Abstract
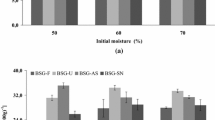
The application of the protein and polysaccharide fractions of barley spent grain as a basis of growth media for probiotic bacteria was studied. High values of biomass yield, cell viability, and organic acid production were observed in the variants of media containing the barley spent grain supplemented with lactose, ascorbic acid, yeast extract, and mineral salts. Cells of lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria had the typical rod-shaped morphology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reid, G., Jass, J., Sebulsky, M.T., and McCormick, J.K., Potential Uses of Probiotics in Clinical Practice, Clin. Microbiol. Rev., 2003, vol. 16, pp. 658–672.
Novik, G.I., Astapovich, N.I., Bogdanovskaya, Zh.N., and Ryabaya, N.E., Production of the Medicinal and Prophylactic Preparation Enterobifidin Using Bifidobacterium adolescentis MS-42, Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol., 2000, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 104–110 [App. Biochem. Microbiol. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 90–95].
Novik, G.I., Structural and Functional Organization of Bifidobacteria, Mikrobiologiya, 1998, vol. 67, no. 3, pp. 376–383 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 67, no. 3, pp. 310–316].
Ventura, M., Sinderen, D., Fitzgerald, G.F., and Zink, R., Insights into the Taxonomy, Genetics and Physiology of Bifidobacteria, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2004, vol. 86, pp. 205–223.
Charalampopoulos, D., Pandiella, S.S., and Webb, C., Growth Studies of Potentially Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria in Cereal-Based Substrates, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2002, vol. 92, pp. 851–859.
Bamba, T., Kanauchi, O., Andoh, A., and Fujiyama, Y., A New Prebiotic from Germinated Barley for Nutraceutical Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis, J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 2002, vol. 17, pp. 818–824.
Kanauchi, O., Serizawa, I., Araki, Y., Suzuki, A., Andon, A., Fujiyama, Y., Mitsuyama, K., Takaki, K., Toyonaga, A., Sata, M., and Bamba, T., Germinated Barley Foodstuff, a Prebiotic Product, Ameliorates Inflammation of Colitis through Modulation of the Enteric Environment, J. Gastroenterol., 2003, vol. 38, pp. 134–141.
Charalampopoulos, D., Wang, R., Pandiella, S.S., and Webb, C., Application of Cereals and Cereal Components in Functional Foods: a Review, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 2002, vol. 15, pp. 131–141.
Lasztity, R., Barley Proteins, The Chemistry of Cereal Proteins, CRC Press, 1984, pp. 117–126.
Ishiwaki, N., Muruyama, H., Awayama, H., Kanauchi, O., and Sato, T., Development of High Value Uses of Spent Grain by Fractionation Technology, Tech. Quart, 2000, vol. 37, pp. 261–265.
Dongowski, G., Huth, M., Gebhardt, E., and Flamme, W., Dietary Fiber-Rich Barley Products Beneficially Affect the Intestinal Tract of Rats, J. Nutr., 2002, vol. 132, pp. 3704–3714.
Schrezenmeir, J. and de Vrese, M., Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics — Approaching a Definition, Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 2001, vol. 73, pp. 361–364.
Szponar, B., Pawlik, K.J., Gamian, A., and Szwajcer Dey, E., Protein Fraction of Barley Spent Grain as a New Simple Medium for Growth and Sporulation of Soil Actinobacteria, Biotechnol. Lett., 2003, vol. 25, pp. 1717–1721.
Novik, G.I., Astapovich, N.I., and Samartsev, A.A., Investigation of the Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Bifidobacteria at the Late Stages of Their Development, Mikrobiologiya, 2001, vol. 70, no. 4, pp. 495–502 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 70, no. 4, pp. 429–435].
Lauer, E. and Kandler, O., Mechanismus der Variation des Verhalthisses Acetat/Lactat bei der Vergarung von Glucose durch Bifidobacterien, Arch. Microbiol., 1976, vol. 110, pp. 271–277.
Novik, G.I., Astapovich, N.I., Kubler, I., and Gamian, A., Characterization of the Cell-Bound Polysaccharides of Bifidobacterium adolescentis 94 BIM, Mikrobiologiya, 2002, vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 205–210 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 173–177].
Szwajcer, DeyE., Rasmussen, J., and Breddam, K., Proline Specific Endopeptidases from Microbial Sources: Isolation of an Enzyme from Xanthomonas sp., J. Bacteriol., 1992, vol. 174, pp. 2454–2459.
Novik, G., Gamian, A., Cruz, Francisco J., and Szwajcer Dey, E., A Novel Procedure for the Isolation of Glycolipids from Bifidobacterium adolescentis 94 BIM Using Supercritical Carbon Dioxide, J. Biotechnol., 2006, vol. 121, pp. 555–562.
Kleyn, J. and Hough, J., The Microbiology of Brewing, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 1971, vol. 25, pp. 583–608.
Das, H. and Singh, S.K., Useful Byproducts from Cellulosic Wastes of Agriculture and Food Industry—a Critical Appraisal, Crit. Rev. Food Scie Nut., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 77–89.
Hosono, A., Lee, J., Ametani, A., Natsume, M., Hirayama, M., Adachi, T., and Kaminogawa, S., Characterization of a Water-Soluble Polysaccharide Fraction with Immunopotentiating Activity from Bifidobacterium adolescentis M101-4, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 1997, vol. 61, pp. 312–316.
Crittenden, R., Laitila, A., Forssell, P., Mättö, J., Saarela, M., Mattila-Sandholm, T., and Myllarinen, P., Adhesion of Bifidobacteria to Granular Starch and Its Implications in Probiotic Technologies, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 67, pp. 3469–3475.
Shukla, T.P., Nutraceutical Novelties: Trends in Proprietary Technology, Cereal Foods World, 1998, vol. 43, pp. 388–389.
Kanauchi, O., Fujiyama, Y., Mitsuyama, K., Araki, Y., Ishii, T., Nakamura, T., Hitomi, Y., Agata, K., Saiki, T., Andoh, A., Toyonaga, A., and Bamba, T., Increased Growth of Bifidobacterium and Eubacterium by Germinated Barley Foodstuff, Accompanied by Enhanced Butyrate Production in Health Volunteers, Jnt. J. Mol. Med., 1999, vol. 3, pp. 175–179.
Janer, C., Arigoni, F., Lee, B.H., Pelaez, C., and Requena, T., Enzymatic Ability of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis to Hydrolyze Milk Proteins: Identification and Characterization of Endopeptidase O, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 71, pp. 8460–8465.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © G.I. Novik, J. Wawrzynczyk, O. Norrlow, E. Szwajcer-Dey, 2007, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2007, Vol. 76, No. 6, pp. 902–907.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novik, G.I., Wawrzynczyk, J., Norrlow, O. et al. Fractions of barley spent grain as media for growth of probiotic bacteria. Microbiology 76, 804–808 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261707060227
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261707060227