Abstract
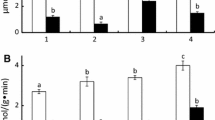
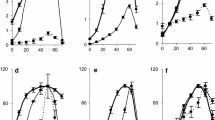
Differences in the degree of separate and combined effects of temperature, pH, and heavy metals (zinc, copper) on the trypsin-and chymotrypsin-like proteinase activities have been established in the whole body of some invertebrate animals—potential objects of fish nutrition: pond snail Lymnaeae stagnalis, orb snail Planorbarius purpura, zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha, oligochaetes Tubifex sp. and Lumbriculus sp. in total, chironomid larvae Chironimus sp. and Ch. riparus, as well as crustacean zooplankton. It has been shown that enzymes of the potential prey at low temperature can compensate the low activity of intestinal proteinases of fish bentho- and planktophages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jancarik, A., Die Verdaung der Hauptnahrstoffe vdeim Karpfen, Z. Fish., 1964, vol. 12, no. 8–10.
Dabrowski, K. and Glogowski, J., The Role of Exogenic Proteolytic Enzymes in Digestion Processes in Fish, Hydrobiologia (Hagua), 1977, vol. 54, pp. 129–134.
Lauff, M. and Hofer, R., Proteolytic Enzymes in Fish Development and the Importance of Dietary Enzymes, Aquacult., 1984, vol. 37, pp. 335–346.
Oozeki, Y. and Bailey, K.M., Ontogenetic Development of Digestive Enzyme Activities in Larval Walleye Pollok, Theragra chalcogramma, Mar. Biol., vol. 122, pp. 177–186.
Dabrowski, K., The Role of Proteolytic Enzymes in Fish Digestion. Cultivation of Fish Fry and Its Live Food, Eur. Maricult., Soc. Bradine. Belgium. Special Publ., 1979, vol. 5, pp. 107–126.
Kurokawa, T., Shiraishi, M., and Suzuki, T., Quantification of Exogenous Protease Derived from Zooplankton in the Intestine of Japanese Sardine (Sardinops melanotictus) Larvae, Aquacult., 1998, vol. 161, pp. 491–499.
Ugolev, A. M., Evolyutsiya pishchevareniya i printsipy evolyutsii funktsii (Evolution of Digestion and the Principles of Evolution of Functions), Leningrad, 1985.
Ugolev, A.M. and Tsvetkova, V.A., Induced Autolysis as an Important Mechanism of the Initial Stages of Ordinary Digestion, Sechenov Fiziol. Zh., 1984, vol. 70, pp. 1542–1550.
Kuz’mina, V.V., Contribution of Induced Autolysis to the Processes of Digestion in Secondary Consumers Exemplified by Hydrobionts, Dokl. RAS, 2000, vol. 339, no. 1, pp. 172–174.
Kuz’mina, V.V. and Golovanova, I.L., Contribution of Prey Proteinases and Carbohydrates in Fish Digestion, Aquacult., 2004, vol. 234, pp. 347–360.
Kuz’mina, V.V., Fiziologo-biokhimicheskie osnovy ekzotrofii ryb (Physiological-Biochemical Grounds of Fish Exotrophy), Moscow, 2005.
Fange, R. and Grove, D., Digestion. Fish Physiology, Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., and Brett, J.R., Eds., New York; San Francisco; London: Acad., 1979, vol. 8, pp. 162–260.
Ugolev, A.M. and Kuz’mina, V.V., Pishchevaritel’nye protsessy i adaptatsii u ryb (Digestive Processes and Adaptations in Fish), St. Petersburg, 1993.
Nemova, N.N., Vnutrikletochnye proteoliticheskie fermenty u ryb (Intracellular Proteolytic Enzymes in Fish), Petrosavodsk, 1996.
Kuz’mina, V.V., Effect of Temperature on the Digestive Hydrolyses in Invertebrate Animals, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 1999, vol. 35, pp. 15–19.
Ocampo, L. and Ezquerra, J.M., Digestive Protease Activity in Juvenile Farfantepenaeus californensis as a Function of Dissolved Oxygen and Temperature, Aquacult. Res., 2002, vol. 33, pp. 1073–1080.
Moiseenko, T.I., Evaluation of Danger under Conditions of the Water Pollution with Metals, Vodn. Res., 1999, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 186–197.
Anson, M., The Estimation of Pepsin, Trypsin, Papain and Cathepsin with Hemoglobin, J. Gen. Physiol., 1938, vol. 22, pp. 79–83.
Nikol’skii, V.N., Ekologiya ryb (Fish Ecology), Moscow, 1974.
Brito, R., Rosas, C., Chimal, M.E., and Gaxiola, G., Effect of Different Diets on Growth and Digestive Enzyme Activity in Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) Early Post-Larvae, Aquacult. Res., 2001, vol. 32, pp. 257–266.
Nemova, N.N., Cathepsins of Animal Tissues, Ekologicheskaya biokhimiya zhivotnykh (Ecological Animal Biochemistry), Petrozavodsk, 1978, pp. 76–88.
Pokrovskii, A.A. and Tutul’yan, V.A., Lizosomy (Lysosomes), Moscow, 1976.
Panin, L.E. and Mayanskaya, N.N., Lizosomy: rol’ v adaptatsii i vosstanovlenii (Lysosomes: Role in Adaptation and Recovery), Novosibirsk, 1987.
Lemos, D., Ezquerra, J.M., and Garcia-Carreno, R., Protein Digestion in Penaeid Shrimp: Digestive Proteinases, Proteinase Inhibitors and Feed Digestibility, Aquacult., 2000, vol. 186, pp. 89–105.
Antonov, V.K., Khimiya proteoliza (Chemistry of Proteolysis), Moscow, 1983.
Lubyanskene, V., Virbitskas, Yu., and Yankyavikyus, K., Obligatnyi simbioz mikroflory pishchevaritel’nogo trakta i organizma (Obligatory Symbiosis of Microflora in the Digestiva Tract and Organism), Vilnyus, 1989.
Shivokene, Ya.S., Simbiontnoe pischchevarenie u gidrobiontov i nasekomykh (Symbiotic Digestion in Hydrobionts and Insects), Vilnyus, 1989.
Sobolev, K.D., Accumulation of Heavy Metals and Content of Vitamins in the Natural Food of Fish from the Pes’vo Lake and the Volkhov River, Aktual’nye problemy vyrashchivaniya i kormleniya ryb na rasnykh etapakh zhiznennogo tsikla (Actual Problems of Nurture and Feeding of Fish at Different Stages of the Life Cycle), St. Petersburg, 2003, pp. 356–361.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.V. Kuz’mina, N.V. Ushakova, 2007, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2007, Vol. 43, No. 5, pp. 404–409.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuz’mina, V.V., Ushakova, N.V. Activities of proteinases in invertebrate animals—Potential objects of fish nutrition. Effects of temperature, pH, and heavy metals. J Evol Biochem Phys 43, 483–489 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093007050040
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093007050040