Abstract
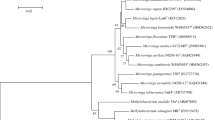
Three strains of gram-negative bacteria were isolated from the mats of colorless sulfur bacteria Thioploca (Lake Baikal). The cells of new strains are motile with peritrichous flagella. Bacteria are aerobic, obligate chemoorganoheterotrophs growing within the pH range of 3.0–8.8 with the optimum at 8.3 and within the temperature range of 5–42°C with the optimum at 28°C. The cells contained menaquinones MK-8 H2 as the major component, as well as MK-7 H2 (less than 15%), while the content of ubiquinone Q8 was at least an order of magnitude lower. The G+C content of DNA in the new strains varied from 67.4 to 69.9 mol %. The level of DNA-DNA hybridization between the strains ranged from 80 to 94%, indicating that all the isolates belonged to one species. Analysis of the 16S rRNA gene nucleotide sequences of the type strain (Gen-Bank HQ400611) revealed close homologues among the known species of the genus Variovorax: 98% resemblance with the type strains of the species V. paradoxus, V. soli, V. ginsengisoli, and V. boronicumulans and 96% similarity with the type strain of V. dokdonensis. However, since the isolates differed significantly in the composition of fatty acids and isoprenoid quinones from the nearest neighbors in the phylogenetic tree, they cannot be related implicitly to the known species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suits, N.S. and Arthur, M.A., Bacterial Production of Anomalously High Dissolved Sulfate Concentrations in Peru Slope Sediments: Steady-State Sulfur Oxidation, or Transient Response to End of El Niño?, Deep-Sea Res., part 1, 2000, vol. 47, no. 10, pp. 1829–1853.
Dermott, R. and Legner, M., Dense Mat-Forming Bacterium Thioploca ingrica (Beggiatoaceae) in Eastern Lake Ontario: Implications to the Benthic Food Web, J.Great Lakes Res., 2002, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 688–697.
Namsaraev, B.B., Dulov, L.E., Dubinina, G.A., Zemskaya, T.I., Granina, L.Z., and Karabanov, E.B., Role of Bacteria in Synthesis and Destruction of Organic matter in the Lake Baikal Microbial Mats, Mikrobiologiya, 1994, vol. 63, no. 2, p. 345–351.
Zemskaya, T.I., Chernitsyna, S.M., Dul’tseva, N.M., Sergeeva, V.N., Pogodaeva, T.V., and Namsaraev, B.B., Colorless Sulfur Bacteria Thioploca from Different Sites in Lake Baikal, Microbiology, 2009, vol. 78, no. 1, pp. 117–124.
Kojima, H., Koizumi, Y., and Manabu, F., Community Structure of Bacteria Associated with Sheaths of Freshwater and Brackish Thioploca Species, Microb. Ecol., 2006, vol. 52, no. 4, p. 765–773.
Prokopenko, M.G., Hammond, D.E., Berelson, W.M., Bernhard, J.M., Stott, L., and Douglas, R., Nitrogen Cycling in the Sediments of Santa Barbara Basin and Eastern Subtropical North Pacific: Nitrogen Isotopes, Diagenesis and Possible Chemosymbiosis between Two Lithotrophs (Thioploca and Anammox)—“Riding on a Glider”, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2006, vol. 242, pp. 186–204.
Ferdelman, T.G., Lee, C., Pantoja, S., Harder, J., Bebout, B., and Fossing, H., Sulfate Reduction and Methanogenesis in a Thioploca-Dominated Sediment off the Coast of Chile, Geochim., Cosmochim. Acta, 1997, vol. 61, pp. 3065–3079.
Brinkhoff, T., Muyzer, G., Wirsen, C.O., and Kuever, J., Thiomicrospira chilensis sp. nov., a Mesophilic Obligately Chemolithoautotrophic Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacterium Isolated from a Thioploca Mat, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1999, vol. 49, pp. 875–879.
van de Graaf, A.A., Mulder, A., de Bruijn, P., Jetten, M.S.M., Robertson, L.A., and Kuenen, J.G., Anaerobic Oxidation of Ammonium is a Biologically Mediated Process, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1995, vol. 61, pp. 1246–1251.
Jetten, M.S., Strous, M., van de Pas-Schoonen, K.T., Schalk, J., van Dongen, U.G., van de Graaf, A.A., Logemann, S., Muyzer, G., van Loosdrecht, M.C., and Kuenen, J.G., The Anaerobic Oxidation of Ammonium, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 1998, vol. 22, no. 5, pp. 421–437.
Zemskaya, T.I., Namsaraev, B.B., Dul’tseva, N.M., Khanaeva, T.A., Golobokova, L.P., Dubinina, G.A., Dulov, L.E., and Vada, E., Ecophysiological Characteristics of the Mat-Forming Bacterium Thioploca in Bottom Sediments of the Frolikha Bay, Northern Baikal, Microbiology, 2001, vol. 70, no. 3, pp. 335–341.
Dubinina, G.A. and Grabovich, M.Yu., Isolation, Cultivation, and Characterization of Macromonas bipunctata, Mikrobiologiya, 1984, vol. 53, no. 5, pp. 748–755.
Pfennig, N. and Lippert, R.D., Uber das Vitamin B12 Bedürfnis Schwefelbacterium, Arch. Microbiol., 1966, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 245–259.
Ryter, A. and Kellenberger, E., Etude u microscope electronique de plasmas contennant de l’acide desoxyribonucleique, Z. Naturforschung, 1958, vol. 13, no. 9, pp. 597–605.
Reynolds, E.S., The Use of Lead Citrate at High pH as an Electron-Opaque Stain in Electron Microscopy, J. Cell Biol., 1963, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 208–213.
Reznikov, A.A., Mulikovskaya, E.P., and Sokolov, I.Yu., Metody analiza prirodnykh vod (Methods of Analysis of natural Waters), Moscow: Gosgeoltekhizdat, 1970.
Bradford, M.H., A Rapid and Sensitive Method for Quantitation of Micrograms Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding, Anal. Biochem., 1976, vol. 72, pp. 248–254.
Karavaiko, G.I., Bogdanova, T.I., Tourova, T.P., Kondrat’eva, T.F., Tsaplina, I.A., Egorova, M.A., Krasilnikova, E.N., and Zakharchuk, L.M., Reclassification of “Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans subsp. thermotolerans” Strain K1 as Alicyclobacillus tolerans sp. nov. and Sulfobacillus disulfidooxidans Dufresne et al. 1996 as Alicyclobacillus disulfidooxidans comb. nov., and Emended Description of the Genus Alicyclobacillus, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 55, pp. 941–947.
Collins, N.D., Analysis of Isoprenoid Quinones, Methods Microbiol., Gottschalk, G., Ed., New York: Academic, 1985, vol. 18, pp. 329–366.
Surkov, A.V., Dubinina, G.A., Lysenko, A.M., Glocker, F.O., and Kuever, J., Dethiosulfovibrio russensis sp. nov., Dethiosulfovibrio marinus sp. nov. and Dethiosulfovibrio acidaminovorans sp. nov., Novel Anaerobic, Thiosulfate- and Sulfur-Reducing Bacteria Isolated from “Thiodendron” Sulfur Mats in Different Saline Environments, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 51, pp. 327–337.
Marmur, J., A Procedure for the Isolation of Deoxyribonucleic Acid from Microorganisms, J. Mol. Biol., 1961, vol. 3, pp. 208–218.
Edvards, U., Rogall, T., Bloekker, H., Ende, M.D., and Boeettge, E.C., Isolation and Direct Complete Nucleotide Determination of Entire Genes, Characterization of Gene Coding for 16S Ribosomal RNA, Nucleic Acids Res., 1989, vol. 17, pp. 7843–7853.
Kolganova, T.V., Kuznetsov, B.B., and Turova, T.P., Designing and Testing Oligonucleotide Primers for Amplification and Sequencing of Archaeal 16S rRNA Genes, Microbiology, 2002, vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 243–246.
Kimura, M., A Simple Method for Estimating Evolutionary Rates of Base Substitutions through Comparative Studies of Nucleotide Sequences, J. Mol. Evol., 1980, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 111–120.
Tourova, T.P., Kovaleva, O.L., Sorokin, D.Y., and Muyzer, G., Ribulose-1.5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase Genes as a Functional Marker for Chemolithoautotrophic Halophilic Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria in Hypersaline Habitats, Microbiology (UK), 2010, vol. 156, pp. 819–827.
Spiridonova, E.M., Berg, I.A., Kolganova, T.V., Ivanovskii, R.N., Kuznetsov, B.B., and Tourova, T.P., An Oligonucleotide Primer System for Amplification of the Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase Genes of Bacteria of Various Taxonomic Groups, Microbiology, 2004, vol. 73, no. 3, pp. 316–325.
Willems, A., Deley, J., Gillis, M., and Kersters, K., Comamonadaceae, a New Family Encompassing the Acidovorans rRNA Complex, Including Variovorax paradoxus gen. nov., comb. nov., for Alcaligenes paradoxus (Davis, 1969), Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1991, vol. 41, pp. 445–450.
Schmalenberger, A., Hodge, S., Bryant, A., Hawkesford, M.J., Singh, B.K., and Kertesz, M.A., The Role of Variovorax and Other Comamonadaceae in Sulfur Transformations by Microbial Wheat Rhizosphere Communities Exposed to Different Sulfur Fertilization Regimes, Environ. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 1486–1500.
Maimaiti, J., Zhang, Y., Yang, J., Cen, Y.-P., Layzell, D.B., Peoples, M., and Dong, Z., Isolation and Characterization of Hydrogen-Oxidizing Bacteria Induced Following Exposure of Soil to Hydrogen Gas and Their Impact on Plant Growth, Environ. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 435–444.
Miwa, H., Ahmed, I., Yoon, J., Yokota, A., and Fujiwara, T., Variovorax boronicumulans sp. nov., a Boron-Accumulating Bacterium Isolated from Soil, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 58, pp. 286–289.
Yoon, J.-H., Kang, S.-J., and Oh, T.-K., Variovorax dokdonensis sp. nov., Isolated from Soil, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 56, pp. 811–814.
Kim, B.-Y., Weon, H.-Y., Yoo, S.-H., Lee, S.-Y., Kwon, S.-W., Go, S.-J., and Stackebrandt, E.S., Variovorax soli sp.nov., Isolated from Greenhouse Soil, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 56, pp. 2899–2901.
Im, W.-T., Liu, Q.-M., Lee, K.J., Kim, S.Y., Lee, S.-T., and Yi, T.-H., Variovorax ginsengisoli sp.nov., a Denitrifying Bacterium Isolated from Soil of a Ginseng Field, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 60, pp. 1565–1569.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.M. Dul’tseva, S.M. Chernitsina, T.I. Zemskaya, 2012, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2012, vol. 81, No. 1, pp. 72–83.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dul’tseva, N.M., Chernitsina, S.M. & Zemskaya, T.I. Isolation of bacteria of the genus Variovorax from the Thioploca mats of Lake Baikal. Microbiology 81, 67–78 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261712010067
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261712010067