and Rhodococcus opacus 557, Add. Synth. Catal., 2004, vol. 346, pp. 367–375.
Ono, K., Nozaki, M., and Hayaishi, O., Purification and Some Properties of Protocatechuate 4,5-Dioxygenase, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1970, vol. 220, no. 2, pp. 224–238.
Stanier, R.Y. and Ingraham, J.L., Protocatechuate Acid Oxidase, J. Biol. Chem., 1954, vol. 210, pp. 799–808.
Haddad, S., Eby, D.M., and Neidle, E.L., Cloning and Expression of the Benzoate Dioxygenase Genes from Rhodococcus sp. Strain 19070, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 67, pp. 2507–2514.
Rodrigues, J.L., Kachel, C.A., Aiello, M.R., Quensen, J.F., Maltseva, O.V., Tsoi, T.V., and Tiedje, J.M., Degradation of Aroclor 1242 Dechlorination Products in Sediments by Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 (ohb) and Rhodococcus sp. Strain RHA1 (fcb), Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 72, pp. 2476–2482.
Thompson, J.D., Higgins, D.G., and Gibson, T.J., CLUSTAL W: Improving the Sensitivity of Progressive Multiple Sequence Alignment through Sequence Weighting, Position Specific Gap Penalties and Weight Matrix Choice, Nucleic Acids Res., 1994, vol. 22, pp. 4673–4680.
Van de Peer, Y. and de Wachter, R., TREECON for Windows a Software Package for the Construction and Drawing of Evolutionary Trees for the Microsoft Windows Environment, Comput. Appl. Biosci., 1994, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 569–570.
Furukawa, K. and Fujihara, H., Microbial Degradation of Polychlorinated Biphenyls: Biochemical and Molecular Features, J. Biosc. Bioeng., 2008, vol. 105, no. 5, pp. 433–449.
Egorova, D.O. and Plotnikova, E.G., Gram-Positive Bacterial Degraders of Chlorinated Biphenyls Promising for Bioremediation of Contaminated Soils, Biotekhnologiya, 2009, no. 3, pp. 72–79.
Witzig, R.H., Hecht, J.H.-J., and Pieper, D.H., Assessment of Toluene/Biphenyl Dioxygenase Gene Diversity in Benzene-Polluted Soils: Links between Benzene Biodegradation and Genes Similar to Those Encoding Isopropylbenzene Dioxygenases, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 72, pp. 3504–3514.
Field, J.A. and Sierra-Alvarez, R., Microbial Transformation of Chlorinated Benzoates, Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol., 2008, vol. 7, pp. 191–210.
Chang, K.H., Xiang, H., and Dunaway Mariano, D., Acyl-Adenylate Motif of the Acyl-Adenylate/Thioester-Forming Enzyme Superfamily: A SiteDirected Mutagenesis Study with the Pseudomonas sp. Strain CBS3 4-Chlorobenzoate: Coensyme A Ligase, Biochemistry, 1997, vol. 36, pp. 15650–15659.
Schmitz, A., Gartemann, K.H., Fiedler, J., Grund, E., and Eichenlaub, R., Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Genes for Dehalogenation of 4-Chlorobenzoate from Arthrobacter sp. Strain SU, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1992, vol. 58, pp. 4068–4071.
Gartemann, K.H. and Eichenlaub, R., Isolation and Characterization of IS1409, an Insertion Element of 4-Chlorobenzoate-Degrading Arthrobacter sp. Strain TM1, and Development of a System for Transposon Mutagenesis, J. Bacteriol., 2001, vol. 183, pp. 3729–3736.
D’Argenio, D.A., Vetting, M.W., Ohlendorf, D.H., and Ornston, L.N., Substitution, Insertion, Deletion, Suppression, and Altered Substrate Specificity in Functional Protocatechuate 3,4-Dioxygenases, J. Bacteriol., 1999, vol. 181, pp. 6478–6487.
Huang, Y., Zhao, K., Shen, X.-H., Jiang, C.-Y., and Liu, S.-J., Genetic and Biochemical Characterization of a 4-Hydroxybenzoate Hydroxylase from Corynebacterium glutamicum, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2008, vol. 78, pp. 75–83.
Wolgel, S.A., Dege, J.E., Perkins-Olson, P.E., Juares-Garcia, C.H., Crawford, R.L., Munck, E., and Lipscomb, J.D., Purification and Characterization of Protocatechuate 2,3-Dioxygenase from Bacillus macerans: A New Extradiol Catecholic Dioxygenase, J. Bacteriol., 1993, vol. 175, pp. 4414–4426.
Mampel, J., Providenti, M.A., and Cook, A.M., Protocatechuate 4,5-Dioxygenase from Comamonas testosteroni T-2: Biochemical and Molecular Properties of a New Subgroup within Class III of Extradiol Dioxygenases, Arch. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 183, pp. 130–139.
Ornston, L.N. and Parke, D., Properties of an Inducible Uptake System for β-Ketoadipate in Pseudomonas putida, J. Bacteriol., 1976, vol. 125, pp. 475–488.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.G. Plotnikova, I.P. Solyanikova, D.O. Egorova, E.S. Shumkova, L.A. Golovleva, 2012, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2012, Vol. 81, No. 2, pp. 159–170.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plotnikova, E.G., Solyanikova, I.P., Egorova, D.O. et al. Degradation of 4-chlorobiphenyl and 4-chlorobenzoic acid by the strain Rhodococcus ruber P25. Microbiology 81, 143–153 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261712020117
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261712020117