Abstract
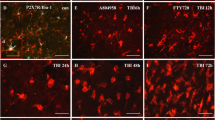
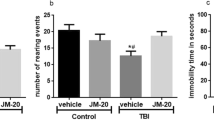
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a multifactorial disease that can lead to the development of neurological diseases. To correct violations of physiological functions, anti-inflammatory cytokines are used, in particular, the IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA). The aim of this work is to evaluate the effectiveness of the rIL-1RA preparation for the correction of post-traumatic neuroinflammation. TBI in rats was simulated by dropping a 115 g weight from a height of 120 cm into the center of the parietal region, and the drug was injected subcutaneously at a dose of 50 mg/kg 60 min after injury. We studied blood corticosterone levels and behavioral responses in the “Open field” test. To characterize the activation pattern of microglia in different parts of the brain, the expression of the Iba1 marker and morphological changes of cells were evaluated. Counting the total number and changing the shape and size of Iba1-positive microglial cells on 7th day after TBI showed that in animals treated with rIL-1RA the number of activated microglial cells was significantly higher than in intact animals, but the degree of their activation was significantly lower. Studies of CNS function disorders after TBI showed that motor and orientation-exploratory activities were significantly inhibited, which, together with the disturbance of the emotional status of the animals, indicates the development of a neurological deficit in intact rats. In animals treated with rIL-1RА, changes in behavioral characteristics were less pronounced. The decrease in neurological deficit in treated animals was directly related to the normalization of the state of microglia. The data obtained in the work indicate that the use of rIL-1RA 1 h after TBI allows correction of motor, orientation-exploratory activity and reduce microglia activation in different parts of the CNS.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
McAllister TW (2011) Neurobiological consequences of traumatic brain injury. Dialog Clin Neurosci13(3): 287–300. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2011.13.2/tmcallister
Helmy EA, Todd BP, Mahoney J, Pieper AA, Ferguson PJ, Bassuk AG (2018) Combined Blockade of Interleukin-1α and -1β Signaling Protects Mice from Cognitive Dysfunction after Traumatic Brain Injury. eNeuro 5(2): 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0385-17.2018
Liu X, Yamashita T, Chen Q, Belevych N, Mckim DB, Tarr AJ, Coppola V, Nath N, Nemeth DP, Syed ZW, Sheridan JF, Godbout JP, Zuo J, Quan N (2015) Interleukin 1 type 1 receptor restore: a genetic mouse model for studying interleukin 1 receptor-mediated effects in specific cell types. Interleukin 1 type 1 receptor restore: a genetic mouse model for studying interleukin 1 receptor-mediated еffects in specific cell types. J Neurosci 35: 2860–2870. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3199-14.2015
Thome JG, Reeder EL, Collins SM, Gopalan P, Robson MJ (2020) Contributions of Interleukin-1 Receptor Signaling in Traumatic Brain Injury. Front Behav Neurosci 13: 287. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00287
Shchekina EG, Ishchenko AM, Shtrygol SY, Drogovoz SM, Simbirtsev AS (2013) Study of the cerebroprotective properties of a recombinant human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) in experiment I. Effect of IL-1Ra on cerebral blood supply, acid-base balance disorders, neuronal destruction and interleukin 1 content in experimental cerebral ischemia in rats. Cytokines and Inflammat 12(1–2): 45–51. (In Russ).
Shchekina EG, Ishchenko AM, Shtrygol SY, Drogovoz SM, Simbirtsev AS (2013) Study of the cerebroprotective properties of the recombinant human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) in experiment II. Cerebroprotective properties of IL-1Ra in ischemic and traumatic brain injury in mice. Cytokines and inflammation 12(3): 29–34. (In Russ).
Pradillo JM, Murray KN, Coutts GA, Moraga A, Oroz-Gonjar F, Boutin H, Moro MA, Lizasoain I, Rothwell NJ, Allan SM (2017) Reparative effects of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in young and aged/co-morbid rodents after cerebral ischemia. Brain Behav Immun 61: 117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.11.013
Smith CJ, Hulme S, Vail A, Heal C, Parry-Jones AR, Scarth S, Hopkins K, Hoadley M, Allan SM, Rothwell NJ, Hopkins SJ, Tyrrell PJ (2018) SCIL-STROKE (Subcutaneous interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in ischemic stroke) A randomized controlled phase 2 trial. Stroke 49: 1210–1216. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.020750
Sun M, Brady RD, Wright DK, Kim HA, Zhang SR, Sobey CG, Johnstone MR, O’Brien TJ, Semple BD, McDonald SJ, Shultz SR (2017) Treatment with an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist mitigates neuroinflammation and brain damage after polytrauma. Brain Behav Immun 66: 359–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.08.005
Helmy A, Guilfoyle MR, Carpenter KL, Pickard JD, Menon DK, Hutchinson PJ (2014) Recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in severe traumatic brain injury: a phase ii randomized control trial. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34: 845–851. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2014.23
Helmy A, Guilfoyle MR, Carpenter KLH, Pickard JD, Menon DK, Hutchinson РJ (2016) Recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist promotes M1 microglia biased cytokines and chemokines following human traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36: 1434–1448. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X15620204
Bergold PJ (2016) Treatment of traumatic brain injury with anti-inflammatory drugs. Exp Neurol 275 (Pt 3): 367–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.05.024
Shanin SN, Fomicheva EE, Filatenkova TA, Serebryanaya NB (2018) Correction of disorders of neuroimmune interactions in experimental traumatic brain injury with recombinant interleukin-2. Med Immunol 20(2): 171–178. https://doi.org/10.15789/1563-0625-2018-2-171-178
Buresh Ya, Bureshova O, Houston DP (1991) Methods and basic experiments to study the brain and behavior. Transl from English Ed AS Batuev. (In Russ).
Graeber MB (2010) Changing face of microglia. Science 330(6005): 783–788. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1190929.
Fomicheva EE, Shanin SN, Filatenkova TA, Serebryanaya NB (2020) IL-2 as a regulator of stress hormones and BDNF in experimental traumatic brain injury. Medical Immunology 22 (4): 647–656. https://doi.org/10.15789/1563-0625-IAR-1973
Muraeva NA (2019) Effect of chronic stress on body weight and immune organs of experimental animals of early age. Volgograd Scientific and Medical Journal 4: 1. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/vliyanie-hronicheskogo-stressa-na-massu-tela-i-immunnyh-organov-eksperimentalnyh-zhivotnyh-rannego-vozrasta
Swanson LW (2004) Brain maps: Structure of the rat brain. A laboratory guide with printed and electronic templates for data, models and schematics (3rd ed). The Netherlands: Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Alekseeva OS, Kirik OV, Gilerovich EG, Korzhevsky DE (2019) Brain microglia: origin, structure and functions. J Evol Biochem Physiol 559(4): 231–241. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0044452919040028
Dunn AJ (2000) Effects of the IL-1 receptor antagonist on the IL-1- and endotoxin-induced activation of the HPA axis and cerebral biogenic amines in mice. Neuroimmunomodulation 7(1): 36–45. https://doi.org/10.1159/000026418
Bartfai T, Sanchez-Alavez M, Andell-Jonsson S, Schultzberg M, Vezzani A, Danielsson E, Conti B (2007) Interleukin-1 system in CNS stress: seizures, fever, and neurotrauma. Ann NY Acad Sci 1113: 173–177. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1391.022
Gądek-Michalska A, Tadeusz J, Rachwalska P, Spyrka J, Bugajski J (2011) Effect of prior stress on interleukin-1β and HPA axis responses to acute stress. Pharmacol Rep 63(6): 1393–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1734-1140(11)70703-4
Johnson JD, O’Connor KA, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2004) The role of IL-1beta in stress-induced sensitization of proinflammatory cytokine and corticosterone responses. Neuroscience 127(3): 569–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.05.04625
Dmitrienko EV, Filatenkova TA, Filatenkova TA, Rybakina EG, Korneva EA (2014) Behavioral reactions of animals after experimental traumatic brain injury: the effect of a drug of nucleotide nature. Bull St-Petersburg Univer 11(3): 180–191. (In Russ).
Umryukhin PE, Grigorchuk OS (2017) Behavior of Rats in an Open Field Test as a Prognostic Indicator of Corticosterobe Levels Before and After Stress. Neurosci Behav Physiol 47(4): 456–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-017-0421-3
Greenhalgh AD, Galea J, Dénes A, Tyrrell PJ, Rothwell NJ (2010) Rapid brain penetration of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in rat cerebral ischaemia: pharmacokinetics, distribution, protection. Br J Pharmacol 160(1): 153–159. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00684.x
McCann SK, Cramond F, Macleod MR, Sena ES (2016) Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist in Animal Models of Stroke: An Update. Transl Stroke Res 7(5): 395–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-016-0489-z
Lassarén P, Lindblad C, Frostell A, Carpenter KLH, Guilfoyle MR, Hutchinson PJA, Helmy A, Thelin EP (2021) Systemic inflammation alters the neuroinflammatory response: a prospective clinical trial in traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflam 18(1): 221. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-021-02264-2
Sjöström EO, Culot M, Leickt L, Åstrand M, Nordling E, Gosselet F, Kaiser C (2021) Transport study of interleukin-1 inhibitors using a human in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier. Brain Behav Immun Health 16: 100307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100307
Zhu L, Liu X, Nemeth DP, DiSabato DJ, Witcher KG, Mckim DB, Oliver B, Le X, Gorantla G, Berdysz O, Li J, Ramani AD, Chen Z, Wu D, Godbout JP, Quan N (2019) Interleukin-1 causes CNS inflammatory cytokine expression via endothelia-microglia bi-cellular signaling. Brain Behav Immun 81: 292–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.06.026
Shimada A, Hasegawa-Ishii S (2021) Increased cytokine expression in the choroid plexus stroma and epithelium in response to endotoxin-induced systemic inflammation in mice. Toxicol Rev 8: 520–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.03.002
Kumar A, Loane DJ (2012) Neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury: opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Brain Behav Immun 26: 1191–2127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2012.06.008
Patlay NI, Sotnikov EB, Tuchina OP (2020) The role of microglial cytokines in the modulation of neurogenesis in the adult brain. J Int Appl and Basic Res 5: 15–23. https://doi.org/10.17513/mjpfi.13062
Ito D, Tanaka K, Suzuki S, Dembo T, Fukuuchi Y (2001) Enhanced expression of Iba1, ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1, after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rat brain. Stroke 32(5): 1208–1215. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.32.5.1208
Serebryanaya NB, Fomicheva EE, Yakutseni PP (2021) Purinergic regulation of neuroinflammation in traumatic brain injury. Advanc Physiol Sci 52(3): 24–40. https://doi.org/10.31857/S0301179821030073
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to express their heartfelt gratitude to Zharkova Maria Sergeevna Ph.D., Senior Researcher of the Department of Pathophysiology at the Institute of Experimental Medicine for her help in the discussion of the results and preparing of the article.
Funding
The work was performed in accordance with the planned research (State Assignment) on “Pathophysiological basis of disorders of the interaction between the nervous and immune systems and the search for innovative ways to correct various forms of pathology” 2019–2021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.N.B.—idea of the work, general management, discussion, writing and editing of the article; F.E.E.—data collection in the experiment, data processing, article writing and editing; Sh.S.N.—data collection in the experiment, data processing, article writing; F.T.A.—data collection and processing, article writing; N.N.S.—planning a morphological study of the animals’ brain, describing the results obtained; D.A.S.—collecting and processing morphological data; I.A.M.—idea of the work, justification of the order of experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no apparent or potential conflicts of interest related to the publication of this article.
Additional information
Translated by A. Dyomina
Russian Text © The Author(s), 2022, published in Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I.M. Sechenova, 2022, Vol. 108, No. 10, pp. 1264–1278https://doi.org/10.31857/S0869813922100077.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fomicheva, E.E., Shanin, S.N., Filatenkova, T.A. et al. Correction of Behavioral Disorders and State of Microglia with Recombinant IL-1 Receptor Antagonist in Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury. J Evol Biochem Phys 58, 1571–1582 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093022050258
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093022050258