Abstract
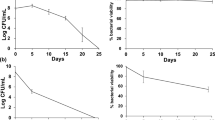
We conducted a comparative study of the effects of α-amino-γ-butyrolactone, the common structural element of extracellular microbial regulators of the homoserine lactone (HSL) group, and of 4-n-hexylresorcinol, an autoregulator of the alkylhydroxybenzene (AHB) group, on the growth and development of grampositive and gram-negative bacteria. We revealed non-species-specific effects of HSL and AHB and characterized their concentration dependencies. The addition of 10−5−10−3 M HSL or 10−5−10−4 M AHB during the exponential growth phase of the cultures grown on balanced media resulted in cell division arrest and accelerated the transition to the stationary phase that culminated in endospore formation in Bacillus cereus, Alicyclobacillus tolerans, and Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans. When bacilli grew under the cultivation conditions that resulted in a low-zero spore percentage, 10−4−10−3 M HSL cancelled the inhibition of spore formation. In the gram-negative bacteria Pseudomonas aurantiaca and Azotobacter vinelandii, AHB at concentrations of 10−4 to (1.5−2.5)×10−4 M induced the formation of dormant cells. Studies with the actinobacterium Streptomyces avermitilis revealed that the HSL effect varied depending on the age of the test cultures. The addition of 10−4 M HSL during the lag phase of a submerged streptomycete culture accelerated its transition to the stationary phase and induced the formation of endospores, the dormant cells that are regarded as alternatives to exospores (conidia). If HSL (3.64 and 4.55 mg per 1 cm2 disc) was locally added to a surface S. avermitilis culture, the growing mycelium formed rings that differed in their density, in the extent of the development of aerial mycelium, and in the presence/absence of exospores. Ring-shaped growth of streptomycete mycelia was also induced by 0.075–0.75 mg of AHB; however, unlike HSL, AHB repressed exospore formation. The data on non-species-specific effects of HSL and AHB suggest that they may perform regulatory functions at the microbial community level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fuqua, C., Winans, S.C., and Greenberg, E.P., Census and Consensus in Bacterial Ecosystems: the LuxR-LuxI Family of Quorum-Sensing Transcriptional Regulators, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 1996, vol. 50, pp. 727–751.
Miller, M.B. and Bassler, B.L., Quorum Sensing in Bacteria, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 55, pp. 165–199.
Waters, C. and Bassler, B.L., Quorum Sensing: cell-to-cell Communication in Bacteria, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol, 2005, vol. 21, pp. 319–346.
Mayville, P., Ji, G., Beavis, R., Yang, H., Goger, M., Novick, R.P., and Muir, T.W., Structure-Activity Analysis of Synthetic Autoinducing Thiolactone Peptides from Staphylococcus aureus Responsible for Virulence, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1999, vol. 96, no. 4, pp. 1218–1223.
Bassler, B.L., Wright, M., and Silverman, M.R., Multiple Signalling Systems Controlling Expression of Luminescence in Vibrio harveyi: Sequence and Function of Genes Encoding a Second Sensory Pathway, Mol. Microbiol., 1994, vol. 13, pp. 273–286.
Chen, X., Schauder, S., Potier, N., Van Dorsselaer, A., Pelczer, I., Bassler, B.L., and Hughson, F.M., Structural Identification of a Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Signal Containing Boron, Nature, 2002, vol. 415, pp. 545–549.
Khokhlov, A.S., Nizkomolekulyarnye mikrobnye autoregulyatory (Low-Molecular Microbial Bioregulators), Moscow: Nauka, 1988.
Huisman, G.W. and Kolter, R., Sensing Starvation: a Homoserine Lactone-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Escherichia coli, Science, 1994, vol. 265, pp. 537–539.
DeLisa, M.P. and Bentley, W.E., Bacterial Autoinduction: Looking Outside the Cell for New Metabolic Engineering Targets, Microb. Cell Fact, 2002, vol. 1, p. 5.
Hengge-Aronis, R., Signal Transduction and Regulatory Mechanisms Involved in Control of the σS (RpoS) Subunit of RNA Polymerase, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2002, vol. 66, no. 3, pp. 373–395.
Svetlichnyi, V.A., Romanova, A.K., and El’-Registan, G.I., Quantitative Content of Membrane-Active Autoregulators in lithoautotrophically grown Psudomonas carboxydoflava, Mikrobiologiya, 1986, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 55–59.
Duda, V.I., Pronin, S.V., El’-Registan, G.I., Kaprel’yants, A.S., and Mityushina, L.L., Formation of Resting Refractive Cells in Bacillus cereus under the Influence of an Autoregulatory Factor, Mikrobiologiya, 1982, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 77–81.
Mulyukin, A.L., Lusta, K.A., Gryaznova, M.N., Kozlova, A.N., Duzha, M.V., Duda, V.I., and El’-Registan, G.I., Formation of Resting Cells by Bacillus cereus and Micrococcus luteus, Mikrobiologiya, 1996, vol. 65, no. 6, pp. 782–789 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 65, no. 6, pp. 683–689].
Bukharin, O.V., Gintsburg, A.L., Romanova, Yu.M., and El’-Registan, G.I., Mekhanizmy vyzhivaniya bakterii (Mechanisms of Bacterial Survival), Moscow: Meditsina, 2005.
Kolpakov, A.I., Il’inskaya, O.N., Bespalov, M.M., Kupriyanova-Ashina, F.G., Gal’chenko, V.F., Kurganov, B.I., and El’-Registan, G.I., Stabilization of Enzymes by Dormancy Autoinducers as a Possible Mechanism of Resistance of Resting Microbial Forms, Mikrobiologiya, 2000, vol. 69, no. 2, pp. 224–230 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 69, no. 2, pp. 180–185].
Martirosova, E.I., Karpekina, T.A., and El’-Registan, G.I., Enzyme Modification by Natural Chemical Chaperons of Microorganisms, Mikrobiologiya, 2004, vol. 73, no. 5, pp. 708–715 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 73, no. 5, pp. 609–615].
Davydova, O.K., Deryabin, D.G., Nikiyan, A.N., and El’-Registan, G.I., Mechanisms of Interaction between DNA and Chemical Analogues of Microbial Anabiosis Autoinducers, Mikrobiologiya, 2005, vol. 74, no. 5, pp. 616–625 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 74, no. 5, pp. 533–541].
Kaprel’yants, A.S., Suleimenova, M.I., Sorokina, A.D., Deborin, G.A., El’-Registan, G.I., Stoyanovich, F.M., Lille, Yu.E., and Ostrovskii, D.N., Structural and Functional Changes in Bacterial and Model Membranes Affected by Phenolic Lipids, Biol. Membr., 1987, vol. 4, pp. 254–261.
Bogdanova, T.I., Mulyukin, A.L., Tsaplina, I.A., El’-Registan, G.I., and Karavaiko, G.I., Effect of the Medium Composition and Cultivation Conditions on Sporulation in Chemolithotrophic Bacteria, Mikrobiologiya, 2002, vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 187–193 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 158–163].
Kuznetsov, V.D., The Study of Variability of Actinomycete Producers of Antibiotics and Other Biologically Active Compounds, Antibiotiki, 1972, vol. 17, no. 7, pp. 666–674.
Suzina, N.E., Mulyukin, A.L., Loiko, N.G., Kozlova, A.N., Shorokhova, A.P., Dmitriev, V.S., Gorlenko, M.V., Duda, V.I., and El’-Registan, G.I., Fine Structure of Mummified Cells of Microorganisms Formed under the Influence of a Chemical Analogue of the Anabiosis Autoinducer, Mikrobiologiya, 2001, vol. 70, no. 6, pp. 776–787 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 70, no. 6, pp. 667–677].
Pearson, J.P., Gray, K.M., Passador, L., Tucker, K.D., Eberhard, A., Iglewski, B.H., and Greenberg, E.B., Structure of the Autoinducer Required for Expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence Genes, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1994, vol. 91, pp. 197–201.
Filippova, S.N., Gorbatyuk, E.V., Poglazova, M.N., Soina, V.S., Kuznetsov, V.D., and El’-Registan, G.I., Endospore Formation by Streptomyces avermitilis in Submerged Culture, Mikrobiologiya, 2005, vol. 74, no. 2, pp. 204–214 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 74, no. 2, pp. 169–178].
Dong, Y.H., Gusti, A.R., Zhang, Q., Xu, J.L., and Zhang, L.H., Identification of Quorum-Quenching N-Acyl Homoserine Lactonases from Bacillus Species, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2002, vol. 68, no. 4, pp. 1754–1759.
Lin, Y.H., Xu, J.L., Hu, J., Wang, L.H., Ong, S.L., Leadbetter, J.R., and Zhang, L.H., Acyl-Homoserine Lactone Acylase from Ralstonia Strain XJ12B Represents a Novel and Potent Class of Quorum-Quenching Enzymes, Mol. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 47, no. 3, pp. 849–860.
Kozubek, A. and Tyman, J.H.P., Resorcinolic Lipids, the Natural Non-Isoprenoid Phenolic Amphiphiles and Their Biological Activity, Chem. Rev., 1999, vol. 99, no. 1, pp. 1–31.
Zakataeva, N.P., Aleshin, V.V., Tokmakova, I.L., Troshin, P.V., and Livshits, V.A., The Novel Transmembrane Escherichia coli Proteins Involved in the Amino Acid Efflux, FEBS Lett., 1999, vol. 452, no. 3, pp. 228–232.
Flagan, S., Ching, W.-K., and Leadbetter, J.R., Arthrobacter Strain VAI-A Utilizes Acyl-Homoserine Lactone Inactivation Products and Stimulates Quorum Signal Biodegradation by Variovorax paradoxus, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 69, no. 2, pp. 909–916.
Sitnikov, D.M., Schineller, J.B., and Baldwin, T.O., Control of Cell Division in Escherichia coli: Regulation of Transcription of ftsQA Involves Both rpoS and SdiA-Mediated Autoinduction, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1996, vol. 93, pp. 336–341.
Goodrich-Blair, H. and Kolter, R., Homocysteine Thiolactone Is a Positive Effector of Sigma (S) Levels in Escherichia coli, FEMS Microbiol. Letts., 2000, vol. 185, pp. 117–121.
Martirosova, E.I., Nikolaev, Yu.A., Krylov, I.A., Shanenko, E.F., Krupyanskii, Yu.F., and El’-Registan, G.I., Application of Alkylhydroxybenzenes for Enhancement of Enzyme Activity and Stability, Khim. tekhnol., 2006 ((in press).
Mulyukin, A.L., Vakhrushev, M.A., Strazhevskaya, N.B., Shmyrina, A.S., Zhdanov, R.I., Suzina, N.E., Duda, V.I., Kozlova, A.N., and El’-Registan, G.I., Effect of Alkylhydroxybenzenes, Microbial Anabiosis Inducers, on the Structural Organization of Pseudomonas aurantiaca DNA and on the Induction of Phenotypic Dissociation, Mikrobiologiya, 2005, vol. 74, no. 2, pp. 157–165 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 74, no. 2, pp. 128–135].
Novak, J., Kopecky, J., and Vanek, Z., Sporulation-Inducing Factor in Streptomyces avermitilis, Folia Microbiol., 1992, vol. 37, no. 6, pp. 463–465.
Il’inskaya, O.N., Kolpakov, A.I., Zelenin, P.V., Kruglova, Z.D., Choidash, B., Doroshenko, E.V., Mulyukin, A.L., and El’-Registan, G.I., The Effect of Anabiosis Autoinducers on the Bacterial Genome, Mikrobiologiya, 2002, vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 194–199 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 164–168].
Doroshenko, E.V., Loiko, N.G., Il’inskaya, O.N., Kolpakov, A.I., Gornova, I.V., and El’-Registan, G.I., Characterization of Bacillus cereus Dissociants, Mikrobiologiya, 2001, vol. 70, no. 6, pp. 811–819 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 70, no. 6, pp. 798–705].
Lazazzera, B.A., Quorum Sensing and Starvation: Signals for Entry Into Stationary Phase, Curr. Opin. Microbiol, 2000, vol. 3, pp. 177–182.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.L. Mulyukin, S.N. Filippova, A.N. Kozlova, N.A. Surgucheva, T.I. Bogdanova, I.A. Tsaplina, G.I. El’-Registan, 2006, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2006, Vol. 75, No. 4, pp. 472–482.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mulyukin, A.L., Filippova, S.N., Kozlova, A.N. et al. Non-species-specific effects of unacylated homoserine lactone and hexylresorcinol, low molecular weight autoregulators, on the growth and development of bacteria. Microbiology 75, 405–414 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261706040072
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261706040072