Abstract
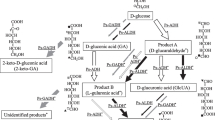
Cellobiose metabolism was studied in Alkaliflexus imshenetskii, a haloalkaliphilic hydrolytic bacterium capable of utilizing certain polymers of plant origin, as well as mono- and disaccharides. The major products of cellobiose fermentation by the bacterium were succinate and acetate, and formate was a minor product. Cellobiose could be split into glucose molecules by both β-glucosidase (hydrolytic pathway) and phosphorylase (phosphorolytic pathway); the activity of the former enzyme was two orders of magnitude higher (3600 nmol/(min mg) versus 36 nmol/(min mg)). In cell extracts of the bacterium, high activities of the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway enzymes—hexokinase, glucose-phosphate isomerase, and phosphofructokinase—were revealed, as well as the activities of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and key enzymes of the Entner-Doudoroff pathway—6-phospho-gluconate dehydratase and 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phospho-gluconate aldolase. Neither the activity of the key enzyme of the hexose-mono-phosphate pathway, 6-phospho-gluconate dehydrogenase, nor the activities of the key enzymes of the modified Entner-Doudoroff pathway, glucose dehydrogenase and 2-keto-3-deoxy-gluconate kinase, were revealed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wood, T.M., Fungal Cellulases, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 1992, vol. 20, pp. 46–53.
Lynd, L.R., Weimer, P.J., van Zyl, W.H., and Pretorius, I.S., Microbial Cellulose Utilization: Fundamentals and Biotechnology, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2002, vol. 66, pp. 506–577.
Zvereva, E.A., Fedorova, T.V., Kevbrin, V.V., Zhilina, T.N., and Rabinovich, M.L., Cellulase Activity of a Haloalkaliphilic Anaerobic Bacterium, Strain Z-7026, Extremophiles, 2006, vol. 10, pp. 53–60.
Zhilina, T.N., Kevbrin, V.V., Tourova, T.P., Lysenko, A.M., Kostrikina, N.A., and Zavarzin, G.A., Clostridium alkalicellum sp. nov., an Obligately Alkaliphilic Cellulolytic Bacterium from a Soda Lake in the Baikal Region, Mikrobiologiya, 2005, vol. 74, pp. 642–653 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 74, no. 5, pp. 557–566].
Hallwell, G., Microbial β-Glucanases, Prog. Ind. Microbiol., 1979, vol. 15, pp. 1–60.
Alexander, J.K., Cellobiose Phosphorylase from Clostridium thermocellum, Methods Enzymol., Ginsburg, V., Ed., N.Y.: Academic Press, 1972, vol. 28, pp. 944–948.
Ng, T.K. and Zeikus, J.G., Differential Metabolism of Cellobiose and Glucose by Clostridium thermocellum and Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum, J. Bacteriol., 1982, vol. 150, pp. 1391–1399.
Lou, J., Dawson, K.A., and Strobel, H.J., Cellobiose and Cellodextrin Metabolism by the Ruminal Bacterium Ruminococcus albus, Curr. Microbiol., 1997, vol. 35, pp. 221–227.
Garnova, E.S. and Krasil’nikova, E.N., Carbohydrate Metabolism of the Saccharolytic Alkaliphilic Anaerobes Halonatronum saccharophilum, Amphibacillus fermentum, and Amphibacillus tropicus, Mikrobiologiya, 2003, vol. 72, pp. 627–632 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 72, no. 5, pp. 558–563].
Zhilina, T.N., Appel, R., Probian, C., Brossa, E.L., Harder, J., Widdel, F., and Zavarzin, G.A., Alkaliflexus imshenetskii gen. nov. sp. nov., a New Alkaliphilic Gliding Carbohydrate-fermenting Bacterium with Propionate Formation from a Soda Lake, Arch. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 182, pp. 244–253.
Pfennig, N. and Lippert, K.D., Über das Vitamin B12-Bedtirfhis phototropher Schwefelbakterien, Arch. Mikrobiol., 1966, vol. 55, pp. 245–246.
Wolin, E.A., Wolin, M.J., and Wolfe, R.S., Formation of Methane by Bacterial Extracts, J. Biol. Chem., 1963, vol. 238, pp. 2882–2886.
Lowry, O.H., Rosenbrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., and Rendall, R.J., Protein Measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent, J. Biol. Chem., 1951, vol. 193, pp. 265–275.
Barnard, E.A., Hexokinases from Yeast, Methods Enzymol., Wood, W.A., Ed., N.Y.: Academic Press, 1975, vol. 42C, pp. 6–20.
Gracy, R.W., Glucosephosphate Isomerase from Catfish Muscle and Liver and from Mammalian Tissues, Methods Enzymol., 1982, vol. 89, pp. 550–558.
Kemp, R.G., Phosphofructokinase from Rabbit Skeletal Muscle, Methods Enzymol., Wood, W.A., Ed., N.Y.: Academic Press, 1975, vol. 42C, pp. 71–77.
Johnsen, U., Selig, M., Xavier K.B., Santos, H., and Schönheit, P., Different Glycolytic Pathways for Glucose and Fructose in the Halophilic Archaeon Halococcus saccharolyticus, Arch. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 175, pp. 52–61.
Lou, J., Dawson, K.A., and Strobel, H.J., Role of Phosphorolytic Cleavage in Cellobiose and Cellodextrin Metabolism by the Ruminal Bacterium Prevotella ruminicola, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1996, vol. 62, pp. 1770–1773.
Zhilina, T.N., Garnova, E.S., Tourova, T.P., Kostrikina, N.A., and Zavarzin, G.A., Halonatronum saccharophilum gen. nov. sp. nov.: A New Haloalkaliphilic Bacterium of the Order Haloanaerobiales from Lake Magadi, Mikrobiologiya, 2001, vol. 70, pp. 77–85 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 70, no. 1, pp. 64–72].
Zhilina, T.N., Garnova, E.S., Tourova, T.P., Kostrikina, N.A., and Zavarzin, G.A., Amphibacillus fermentum sp. nov. and Amphibacillus tropicus sp. nov., New Alkaliphilic, Facultatively Anaerobic, Saccharolytic Bacilli from Lake Magadi Mikrobiologiya, 2001, vol. 70, pp. 825–837 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 70, no. 6, pp. 711–722].
Doelle, H.W., Bacterial Metabolism, New York: Academic Press, 1975.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.N. Detkova, V.V. Kevbrin, 2009, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2009, Vol. 78, No. 3, pp. 304–309.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Detkova, E.N., Kevbrin, V.V. Cellobiose catabolism in the haloalkaliphilic hydrolytic bacterium Alkaliflexus imshenetskii . Microbiology 78, 267–272 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261709030023
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261709030023