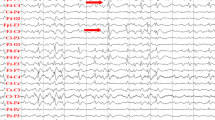
Abstract
Dexamethasone is a synthetic glucocorticosteroid with anti–inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. In order to identify new targets for pharmacotherapy, as well as to study immune mechanisms in the pathogenesis of epilepsy, the influence of dexamethasone on audiogenic epilepsy and catalepsy in Krushinsky–Molodkina (KM) rats has been studied. The chronic (but not acute) infusion of dexamethasone decreased the audiogenic seizure fits intensity in male rats of Krushinsky–Molodkina (KM) strain which is highly susceptible to audiogenic epilepsy, but was accompanied by part of animal deaths. In a month after dexamethasone injections the audiogenic sensitivity of the rescued animals restored to the control levels. The “0” strain rats, bred from F2 KM x Wistar hybrids, no dexamethasone induced mortality was found. The acute and chronic dexamethasone action in rats of “0” strain induced the emergence of catalepsy after the sound exposure, although the audiogenic seizure was found only in one animal. The chronic and acute dexamethasone decreased the postictal catalepsy in KM rats. Thus, pro-inflammatory mechanisms are involved in the pathogenesis of audiogenic epilepsy. Dexamethasone had a distinct anticonvulsant effect in the chronic experiment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Svob Strac D, Pivac N, Smolders IJ, Fogel WA, De Deurwaerdere P, Di Giovanni G (2016) Monoaminergic Mechanisms in Epilepsy May Offer Innovative Therapeutic Opportunity for Monoaminergic Multi-Target Drugs. Front Neurosci 10: 492. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00492
Fazilet D, Karadenizli S, Özsoy OD, Eraldemir FC, Şahin D, Ateş N (2017) The Effects of Adenosinergic Modulation on Cytokine Levels in a Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizure Model. Neuroimmunomodulation 24(1): 54–59.
Aydin L, Erkan Y, Yeşim K, Taner S, Ersin O (2017) Effect of melatonin on cytokine levels in a hyperthermia-induced febrile seizure model. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 63(11): 11–16.
Rincón-López C, Tlapa-Pale A, Medel-Matus JS, Martínez-Quiroz J, Rodríguez-Landa JF, López-Meraz ML (2017) Interleukin-1β increases neuronal death in the hippocampal dentate gyrus associated with status epilepticus in the developing rat. Neurologia 32(9): 587–594.
Sawyer NT, Escayg A (2010) Stress and epilepsy: multiple models, multiple outcomes. J Clin Neurophysiol 27(6): 445–452. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNP.0b013e3181fe0573
Godoy LD, Rossignoli MT, Delfino-Pereira P, Garcia-Cairasco N, Umeoka EHL (2018) A Comprehensive Overview on Stress Neurobiology: Basic Concepts and Clinical Implications. Front Behav Neurosci 12: 127.
de Deus JL, Amorim MR, de Barcellos Filho PCG, de Oliveira JAC, Batalhão ME, Garcia-Cairasco N, Cárnio EC, Leão RM, Branco LGS, Cunha AOS (2020) Inflammatory markers in the hippocampus after audiogenic kindling. Neurosci Lett 721: 134830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2020.134830 NT
Vezzani A, Moneta D, Richichi C, Aliprandi M, Burrows SJ, Ravizza T, Perego C, De Simoni MG (2002) Functional role of inflammatory cytokines and antiinflammatory molecules in seizures and epileptogenesis. Epilepsia 43 (Suppl 5): 30–35.
Espinosa-Garcia C, Zeleke H, Asheebo RA (2021) Impact of Stress on Epilepsy: Focus on Neuroinflammation—A Mini Review Neuroinflammation—A Mini Review. Int J Mol Sci 22: 4061.
Horvath RA, Sütő Z, Cseke B, Schranz D, Darnai G, Kovacs N, Janszky I, Janszky J (2022) Epilepsy is overrepresented among young people who died from COVID-19: Analysis of nationwide mortality data in Hungary. Seizure: Eur J Epilepsy 94: 136–141.
Lehtimaki KA, Keränen T, Palmio J, Mäkinen R, Hurme M, Honkaniemi J, Peltola J (2011) Increased plasma levels of cytokines after seizures in localization-related epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand 116(4): 226–230.
Li G, Bauer S, Nowak M, Norwood B, Tackenberg B, Rosenow F, Knake S, Oertel WH, Hamer HM (2011) Cytokines and epilepsy. Seizure 20(3): 249–256.
Plata-Salaman CR, Ilyin SE, Turrin NP, Gayle D, Flynn MC, Romanovitch AE, Kelly ME, Bureau Y, Anisman H, McIntyre DC (2000) Kindling modulates the IL-1beta system, TNF-alpha, TGF-beta1 and neuropeptide mRNAs in specific brain regions. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 75(2): 248–258.
Tolmacheva EA, Oitzl MS, van Luijtelaar G (2012) Stress, glucocorticoids and absences in a genetic epilepsy model. Horm Behav 61(5): 706–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.03.004
Kalueff AV, Lehtimaki KA, Ylinen A, Honkaniemi J, Peltola J (2004) Intranasal administration of human IL-6 increases the severity of chemically induced seizures in rats. Neurosci Lett 365(2): 106–110.
Balosso S, Ravizza T, Perego C, Peschon J, Campbell IL, De Simoni MG, Vezzani A (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits seizures in mice via p75 receptors. Ann Neurol 57: 804–812.
Benedek TG (2011) History of the development of corticosteroid therapy. Clin Exp Rheumatol 29(5 Suppl 68): S5–S12.
Giles AJ, Hutchinson MND, Sonnemann HM, Jung J, Fecci PE, Ratnam NM, Zhang W, Song H, Bailey R, Davis D, Reid CM, Park DM, Gilbert MR (2018) Dexamethasone-induced immunosuppression: mechanisms and implications for immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer 6(1): 51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0371-5
Ghanshyam N, Pandey HS, Rizavi RB, Xinguo R (2019) Increased protein and mRNA expression of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF), decreased CRF receptors and CRF binding protein in specific postmortem brain areas of teenage suicide subjects. Psychoneuroendocrinology 106: 233–243.
Smits HHK, Grünberg K, Derijk RH, Sterk PJ, Hiemstra PS (1998) Cytokine release and its modulation by dexamethasone in whole blood following exercise. Clin Exp Immunol 111(2): 463–468.
Rensen N, Gemke RBJ, van Dalen EC, Rotteveel J, Kaspers GJL (2017) Hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis suppression after treatment with glucocorticoid therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 11(11): CD008727.
Mariann F, Petrovski G, Pásztor D, Gogolák P, Rajnavölgyi E, Berta A (2014) Effects of Awakening and the Use of Topical Dexamethasone and Levofloxacin on the Cytokine Levels in Tears Following Corneal Transplantation. J Immunol Res 2014: 570685.
Geeta R, Olivia C, Meisner OC, Philipp MT (2015) Anti-inflammatory effects of dexamethasone and meloxicam on Borrelia burgdorferi-induced inflammation in neuronal cultures of dorsal root ganglia and myelinating cells of the peripheral nervous system. J Neuroinflammat 12: 240.
Ramos AB, Cruz RA, Villemarette-Pittman NR, Olejniczak PW, Mader EC Jr (2019) Dexamethasone as Abortive Treatment for Refractory Seizures or Status Epilepticus in the Inpatient Setting. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep 7: 2324709619848816. https://doi.org/10.1177/2324709619848816
Webster KM, Sun M, Crack P, O’Brien TJ, Shultz SR, Semple BD (2017) Inflammation in epileptogenesis after traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammat 14(1): 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0786-1
Jeon YJ, Han SH, Lee YW, Lee M, Yang KH, Kim HM (2000) Dexamethasone inhibits IL-1 beta gene expression in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells by blocking NF-kappa B/Rel and AP-1 activation. Immunopharmacology 48(2): 173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0162-3109(00)00199-5
Jang BC, Lim KJ, Suh MH, Park JG, Suh SI (2007) Dexamethasone suppresses interleukin-1beta-induced human beta-defensin 2 mRNA expression: involvement of p38 MAPK, JNK, MKP-1, and NF-kappaB transcriptional factor in A549 cells. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 51(1): 171–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-695X.2007.00293.x
Al-Shorbagy MY, Bahia M, El Sayeh BM, Abdallah DM (2012) Diverse effects of variant doses of dexamethasone in lithium-pilocarpine induced seizures in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 90(1): 13–21.
Fazekas I, Szakacs R, Mihaly A, Zador Z, Krisztin-Peva B, Juhasz A, Janka Z (2006) Alterations of seizure-induced c-fos immunolabelling and gene expression in the rat cerebral cortex following dexamethasone treatment. Acta Histochem 108: 463–473.
Di Giannuario A, Pieretti S, Sagratella S, Loizzo A (2001) Dexamethasone blocking effects on mu- and delta-opioid-induced seizures involves kappa-opioid activity in the rabbit. Neuropsychobiology 43(3): 213–220. https://doi.org/10.1159/000054892
Roberts AJ, Keith LD (1995) Corticosteroids enhance convulsion susceptibility via central mineralocorticoid receptors. Psychoneuroendocrinology 20(8): 891–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4530(95)00016-x
Reddy DS (2013) Role of hormones and neurosteroids in epileptogenesis. Front Cell Neurosci 31(7): 115. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2013.00115
Sawyer NT, Papale LA, Eliason J, Neigh GN, Escayg A (2014) Scn8a voltage-gated sodium channel mutation alters seizure and anxiety responses to acute stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 39: 225–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.09.018
Schridde U, van Luijtelaar G (2004) Corticosterone increases spike-wave discharges in a dose- and time-dependent manner in WAG/Rij rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 78(2): 369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2004.04.012
Beckley EH, Fretwell AM, Tanchuck MA, Gililland KR, Crabbe JC, Finn DA (2008) Decreased anticonvulsant efficacy of allopregnanolone during ethanol withdrawal in female Withdrawal Seizure-Prone vs. Withdrawal Seizure-Resistant mice. Neuropharmacology 54(2): 365–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.10.006
Umeoka EH, Garcia SB, Antunes-Rodrigues J, Elias LL, Garcia-Cairasco N (2011) Functional characterization of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis of the Wistar Audiogenic Rat (WAR) strain. Brain Res 1381: 141–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2011.01.042
Valentim-Lima E, de Oliveira JAC, Antunes-Rodrigues J, Reis LC, Garcia-Cairasco N, Mecawi AS (2021) Neuroendocrine changes in the hypothalamic-neurohypophysial system in the Wistar audiogenic rat (WAR) strain submitted to audiogenic kindling. J Neuroendocrinol 33(7): e12975. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12975
Semiokhina AF, Fedotova IB, Poletaeva II (2006) Rats of Krushinsky-Molodkina strain: studies of audiogenic epilepsy, vascular pathology, and behavior. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova 56(3): 298–316. (In Russ).
Fedotova IB, Kostyna ZA, Surina NM (2012) Laboratory rat selection for the trait “the absence of audiogenic seizure proneness”. Genetika 48(6): 685–691. (In Russ).
Fedotova IB, Surina NM, Malikova LA, Raevskiĭ KS, Poletaeva II (2008) The investigation of cataleptic muscle tonus changes in rats after audiogenic seizures. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova 58(5): 620–627. (In Russ).
Kulikov AV, Bazovkina DV, Kondaurova EM, Popova NK (2008) Genetic structure of hereditary catalepsy in mice. Genes Brain Behav 7(4): 506–512. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-183X.2008.00387.x
Fedotova IB, Polikarpova AV, Perepelkina OV, Nikolaev GM, Smirnova OB, Poletaeva II (2018) The plasma cortocosterone levels in in rats with different audiogenic epilepsy proneness. Pathogenesis 16(3): 64–67. (In Russ).
Uddin MN, Siddiq A, Oettinger CW, D’Souza MJ (2011) Potentiation of pro-inflammatory cytokine suppression and survival by microencapsulated dexamethasone in the treatment of experimental sepsis. J Drug Target 19(9): 752–760. https://doi.org/10.3109/1061186X.2011.561856
Müller-Guzzo GEF, Rodrigues LK, Regla VR, Simon CA (2018) Effect of dexamethasone on seizures and inflammatory profile induced by Kindling Seizure Model. J Neuroimmunol 325: 92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.10.005
Garcia-Curran MM, Hall AM, Patterson KP, Shao M, Eltom N, Chen K, Dubé CM, Baram TZ (2019) Dexamethasone attenuates hyperexcitability provoked by experimental febrile status epilepticus. ENEURO 15(6): 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0430-19.2019
Vizuete AFK, Hansen F, Negri E, Leite MC, de Oliveira DL, Gonçalves CAJ (2018) Effects of dexamethasone on the Li-pilocarpine model of epilepsy: protection against hippocampal inflammation and astrogliosis. Neuroinflammation 15(1): 68. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1109-5
Forss M, Batcheller G, Skrtic S, Johannsson G (2012) Current practice of glucocorticoid replacement therapy and patient-perceived health outcomes in adrenal insufficiency—a worldwide patient survey. BMC Endocr Disord 12: 8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6823-12-8
Chopde CT, Hote MS, Mandhane SN, Muthal AV (1995) Glucocorticoids attenuate haloperidol-induced catalepsy through adrenal catecholamines. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 102(1): 47–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01276564
Capasso A, Di Giannuario A, Loizzo A, Pieretti S, Sorrentino L (1995) Dexamethasone reduces the behavioural effects induced by baclofen in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 47(5): 425–430. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.1995.tb05823.x
Capasso A, Di Giannuario A, Loizzo A, Pieretti S, Sorrentino L (1996) Dexamethasone modifies the behavioral effects induced by clonidine in mice. Pharmacology 27(8): 1429–1434. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-3623(95)02144-2
Firstova JJ, Abaimov DA, Surina NM, Poletaeva II, Fedotova IB, Kovalev GI (2012) Binding of specific ligand by D2- and NMDA-receptors of striatum cells in two rat strains predisposed and resistant to audiogenic seizures. Bull Exp Biol Med 154(2): 196–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-012-1910-6
Ozer H, Ekinci AC, Starr MS (1997) Dopamine D1- and D2-dependent catalepsy in the rat requires Dopamine D1- and D2-dependent catalepsy in the rat requires functional NMDA receptors in the corpus striatum, nucleus accumbens and substantia nigra pars reticulata. Brain Res 777(1–2): 51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(97)00706-3
Myslobodsky MS, Mintz M, Kofman O (1981) Pharmacologic analysis of the postictal immobility syndrome in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15(1): 93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-3057(81)90345-2
Funding
This work was supported by the Lomonosov Moscow State University State Program No.121032500080-8 and the Interdisciplinary Research and Education School “Brain, Cognitive Systems, Artificial Intelligence” of Moscow State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.M.S.—data collection, primary processing, article writing and editing, I.B.F.—providing the experimental base, data processing, article editing, I.I.P—article writing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have neither evident nor potential conflict of interest related to the publication of this article.
Additional information
Translated by A. Dyomina
Russian Text © The Author(s), 2022, published in Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I.M. Sechenova, 2022, Vol. 108, No. 7, pp. 850–860https://doi.org/10.31857/S0869813922070056.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Surina, N.M., Fedotova, I.B. & Poletaeva, I.I. The Effects of Acute and Chronic Infusions of Dexamethasone on Audiogenic Seizures and Catalepsy in Rats of Krushinsky–Molodkina and “0” Strains. J Evol Biochem Phys 58, 1110–1118 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093022040147
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093022040147