Abstract
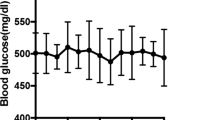
Comparison of amplitude-time characteristics of fast extensor digitorum longus muscles (m. EDL) isolated from control rats and rats with model of acute streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus (DM) 12 and 30 days after treatment with streptozotozin did not reveal significant changes of strength of single normalized contractile responses as compared with control. In slow (m. Soleus) muscles of rats with the 30-day long SD, essential changes of the amplitude-time characteristics of such contractile responses were observed: a decrease of their amplitude and an increase of duration. In the diabetic rats treated with insulin there develops resistance of skeletal muscles of both types to action of exogenous insulin. Both in control and in diabetic animals the exhausting stimulation of m. EDL with trains from 5 impulses did not reveal significant differences at early (up to 3 min) terms of development of fatigue. Under similar conditions, fatigue of m. Soleus in rats of the both diabetic groups developed significantly faster as compared with control (already in 30 s after the beginning of stimulation). Insulin at a concentration of 0.5–1 nM produced a dose-dependent decrease of amplitude of single contractile responses in fast and slow muscles of rats with the acute SD model (the negative inotropic action). Earlier, we demonstrated in healthy rats the similar action of insulin, but at the higher concentrations [1]. Insulin at a concentration of 10 nM did not produce an essential effect on dynamics of depression of responses in the course of development of fatigue at tetanical stimulation of m. EDL and m. Soleus both in control and in diabetic rats, but affected essentially the dynamics of change of duration of the half-decay (Thd) of their tetanical responses. The presence of insulin in the washing solution led to stabilization of the period of muscle relaxation in the course of development of fatigue in all studied animal groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kubasov, I.V., Arutyunyan, F.S., Dobretsov, M.G., and Matrosova, E.V., Negative inotropic action of insulin on contractile and electrical responses rat skeletal muscles, Ross. Fiziol. Zh. im. I.M. Sechenova (in press).
Gordon, C.S., Serino, A.S., Krause, M.P., Campbell, J.E., Cafarelli, E., Adegoke, O.A., Hawke, T.J., and Riddell, M.C., Impaired growth and force production in skeletal muscles of young partially pancreatectomized rats: a model of adolescent type 1 diabetic myopathy?, PLoS One, Nov 17; 2010, 5(11):e14032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014032.
William, W. and Hofmann, M.D., Comparison of stimulation and insulin effects on denervated mouse soleus muscles, Muscle & Nerve, 1991, vol. 14, pp. 748–755.
Algenstaedt, P., Antonetti, D.A., Yaffe, M.B., and Kahn, C.R., Insulin receptor substrate proteins create a link between the tyrosine phosphorylation cascade and the Ca-ATPases in muscle and heart, J. Biol. Chem., 1997, vol. 272, pp. 23696–23702.
Clausen, T., Na+-K+ Pump regulation and skeletal muscle contractility, Physiol. Rev., 2003, vol. 83, pp. 1269–1324.
Stephenson, G.M., O’Callagan, A., and Stephenson, D.G., Single-fiber study of contractile and biochemical properties of skeletal muscles in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, Diabetes, 1994, vol. 43, pp. 622–628.
Lesniewski, L.A., Miller, T.A., and Armstrong, R.B., Mechanism of force loss in diabetic mouse skeletal muscle, Muscle & Nerve, 2003, vol. 28, pp. 493–500.
Brotto, M., Brotto, L., Jin, J.-P., Nosek, T.M., and Romani, A., Temporal adaptive changes in contractility and fatigability of diaphragm muscles from streptozotocin-diabetic rats, J. Biomed. Biotechnol., 2010. vol. 2010: 931903; doi: 10.1155/2010/931903.
Chonkar, A., Hopkin, R., Adeghate, E., and Singh, J., Contraction and cation contents of skeletal soleus and EDL muscles in age-matched control and diabetic rats, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 2006, vol. 1084, pp. 442–451.
Dobretsov, M., Romanovsky, D., Smith, A.G., and Stimers, J.R., Diabetic neuropathy and pain, Mechanisms of Pain in Peripheral Neuropathy, Dobretsov, M. and Zhang, J.-M., Eds., Kerala, India, Research Signpost., 2009, pp. 255–294.
Nordquist, L. and Sjöquist, M., Improvement of insulin response in the streptozotocin model of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. insulin response with and without a long-acting insulin treatment, Animal, 2009, vol. 3, pp. 685–689.
Elçioğlu, K.H., Kabasakal, L., Cetinel, S., Conturk, G., Sezen, S.F., and Ayanoğlu-Dülger, G., Changes in caveolin-1 expression and vasoreactivity in the aorta and corpus cavernosum of fructose and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2010, vol. 642, pp. 113–120.
Erdal, N., Gürgül, S., Demirel, C., and Yildiz, A., The Effect of insulin therapy on biomechanical deterioration of bone in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus in rats, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract., 2012, vol. 97, pp. 461–467.
Hundal, H.S., Marette, A., Mitsumoto, Y., Ramlal, T., Blostein, R., and Klip, A., Insulin induces translocation of the 2 and 1 subunits of the Na+/K+-ATPase from intracelluar compartments to the plasma membrane in mammalian skeletal muscle, J. Biol. Chem., 1992, vol. 267, pp. 5040–5043.
Marette, A., Krischer, J., Lavoie, L., Ackerley, C., Carpentier, J.L., and Klip, A., Insulin increases the Na+-K+-ATPase alpha-2 subunit in the surface of rat skeletal muscle: morphological evidence, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol., 1993, vol. 265, pp. 1716–1722.
Overgaard, K., Nielsen, O.B., and Clausen, T., Effects of reduced electrochemical Na+ gradient on contractility in skeletal muscle: role of the Na+-K+ pump, Eur. J. Physiol., 1997, vol. 434, pp. 457–465.
Chibalin, A.V., Kovalenko, M.V., Ryder, J.W., Feraille, E., Wallberg-Hendriksson, H., and Zierath, J.R., Insulin- and glucose-induced phosphorylation of the Na+,K+-adenosine triphosphatase alpha-subunits in rat skeletal muscle, Endocrinol., 2001, vol. 142, pp. 3474–3482.
Sweeney, G., Niu, W., Canfield, V.A., Levenson, R., and Klip, A., Insulin increases plasma membrane content and reduces phosphorylation of Na+-K+ pump 1-subunit in HEK-293 cells, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol., 2001, vol. 281, pp. 1797–1803.
Eibschutz, B., Lopaschuk, G.D., McNeill, J.H., and Katz, S., Ca2+-transport in skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum of the chronically diabetic rat, Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol., 1984, vol. 45, pp. 301–304.
Taira, Y., Hata, T., Ganguly, P.K., Elimban, V., and Dhalla, N.S., Increased sarcolemmal Ca2+ transport activity in skeletal muscle of diabetic rats, Am. J. Physiol., 1991, vol. 260, pp. 626–632.
Markuns, J.F., Napoli, R., Hirshman, M.F., Davalli, A.M., Cheatham, B., and Goodyear, L.J., Effects of streptozocin-induced diabetes and islet cell transplantation on insulin signaling in rat skeletal muscle, Endocrinol., 1999, vol. 140, pp. 106–111.
Searls, Y.M., Loganathan, R., Smirnova, I.V., and Stehno-Bittel, L., Intracellular Ca2+ regulating proteins in vascular smooth muscle cells are altered with type 1 diabetes due to the direct effects of hyperglycemia, Cardiovasc. Diabetol., 2010. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-9-8.
Touw, K., Chakraborty, S., Zhang, W., Obukhov, A.G., Tune, J.D., Gunst, S.J., and Herring, B.P., Altered calcium signaling in colonic smooth muscle of type 1 diabetic mice, Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol., 2012, vol. 302, pp. 66–76.
Mandavia, C.H, Aroor, A.R, Demarco, V.G., and Sowers, J.R., Molecular and metabolic mechanisms of cardiac dysfunction in diabetes, Life Sci., 2013, vol. 92, pp. 601–608.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.V. Kubasov, R.S. Arutyunyan, M.G. Dobretsov, A.O. Shpakov, E.V. Matrosova, 2014, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2014, Vol. 50, No. 2, pp. 121–129.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubasov, I.V., Arutyunyan, R.S., Dobretsov, M.G. et al. Effect of insulin on characteristics of contractile responses of fast and slow skeletal muscles of rats with acute streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Evol Biochem Phys 50, 136–145 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093014020069
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093014020069