Abstract
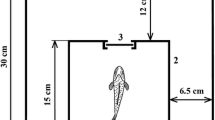
Effects of serotonin-modulated anticonsolidation protein (SMAP) that has property to impair formation of memory trace in mammals and of learning and memory in teleost fish was studied in the learning model of active avoidance. The experiment was performed in three stages: (1) fry of carp Cyprinus carpio L. was injected intracerebroventricularly with the SMAP at a dose of 0.3 μg/g; control individuals were administered with equal amount of the buffered saline for poikilothermic animals; (2) 24 h after injection, fish were learned the conditioned reflex of active avoidance; (3) 48 h after the learning the testing of the skill was perfomed. The administration of the protein was shown to lead to impairment of reproduction of the skill in the fish: the latent time of the skill reproduction in experimental individuals exceeded that in control fish more than two times, while the number of individuals succeeding the task in the expreimental group was insignificantly lower than in the control group. However, unlike mammals, injection of the SMAP in this model produced no effect on the process of learning in carps. Thus, there was first demonstrated the inhibiting effect of the SMAP whose concenration correlated positively with the content of the neurotransmitter serotonin in brain on consolidation of memory traces in teleost fish.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rodríguez, F., Broglio, C., Durán, E., Gómez, A., and Salas, C., Neural Mechanisms of Learning in Teleost Fish, Fish Cognition and Behavior, Oxford: Blackwell Publ., 2006, pp. 243–277.
Rodriguez, F., Durán, E., Gómez, A., Ocaña, F.M., Ávarez, E., Jiménez-Moya, F., Broglio, C., and Salas, C., Cognitive and Emotional Functions of the Teleost Fish Cerebellum, Brain Res. Bull., 2005, vol. 66, pp. 365–370.
Broglio, C., Gómez, A., Durán, E., Ocaña, F.M., Jiménez-Moya, F., Rodríguez, F., and Salas, C., Hallmarks of a Common Forebrain Vertebrate Plan: Specialized Pallial Areas for Spatial, Temporal and Emotional Memory in Actinopterygian Fish, Brain Res. Bull., 2005, vol. 66, pp. 277–281.
Broglio, C., Rodríguez, F., Gómez, A., Arias, J.L., and Salas, C., Selective Involvement of the Goldfish Lateral Pallium in Spatial Memory, Behav. Brain Res., 2010, vol. 210, no. 2, pp. 191–201.
Csányi, V., Csizmadia, G., and Miklosi, A., Long-Term Memory and Recognition of Another Species in the Paradise Fish, Animal Behaviour, 1989, vol. 37, no. 6, pp. 908–911.
Zion, B., Karplus, I., Grinshpon, J., Rosenfeld, L., and Barki, A., Periodic Reinforcement of Acoustically Conditioned Behavior in St. Peter’s fish, Sarotherodon galilaeus, for Ranching Purposes, Aquaculture, 2011, vol. 315, no. 3–4, pp. 394–399.
Walton, A.G. and Moller, P., Maze Learning and Recall in a Weakly Electric Fish, Mormyrus rume proboscirostris Boulenger (Mormyridae, Teleostei), Ethology, 2010, vol. 116, pp. 904–919.
Kruglikov, R.I., Regulating Influence of Serotonin on Protein Metabolism of the Brain during Process of Consolidation, Neirokhimicheskie mekhanizmy obucheniya i pamyati (Neurochemical Mechanisms of Learning and Memory), Moscow: Nauka, 1981, pp. 161–173.
Sitaraman, D., Zars, M., Laferriere, H., Chen, Y.C., Sable-Smith, A., Kitamoto, T., Rottinghaus, G.E., and Zars, T., Serotonin Is Necessary for Place Memory in Drosophila, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2008, vol. 105, no. 14, pp. 5579–5584.
Cassel, J.-Ch., Experimental Studies on the Role(s) of Serotonin in Learning and Memory Functions, Handbook of Behavioral Neuroscience, 2010, vol. 21, pp. 429–447.
Harvey, J.A., Serotonergic Regulation of Associative Learning, Behav. Brain Res., 1995, vol. 73, no. 1–2, pp. 47–50.
Barrionuevo, M., Aguirre, N., Del Río, J., and Lasheras, B., Serotonergic Deficits and Impaired Passive-Avoidance Learning in Rats by MDEA: A Comparison with MDMA, Pharm. Biochem. Behav., 2000, vol. 65, no. 2, pp. 233–240.
Getsova, V.M., Jork, R., and Wetzel, W., Mechanisms of Serotonin Participation in the Consolidation of Temporary Connections, Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deiat. im. I.P. Pavlova, 1980, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 988–990.
Essman, W.B., Brain 5-Hydroxytriptamine and Memory Consolidation, Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmacol., New-York: Raven Press, 1974, vol. 11, pp. 265–274.
Santucci, A.C., Knott, P.J., and Haroutunian, V., Excessive Serotonin Release, not Depletion to Memory Impairments in Rats, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 1996, vol. 295, no. 1, pp. 7–17.
Vanderwolf, C.H., A General Role for Serotonin in the Control of Behavior: Studies with Intracerebral 5,7-Dihydroxytryptamine, Brain Res., 1989, vol. 504, no. 2, pp. 192–198.
Barziali, A., Kennedy, T.E., Sweatt, J.D., and Kandel, E.R., 5-HT Modulates Protein Synthesis and the Supression of Specific Proteins during Long-Term Facilitation in Aplysia Sensory Neurons, Neuron, 1989, vol. 2, pp. 1577–1586.
Abel, T. and Kandel, E., Positive and Negative Regulatory Mechanisms that Mediate Long-Term Memory Storage, Brain Res. Rev., 1998, vol. 26, no. 2–3, pp. 360–378.
Mekhtiev, A.A., Detection of Protein with Anticonsolidation Properties in the Rat Brain, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2000, vol. 130, no. 8, pp. 739–742.
Mekhtiev, A.A., Gaisina, A.A., Palatnikov, G.M., and Kasimov, R.Y., Decrease in Activity of the Serotoninergic System during Mutagenesis, Byull. Eksper. Biol. Med., 2006, vol. 142, no. 6, pp. 657–659.
Prazdnikova, N.V., Some Data on Study of the Higher Nervous Activity in Fish by the Method of Food Locomotory Conditioned Reflex, Trudy soveshchaniya po fiziologii ryb (Proceedings of the Meeting on Fish Physiology), Moscow: Izdat. Akad. Nauk, 1958, pp. 31–37.
Guseinov, Sh.B. and Mekhtiev, A.A., Change of the Level of Serotonin-Modulated Anticonsolidation Protein in the Rat Cerebral Cortex in the Process of Learning in the Shuttle-Box, Izv. NAN Azrbaijan, Ser. Biol., 2010, vol. 65, no. 1–2, pp. 110–115.
Garina, D.V. and Mekhtiev, A.A., Role of Serotonin-Modulated Anticonsolidation Protein in Consolidation of Memory Traces in the Goldfish Carassius auratus, Izv. PGPU im. V.G. Belinskogo, 2012, no. 29, pp. 201–205.
Guseinov, Sh.B. and Mekhtiev, A.A., The Role of Serotonin-Modulated Anticonsolidation Protein in Memory Formation in Rats in a Shuttle Box, Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deiat. im. I.P. Pavlova, 2012, vol. 62, no. 2, pp. 208–215.
Mekhtiev, A.A. and Movsum-zade, S.K., Antimutagenic Activity of Serotoninergic System and Its Mechanisms in Acipenser gueldenstaedti persicus and Carassius auratus, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 2008, vol. 44, no. 5, pp. 476–481.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.V. Garina, A.A. Mekhtiev, 2014, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2014, Vol. 50, No. 1, pp. 44–50.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garina, D.V., Mekhtiev, A.A. Effect of serotonin-modulated anticonsolidation protein on formation of long-term memory in the learning model of active avoidance in the carp (Cyprinus carpio). J Evol Biochem Phys 50, 49–56 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093014010071
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093014010071