Abstract
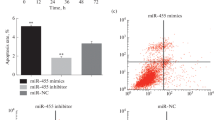
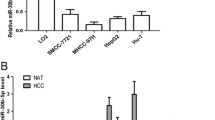
Liver cancer is one of the most common cancers with an unsatisfactory prognosis and high mortality rate. The ability of liver cancer cells to evade apoptosis results in the poor therapeutic effect of existing treatments and high rates of tumor recurrence and metastasis. This study investigated the effects of abnormal miR-338-3p expression on the ability of liver cancer cells to avoid apoptosis and the mechanism for that avoidance. The levels of miR-338-3p in liver tumor tissues and in different liver cancer cell lines were analysed by qRT-PCR which demonstrated its downregulation in liver tumor tissues and cells, especially in the Huh7 cells. Cell viability and apoptosis rates of Huh7 liver cancer cells were evaluated using the CCK-8 assay, clone formation assay, flow cytometry, and TUNEL assay. whereas the expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins (Bax, caspase-3, Cyt C, and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein [XIAP]) were analyzed by Western blotting. Next, the target relationship between miR-338-3p and Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) was identified by conducting a dual luciferase reporter gene assay. Overexpression of miR-338-3p was found to inhibit cell viability and promote the apoptosis of Huh7 cells. Additionally, an upregulation of miR-338-3p significantly promoted Bax, caspase-3, and Cyt C expression, and suppressed XIAP and SIRT6 expression. Notably, SIRT6 was proven to be a target gene of miR-338-3p, and SIRT6 overexpression was shown to reverse the anti-tumor effect of miR-338-3p upregulation in Huh7 cells. Furthermore, the apoptosis induction effect of Cisplatin was reduced by SIRT6, but restored by miR-338-3p. In conclusion, this study demonstrated that miR-338-3p increased apoptosis in liver cancer cell Huh7 by inhibiting SIRT6, and thereby enhanced the cytocidal effect of the apoptosis inducer Cisplatin. These results suggest miR-338-3p as a target for treating liver cancer, which might provide a new therapeutic strategy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71: 209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tapper EB, Parikh ND (2018) Mortality due to cirrhosis and liver cancer in the United States, 1999–2016: observational study. BMJ 362: k2817. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k2817
Fu J, Wang H (2018) Precision diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer in China. Cancer Lett 412: 283–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.10.008
Zheng R, Qu C, Zhang S, Zeng H, Sun K, Gu X, Xia C, Yang Z, Li H, Wei W (2018) Liver cancer incidence and mortality in China: temporal trends and projections to 2030. Chin J Cancer Res 30: 571. https://doi.org/10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2018.06.01
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35: 495–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337
Fernald K, Kurokawa M (2013) Evading apoptosis in cancer. Trends Cell Biol 23: 620–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2013.07.006
Carneiro BA, El-Deiry WS (2020) Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 17: 395–417. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-020-0341-y
Grillone K, Riillo C, Scionti F, Rocca R, Tradigo G, Guzzi PH, Alcaro S, Di Martino MT, Tagliaferri P, Tassone P (2020) Non-coding RNAs in cancer: platforms and strategies for investigating the genomic “dark matter”. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39: 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01622-x
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR, Soleymani Fard S, Ghaffari SH (2019) An overview of microRNAs: biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol 234: 5451–5465. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27486
Ardekani AM, Naeini MM (2010) The role of microRNAs in human diseases. Avicenna journal of medical biotechnology 2: 161–179.
Lu M, Huang H, Yang J, Li J, Zhao G, Li W, Li X, Liu G, Wei L, Shi B (2019) miR-338-3p regulates the proliferation, apoptosis and migration of SW480 cells by targeting MACC1. Exp Ther Med 17: 2807–2814. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-017-0415-9
Zhang G, Zheng H, Zhang G, Cheng R, Lu C, Guo Y, Zhao G (2017) MicroRNA-338-3p suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting sphingosine kinase 2. Cancer Cell Int 17: 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-017-0415-9
Cao Y, Shi X, Liu Y, Xu R, Ai Q (2018) MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells through targeting Cyclin-dependent kinase 4. Oncol Res 27: 117–124. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504018X15213031799835
Huang XH, Wang Q, Chen JS, Fu XH, Chen XL, Chen LZ, Li W, Bi J, Zhang LJ, Fu Q (2009) Bead-based microarray analysis of microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: miR-338 is downregulated. Hepatol Res 39: 786–794. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1872-034X.2009.00502.x
Liu P, Zhang H, Liang X, Ma H, Luan F, Wang B, Bai F, Gao L, Ma C (2015) HBV preS2 promotes the expression of TAZ via miRNA-338-3p to enhance the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 6: 29048. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4804
Wang G, Sun Y, He Y, Ji C, Hu B, Sun Y (2015) MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by target forkhead box P4 (FOXP4). Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8: 337–344.
Shen H, Li H, Zhou J (2022) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0032683 inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by sponging microRNA-338-5p. Bioengineered 13: 2321–2335. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.2024961
Fiorentino F, Mai A, Rotili D (2021) Emerging Therapeutic Potential of SIRT6 Modulators. J Med Chem 64: 9732–9758. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00601
Gonzalez Herrera KN, Lee J, Haigis MC (2015) Intersections between mitochondrial sirtuin signaling and tumor cell metabolism. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 50: 242–255. https://doi.org/10.3109/10409238.2015.1031879
Vitiello M, Zullo A, Servillo L, Mancini FP, Borriello A, Giovane A, Della Ragione F, D’Onofrio N, Balestrieri ML (2017) Multiple pathways of SIRT6 at the crossroads in the control of longevity, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases. Ageing Res Rev 35: 301–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.10.008
Zhang C, Yu Y, Huang Q, Tang K (2019) SIRT6 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 20: 1575–1582. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10398
Khongkow M, Olmos Y, Gong C, Gomes AR, Monteiro LJ, Yague E, Cavaco TB, Khongkow P, Man EP, Laohasinnarong S, Koo CY, Harada-Shoji N, Tsang JW, Coombes RC, Schwer B, Khoo US, Lam EW (2013) SIRT6 modulates paclitaxel and epirubicin resistance and survival in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 34: 1476–1486. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgt098
Garcia-Peterson LM, Ndiaye MA, Singh CK, Chhabra G, Huang W, Ahmad N (2017) SIRT6 histone deacetylase functions as a potential oncogene in human melanoma. Genes Cancer 8: 701–712. https://doi.org/10.18632/genesandcancer.153
Liu Y, Xie QR, Wang B, Shao J, Zhang T, Liu T, Huang G, Xia W (2013) Inhibition of SIRT6 in prostate cancer reduces cell viability and increases sensitivity to chemotherapeutics. Protein Cell 4: 702–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-013-3054-5
Ran L-K, Chen Y, Zhang Z-Z, Tao N-N, Ren J-H, Zhou L, Tang H, Chen X, Chen K, Li W-Y (2016) SIRT6 overexpression potentiates apoptosis evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma via BCL2-associated X protein-dependent apoptotic pathway. Clin Cancer Res 22: 3372–3382. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1638
Zhou HZ, Zeng HQ, Yuan D, Ren JH, Cheng ST, Yu HB, Ren F, Wang Q, Qin YP, Huang AL, Chen J (2019) NQO1 potentiates apoptosis evasion and upregulates XIAP via inhibiting proteasome-mediated degradation SIRT6 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Commun Signal 17: 168. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-019-0491-7
Tan W, Liu B, Qu S, Liang G, Luo W, Gong C (2018) MicroRNAs and cancer: Key paradigms in molecular therapy. Oncol Lett 15: 2735–2742. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.7638
Mirzaei S, Zarrabi A, Asnaf SE, Hashemi F, Zabolian A, Hushmandi K, Raei M, Goharrizi MASB, Makvandi P, Samarghandian S (2021) The role of microRNA-338-3p in cancer: growth, invasion, chemoresistance, and mediators. Life Sci 268: 119005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.119005
Sun F, Yu M, Yu J, Liu Z, Zhou X, Liu Y, Ge X, Gao H, Li M, Jiang X (2018) miR-338-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer by targeting PTP1B. Cell Death Dis 9: 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0611-0
Sun S, Wang R, Yi S, Li S, Wang L, Wang J (2021) Roles of the microRNA-338-3p/NOVA1 axis in retinoblastoma. Mol Med Report 23: 394. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2021.12033
Xiao G, Wang Q, Li B, Wu X, Liao H, Ren Y, Ai N (2018) MicroRNA-338-3p suppresses proliferation of human liver cancer cells by targeting SphK2. Oncol Res 26: 1183–1189. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504018X15151495109394
Masri S (2015) Sirtuin-dependent clock control: new advances in metabolism, aging and cancer. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 18: 521–527. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0000000000000219
Martinez-Pastor B, Mostoslavsky R (2012) Sirtuins, metabolism, and cancer. Front Pharmacol 3: 22. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2012.00022
Han LL, Jia L, Wu F, Huang C (2019) Sirtuin6 (SIRT6) promotes the EMT of hepatocellular carcinoma by stimulating autophagic degradation of E-cadherin. Mol Cancer Res 17: 2267–2280. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-19-0321
Funding
This research is supported by the Program from Science and Technology (Medical and Health) of Shaoxing (Grant no. 2020A13061 and no. 2018C30025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study design/planning: G.X and Q.W; Data collection/entry: G.X, M.D and Z.Z; Data analysis/statistics: W.Z, J.C and Y.F; Data interpretation: G.X, Q.W and M.D; Preparation of manuscript: G.X and Q.W; Literature analysis/search: G.X and Q.W; Funding collection: G.X. All authors have reviewed the manuscript and consented the submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethic statement
This research is agreed by the ethic committee of Affiliated Hospital of Shaoxing University (2020A13061), and informed consent were obtained from the patients.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests regarding this research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, G., Wang, Q., Ding, M. et al. miR-338-3p Inhibits Apoptosis Evasion in Huh7 Liver Cancer Cells by Targeting Sirtuin 6. J Evol Biochem Phys 58, 1413–1424 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S002209302205012X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S002209302205012X