Abstract
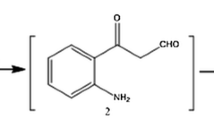
Comparative substrate-inhibitor analysis of catalytic properties of liver monoamine oxidases (MAO) was performed in the mature males of the American mink Mustela vison and the European mink Mustela lutreola. The action on the MAO activity was studied of alkaloids of the benzo[c]phenanthridine group: sanguinarine and chelidonine, diisoquinoline alkaloid berberine, medicinal agents “Ukrain” and “Sanguirythrin” as well as derivatives of 2-propylamine: deprenyl and chlorgylin. The latter turned out to be irreversible inhibitor of the MAO A form, whereas deprenyl-irreversible inhibitor of the MAO B form in both studied mink species. The selectivity of action of each inhibitor on the corresponding liver MAO form for the species M. vison was one order of magnitude stronger than for the species M. lutreola. All studied alkaloids as well medicinal agents on their basis have been shown to be specific irreversible inhibitors of the intermediate strength of the liver MAO A form of both mink species. They inhibit the enzymatic deamination of serotonin, tyramine, and tryptamine without affecting the deamination reaction of benzylamine and β-phenylethylamine (at concentrations of 10 mM and lower). Out of five studied isoquinoline agents, the medication “Ukrain” and alkaloid chelidonine have the highest inhibitory action; the agent “Sanguirythrin” and alkaloids berberine and sanguinarine produce the weaker monoamine oxidase effect. The revealed specificity of action of the studied inhibitors is an indirect evidence for the presence in the liver enzymes of both mink species, like in the rat liver enzyme, of several molecular forms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kopin, I.J., The Relationship of Early Studies of Monoamine Oxidase to Present Concepts, J. Neural. Transm., 2006, vol. 71, pp. 79–86.
Gorkin, V.Z., Aminoksidazy i ikh znachenie v meditsine (Amine Oxidases and Their Significance in Medicine), Moscow, 1981.
Bortolato, M., Chen, K., and Shin, J.C., Monoamine Oxidase Inactivation: from Pathophysiology to Therapeutics, Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev., 2008, vol. 60, nos. 13, 14, pp. 1527–1533.
Krivchenkova, R.S., Current Achievements in Biochemistry of Tetrahydroisoquinolines and β-Carbolines (Tryptolines), Vopr. Med. Khim., 1983, vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 7–16.
Naoi, M., Maruyama, W., and Nagy, G.M., Dopamine-Derived Salsolinol Derivatives as Endogenous Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: Occurrence, Metabolism and Function in Human Brains, Neurotoxicol., 2004, vol. 25, no. 1, 2, pp. 193–204.
Holt, A., Sharman, D.F., and Callingham, B.A., Effects in vitro of Procarbazine Metabolites on Some Amine Oxidase Activities in the Rat, J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 1992, vol. 44, pp. 494–499.
Patsenka, A. and Antkiewicz-Michakuk, L., Inhibition of Rodent Brain Monoamine Oxidase and Tyrosine Hydroxylase by Endogenous Compounds—1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline Alkaloids, Pol. J. Pharmacol., 2004, vol. 56, pp. 727–734.
Lee, S.S., Lee, J.J., Cheong, M.J., Kim, Y.H., Kim, Y., Yun, Y.P., Lee, C.K., and Lee, M.K., In hibitory Effects of Ethaverine, a Homologue of Papaverine, on Monoamine Oxidase Activity in Mouse Brain, Biol. Pharm. Bull., 2001, vol. 24, pp. 838–840.
Lee, S.S., Kai, M., and Lee, M.K., Inhibitory Ef fects of Sanguinarine on Monoamine Oxidase Activity in Mouse Brain, Phytother. Res., 2001, vol. 15, pp. 167–169.
Katz, S. and Cohen, G., A Comparison of 6,7-Dihydroxytetrahydroisoquinoline, Salsolinol and Tetrahydropapaveroline as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase within the Adrenergic Nerve Plexus of the Isolated Mouse Atrium, Res. Comm. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol., 1976, vol. 13, pp. 217–224.
Yagodina, O.V., Nikol’skaya, E.B., and Faddeeva, M.D., Inhibition of Activity of Mitochondrial Monoamine Oxidase by Alkaloids from Celandine and Makleiya and Medicinal Drugs on Their Basis, Tsitologiya, 2003, vol. 45, pp. 1032–1036.
Balitskii, K.P. and Vorontsova, A.L., Preparations of Celandine, Lekarstvennye rasteniya i rak (Medicinal Plants and Cancer), Kiev, 1982.
Yagodina, O.V., Comparative Study of Catalytic Properties of Monoamine Oxidase in Liver of Mink and Rat, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 2008, vol. 44, pp. 570–575.
Yagodina, O.V., Sensitivity of Monoamine Oxidase of Liver of the Mink Mustela vison to Some Isoquinoline Alkaloids, Dokl. RAN, 2007, vol. 415, pp. 566–568.
Ocherki po fiziologii pushnykh zverei (Essays on Physiology of Fur Animals), Berestov, V.A., Ed., Leningrad, 1987.
Novitski, J.V., Biological Properties of “Ukrain” under Experimental and Clinical Conditions, Mezdunar. Med. Obzory (Intern. Med. Reviews), 1993, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 5–10.
Moralev, S.N. and Rozengart, E.V., Comparative Enzymology of Cholinesterases, International University Lines, Biotechnology Series, no. 6, La Jolla (CA), 2007.
Brestkin, A.P., Kuznetsova, L.P., Moralev, S.N., Rozengart, E.V., and Epshtein, L.M., Kholinesterazy nazemnykh zhivotnykh i gidrobiontov (Cholinesterases of Terrestrial Animals and Hydrobionts), Vladivostok, 1997.
Kovelman, I.R., Tochilkin, A.I., and Gorkin, V.Z., About the Structure and Activity of Ir reversible Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase, Khim-Farm. Zh., 1990, vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 4–12.
Walterova, D., Ulrichova, J., Preininger, V., Simanek, V., Lenfeld, J., and Lasovsky, J., Inhibition of Liver Alanine Aminotransferase Activity by Some Benzophenanthridine Alkaloids, J. Med. Chem., 1981, vol. 24, pp. 1100–1103.
Faddeeva, M.D. and Belyaeva, T.N., Sanguinarine and Elipticine: the Cytotoxic Alkaloids Isolated from Known Antitumor Plants and Intracellular Targets of Their Action, Tsitologiya, 1997, vol. 39, nos. 2, 3, pp. 181–208.
Kidd, A.G., Bowman, J., Lesbarreres, D., and Schulte-Hostedde, A., Hybridization between Es caped Domestics and Wild American Mink (Neovison vison), Mol. Ecol., 2009, vol. 18, pp. 1175–1186.
Lode, T., Cormier, J.P., and LeJacgues, D., Decline in Endangered Species as an Indication of Anthropic Pressures: The Case of European Mink Mustela lutreola Western Population, Environ. Manage, 2001, vol. 28, pp. 727–735.
Gorkin, V.Z., Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors and the Transformation of Monoamine Oxidases, Monoamine Oxidase and Its Inhibition, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1976, pp. 61–81.
Massie, M.J. and Holland, J.C., Diagnostic and Treatment of Depression in the Cancer Patients, J. Clin. Psychiatry, 1984, vol. 45, no. 3 (2), pp. 25–29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O. V. Yagodina, 2010, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2010, Vol. 46, No. 5, pp. 380–386.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yagodina, O.V. Comparative substrate-inhibitor analysis of mink liver monoamine oxidases. J Evol Biochem Phys 46, 453–460 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S002209301005004X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S002209301005004X