Abstract
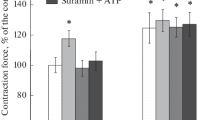
At a short-term tetanic stimulation of fast muscle in response to subsequent single stimulation there is recorded a temporary increase of the strength of single contractions that returns to the initial background after 6–10 min. This phenomenon is called posttetanic potentiation (PTP) and is recorded only in fast muscles. The goal of the present work was a study of effect of motor innervation on the course of PTP in rat m. extensor digitorum longus (m. Edl). It has been established that the first signs of effect of motor denervation on the PTP course after section of sciatic nerve in the area of popliteal fossa are recorded as early as at the 4th day after denervation and are expressed in a decrease of strength of single contractions after cessation of tetanic stimulation. These changes reach its maximum at the 14–15th day after denervation when effect of PTP in denervated muscle does not appear at all. Pharmacological analysis of the studied phenomenon has shown that dantrolen (10 μM) suppresses amplitude of the single contraction, but does not prevent the appearance of PTP in intact muscle. In the denervated m. Edl, instead of the appearance of PTP, after a brief slight increase, a gradual decrease of the strength of contraction is recorded. Thus, it can be concluded that no significant PTP changes are present under action of dantrolen. It has been established that after the 10-min muscle incubation in Ringer’s solution with caffeine (4 mM), strength of the single contraction in intact and denervated muscles increases by approximately equal value. Tetanization of intact muscle increases strength of the single contraction approximately by 7% more than this occurs after incubation with caffeine, i.e., this substance reduces the capability of muscle for the appearance of PTP. On denervated muscle, caffeine increases strength of singly contraction, but does not potentiate development of PTP. The obtained data allow concluding about the existence of different mechanisms underlying the pretetatnic contraction and posttetanic potentiation of the single contraction. The main difference between two types of contractions can be recruiting of additional DICR-channels in the process of contraction under conditions of PTP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kotias, B.A., Venosa, R.A., and Horovitz, P., Denervated Frog Skeletal Muscle: Some Electrical and Mechanical Properties, Pflugers Arch., 1984, vol. 400, pp. 262–268.
Close, R. and Hoh, J., The After-Effects of Repetitive Stimulation on the Isometric Twitch Contraction of Rat Skeletal Muscle, J. Physiol. (London), 1968, vol. 197, pp. 461–477.
Bogus, D., Lewis, D., and Luck, J., Posttetanic Effects in Motor Units of Fast and Slow Twitch Muscle of the Cat, J. Physiol. (London), 1981, vol. 237, pp. 291–323.
Krarup, Ch., Enhancement and Diminution of Mechanical Tension Evoked by Staircase and by Tetanus in Rat Muscle, J. Physiol. (London), 1981, vol. 311, pp. 355–372.
Buller, A., Kean, C., Ranatunga, K., and Smith, J., Post-Tetanic Depression of Twitch in the Cat Soleus Muscle, Exp. Neurol., 1981, vol. 73, pp. 78–89.
Arutyunyan, R.S. and Nasledov, G.A., Effect of Supporting Unloading on the Trace Reactions in Fast and Slow Rat Muscles, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., Suppl., 2005, vol. 41, pp. 61–78.
Fambrough, D., Control of Acetylcholine Receptors in Skeletal Muscle, Physiol. Rev., 1979, vol. 59, pp. 165–227.
Orbeli, L.A., Evolyutsiya nervno-myshechnogo pribora (Evolution of the Neuromuscle Apparatus), Isbr. Trudy, Moscow, 1961, pp. 183–192.
Tubman, A., Rassier, D., and Macintosh, B., Attenuation of Myosin Light Chain Phosphorylation and Posttetanic Potentiation in Atrophied Skeletal Muscle, Pflugers Arch., 1997, vol. 434, pp. 848–851.
Finol, H., Lewis, D., and Owens, R., The Effects of Denervation on Contractile Properties of Rat Skeletal Muscle, J. Physiol. (London), 1981, vol. 319, pp. 81–92.
Krarup, Ch., The Effect of Dantrolen on the Enhancement and Diminution of Tension Evoked by Staircase and by Tetanus in Rat Muscle, J. Physiol. (London), 1981, vol. 311, pp. 389–400.
Endo, M., Calcium Release from Sarcoplasmic Reticulum, Physiol. Rev., 1977, vol. 57, pp. 71–108.
Dux, L., Muscle Relaxation and Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Function in Different Muscle Types, Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol., 1993, vol. 122, pp. 69–141.
Melzer, W., Herrman-Frank, A., and Ludgau, H., The Role of Ca2+ Ions in Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Skeletal Muscle Fibers, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1995, vol. 1241, pp. 59–116.
Herrman-Frank, A., Luttgau, H., and Stephenson, G., Caffeine and Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Skeletal Muscle: a Stimulating Story, J. Musc. Res. Cell. Motil., 1999, vol. 20, pp. 223–237.
Lamb, G., Cellini, M., and Stephenson, D., Different Ca2+ Releasing Action of Caffeine and Depolarization in Skeletal Muscle Fibers of the Rat, J. Physiol. (London), 2001, vol. 531, pp. 715–728.
Fryer, M. and Neering, J., Actions of Caffeine on Fast and Slow Twitch Muscles of Rat, J. Physiol. (London), 1989, vol. 416, pp. 435–454.
Macintosh, B. and Gardner, F., Posttetanic Potentiation and Skeletal Muscle Fatigue: Interaction with Caffeine, Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 1987, vol. 65, pp. 260–268.
Rassier, D., Tubman, A., and Macintosh, B., Caffeine and Length Dependence of Staircase Potentiation in Skeletal Muscle, Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 1998, vol. 76, pp. 975–982.
Sellin, L. and Thesleff, S., Alteration in Membrane Electrical Properties during Long-Term Denervation of Rat Skeletal Muscle, Acta Physiol. Scand., 1980, vol. 108, pp. 243–246.
Syrovy, J., Guttman, E., and Melichna, J., Differential Responses of Myosin ATPase Activity and Contraction Properties of Fast and Slow Rabbit Muscle, Experientia, 1971, vol. 27, pp. 1426–1427.
Jaweed, M., Herbison, G., and Ditunno, J., Denervation and Reinnervation of Fast and Slow Muscle. A Histochemical Studying Rats, J. Histoch. Cytochem., 1975, vol. 23, pp. 808–827.
Stephenson, D., Lamb, G., and Stephenson, G., Events of the Excitation-Contraction-Relaxation (E-C-R) Cycle in Fast and Slow Twitch Mammalian Muscle Fibers Related to Muscle Fiber Fatigue, Acta Physiol. Scand., 1998, vol. 162, pp. 229–245.
Beard, N., Sakowska, M., Dulhunty, A., and Laver, D., Calsequestrin Is an Inhibitor of Skeletal Muscle Ryanodine Receptor Calcium Release Channels, Biophys. J., 2002, vol. 82, pp. 310–320.
Beard, N., Lever, D., and Dulhunty, A., Calsequestrin and Calcium Release Channel of Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle, Progr. Biophys. Molec. Biol., 2004, vol. 85, pp. 33–69.
Krutetskaya, Z. and Lebedev, O., Mechanisms of Ca2+ Signalization in Cells, Tsitologiya, 2001, vol. 43, pp. 5–32.
Timerman, A., Ogunbumni, E., Freund, E., Wiederrecht, G., Marks, A., and Fleischer, S., The Calcium Release Channel of Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Is Modulated by FK-506-Binding Protein: Dissociation and Reconstitution of FICBP-12 to the Calcium Release Channel of Skeletal Muscle Sarcoplasmic Reticulum, J. Biol. Chem., 1993, vol. 268, pp. 22 992–22 999.
Athern, G., Junankar, P., and Dulhunty, A., Single Channel Activity of the Ryanodine Receptor Calcium Release is Modulated by FK-506, FEBS Lett., 1994, vol. 352, pp. 369–374.
Pereon, Y., Sorrentino, V., Dettban, C., Noireaud, J., and Palade, P., Dihydropyridine Receptor and Ryanodine Gene Expression in Long-Term Denervation Rat Muscles, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm., 1997, vol. 240, pp. 612–617.
Radzyukevich, T. and Heiny, J., Regulation of Dihydropyridine Receptor Gene Expression in Mouse Skeletal Muscles by Stretch and Disuse, Am. J. Physiol. (Cell Physiol.), 2004, vol. 287, pp. C1445–C1452.
Mickelson, J. and Louis, C., Malignant Hyperthermia: Excitation-Contraction Coupling Ca2+ Release Channel and Cell Ca2+ Regulation Defects, Physiol. Rev., 1996, vol. 76, pp. 537–592.
Palnitcar, S., Mickelson, J., Louis, C., and Parness, J., Pharmacological Distinction between Dantrolen and Ryanodine Binding Sites: Evidence from Normal and Malignant Hyperthermia-Susceptible Porcine Skeletal Muscle, Biochem. J., 1997, vol. 326, pp. 847–852.
Lamb, G. and Cellini, M., High Intracellular Ca2+ Alter Sarcoplasmic Skinned Skeletal Muscle Fibers of the Rat, J. Physiol. (London), 1999, vol. 519, pp. 815–827.
Franzini-Armstrong, C. and Protasi, F., Ryanodine Receptors of Striated Muscle: a Complex Channel Capable of Multiple Interactions, Physiol. Rev., 1997, vol. 77, pp. 699–727.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © R. S. Arutyunyan, S. V. Kuznetsov, 2010, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2010, Vol. 46, No. 1, pp. 66–73.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arutyunyan, R.S., Kuznetsov, S.V. Effect of neurogenic inactivity on posttetanic responses of rat fast muscle. J Evol Biochem Phys 46, 77–86 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093010010093
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093010010093