Abstract
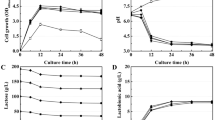
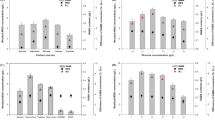
Lactobacillus bifermentans was used to produce the intracellular enzymes L-arabinose isomerase and D-xylose isomerase. Various factors of cultivation (temperature, pH, and incubation period) and culture medium composition (mineral salts, carbon source, and nitrogen source) were studied to select the conditions that maximize production of these enzymes. Arabinose isomerase and xylose isomerase activities were 9.4 and 7.24 U/ml, respectively. They were highest at 9 h of cultivation in the optimized medium, 1.6 times higher than that in the basic MRS broth. The optimal medium composition and cultivation conditions were determined. For optimal growth, the strain required Tween 80 (1 g/l) and a source of inorganic nitrogen (e.g., ammonium citrate). The bacterium had no requirement for sodium acetate for either growth or production of isomerases. The production rate of enzymes was increased when metal ions were added, primarily manganese (2.5 mM).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, X.F., Xu, F., Sun, R.C., Geng, Z.C., Fowler, P., and Baird, M.S., Characteristics of Degraded Hemicellulosic Polymers Obtained from Steam Exploded Wheat Straw, Carbohydr. Polym., 2005, vol. 60, pp. 15–26.
Sun, R.C. and Tomkinson, J., Characterization of Hemicelluloses Obtained by Classical and Ultrasonically Assisted Extractions from Wheat Straw, Carbohydr. Polym., 2002, vol. 50, pp. 263–271.
Sun, R.C. and Hughes, S., Fractional Extraction and Physico-Chemical Characterization of Hemicelluloses and Cellulose from Sugar Beet Pulp, Carbohydr. Polym., 1998, vol. 36, pp. 293–299.
Kim, B.C., Lee, Y.H., Lee, H.S., Lee, D.W., Choe, E.A., and Pyun Y.R., Cloning, Expression and Characterization of L-Arabinose Isomerase from Thermotoga neapolitana: Bioconversion of D-Galactose to D-Tagatose Using the Enzyme, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2002, vol. 212, pp. 121–126.
Wovcha, M.G., Steuerwald, D.L., and Brooks, K.E. Amplification of D-Xylose and D-Glucose Isomerase Activities in Escherichia coli by Gene Cloning, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1983, vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 1402–1404.
Richard, P., Verho, R., Putkonen, M, Londesborough, J., and Penttila, M., Production of Ethanol From L-arabinose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae Containing a Fungal L-Arabinose Pathway, FEMS Yeast Res., 2003, pp. 85–189.
Patrick, J.W., and Lee, N., Purification and Properties of an L-Arabinose Isomerase from Escherichia coli, J. Biol. Chem., 1968, vol. 243, pp. 4312–4318.
Bothast, R.J., Nichols, N.N. and Dien, B.S. Fermentation with New Recombinant Organisms, Biotechnol. Prog., 1999, vol. 15, pp. 867–875.
Zhang, M., Eddy, C, Deanda, K., Finkestein, M, and Picataggio, S., Metabolic Engineering of a Pentose Metabolism Pathway in Ethanologenic Zymomonas mobilis, Science, 1995, vol. 267, pp. 240–243.
Deanda, K., Zhang, M., Eddy, C., and Picataggio, S., Development of an Arabinose-Fermenting Zymomonas mobilis Strain by Metabolic Pathway Engineering, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1996, vol. 62, no. 12, pp. 4465–4470.
Dien, B.S., Cotta, M.A., and Jeffries, T.W., Bacteria Engineered for Fuel Ethanol Production: Current Status, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol, 2003, vol. 63, pp. 256–266.
Chandrakant, P. and Bisaria, V.S., Simultaneous Bioconversion of Glucose and Xylose to Ethanol by Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the Presence of Xylose Isomerase, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2000, vol. 53, pp. 301–309.
Lee, C.Y., Bhatnagar, K., Saha, B.C., Lee, Y.E., and Takagi, M., Imanaka, T., Bagdasarian, M., and Zeikus, J.G., Cloning and Expression of the Clostridium thermosulfurogenes Glucose Isomerase Gene in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1990, vol. 56, no. 9, pp. 2638–2643.
Borgi, A., Srih-Belguith, K., Ben Ali, M., Mezghani, M., Tranier, S., Haser, R., and Bejar, S., Glucose Isomerase of the Streptomyces sp. SK Strain: Purification, Sequence Analysis and Implication of Alanine 103 Residue in the Enzyme Thermostability and Acidotolerance, Biochimie, 2004, vol. 86, pp. 561–568.
Pawar, S.A. and Deshpande, V.V., Characterization of Acid-Induced Unfolding Intermediates of Glucose/Xylose Isomerase, Eur. J. Biochem., 2000, vol. 267, pp. 6331–6338.
Bhosale, S.H., Rao, M.B., and Deshpande, V.V., Molecular and Industrial Aspects of Glucose Isomerase, Microbiol. Rev., 1996, vol. 60, no. 2, pp. 280–300.
Deshmukh, S.S., Deshpande, M.V., and Shankar, V., Medium Optimization for the Production of Glucose Isomerase from Thermophilic Streptomyces thermonitrificans, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 1994, vol. 10, pp. 264–267.
Chauhan, K., Trivedi, U., and Patel, K.C., Statistical Screening of Medium Components by Plackett-Burman Design for Lactic Acid Production by Lactobacillus sp. KCP01 Using Date Juice, Bioressour. Technol., 2006 (in press).
Lee, D.W., Choe, E.A., Kim, S.B., Eom, S.H., Hong, Y.H., Lee, S.J., Lee, H.S., Lee, D.Y., and Pyun, Y.R., Distinct Metal Dependence for Catalytic and Structural Functions in the L-Arabinose Isomerases from the Mesophilic Bacillus halodurans and the Thermophilic Geobacillus stearothermophilus, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 2005, vol. 434, pp. 333–343.
Lee, M.T., Chen, W.C., and Chou, C.C., Medium Improvement by Orthogonal Array Designs for Cholesterol Oxidase Production by Rhodococcus equi, No. 23, Process Biochem., 1997, vol. 32, pp. 697–703.
Bakhtiari, M.R., Faezi, M.G., Fallahpour, M., Noohi, A., Moazami, N., and Amidi, Z., Medium Optimization by Orthogonal Array Designs for Urease Production by Aspergillus niger PTCC5011, Process Biochem., 2006, vol. 41, pp. 547–551.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The text was submitted by the authors in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Givry, S., Duchiron, F. Optimization of culture medium and growth conditions for production of L-arabinose isomerase and D-xylose isomerase by Lactobacillus bifermentans . Microbiology 77, 281–287 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261708030053
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261708030053