Abstract
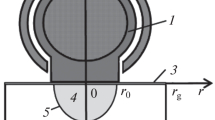
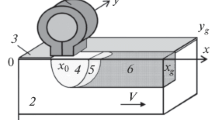
Crystallization processes in the case of modification of the surface layer of an iron-based alloy (Fe–C) subjected to a pulse action of a high-frequency electromagnetic field for substrate heating and melting are numerically simulated. The processes of heating, melting, and subsequent solidification of the metal are studied with the use of a mathematical model that describes thermodynamic phenomena. It is postulated that refractory nano-sized particles uniformly distributed over the melt volume favor rapid crystallization during melt undercooling owing to heterogeneous nucleation. It is found that the nucleation and crystallization conditions in different areas of the melt volume are essentially different, and the maximum number of crystallization centers arise in regions where heat removal proceeds with the greatest rate. The particle size distribution in the crystalline structure in the solidified metal volume is estimated.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. M. Poate, G. Foti, and D. C. Jacobson, Surface Modification and Alloying by Laser, Ion, and Electron Beams (Plenum Press, New York, 1983).
A. N. Cherepanov, V. O. Drozdov, A. G. Malikov, et al., “Effect of Nanostructured Powder Composition on the Characteristics of the Surface Layer of Steel in Laser Treatment," Tyazh. Mashinostr., No. 6, 2–4 (2016).
N. H. Fletcher, “Size Effect in Heterogeneous Nucleation," J. Chem. Phys. 29 (3), 572–576 (1958).
A. L. Greer, “Overview: Application of Heterogeneous Nucleation in Grain-Refining of Metals," J. Chem. Phys. 145, 211704 (2016).
A. N. Cherepanov and V. T. Ovcharenko, “Effect of Nanostructured Composite Powders on the Structure and Strength Properties of the High Temperature Inconel 718 Alloy," Phys. Metals Metallography 116 (12), 1279–1284 (2015).
V. P. Saburov, A. N. Cherepanov, M. F. Zhukov, and G. V. Galevskii, Plasmochemical Synthesis of Fine-Grain Powders and their Application for Modified Metals and Alloys (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1995) [in Russian].
M. C. Flemings, Solidification Processing (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1974).
Y. Z. Chen, F. Liu, G. C. Yang, and Y. H. Zhou, “Nucleation Mechanisms Involving in Rapid Solidification of Undercooled Ni80.3B19.7 Melts," Intermetallics 19, 221–224 (2011). DOI: 10.1016/j.intermet.2010.08.010.
V. N. Popov, A. N. Cherepanov, and V. G. Shchukin, “Modeling of Modification of the Surface Layer of a Metal with Nanoparticles under Pulsed Induction Heating," Vestn. Mosk. Gos. Tekhn. Univ. im. N. E. Bauman, Ser. Estestv. Nauki, No. 2, 82–96 (2018).
D. Turnbull, “Formation of Crystal Nuclei in Liquid Metals," J. Appl. Phys. 21, 1022–1028 (1950).
V. N. Popov, A. N. Cherepanov, and V. G. Shchukin, “Numerical Simulation of Solidification of an Iron-Based Binary Alloy Modified with Nanoscale Particles," Teplofiz. Aeromekh. 27 (3), 475–482 (2020) [Thermophys. Aeromech. 27 (3), 449–456 (2020)].
V. N. Popov and A. N. Cherepanov, “Modeling of the Alloy Solidification Modified by Refractory Nano-Size Particles," Europ. Phys. J. Spec. Topics 229 (2/3), 467–474 (2020).
F. Li, J. Ning, T. Wang, and S. Y. Liang, “Analytical Modeling and Sensitivity Analysis of the Temperature Distribution in the Planar Scanning Induction Heating Based on 2D Moving Heat Source," J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 33 (10), 5093–5102 (2019). DOI: 10.1007/s12206-019-0948-z.
V. Rudnev, D. Loveless, R. Cook, and M. Black, Handbook of Induction Heating (Marcell Dekker, Inc., New York, 2003).
A. N. Kolmogorov, “On the Statistical Theory of Metal Crystallization," Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Mat. 1 (3), 355–359 (1937).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Prikladnaya Mekhanika i Tekhnicheskaya Fizika, 2021, Vol. 63, No. 4, pp. 27-38. https://doi.org/10.15372/PMTF20220403.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shchukin, V.G., Popov, V.N. & Shmagunov, O.A. MODELING OF CRYSTALLIZATION IN A METAL SURFACE LAYER MODIFIED WITH NANOPARTICLES UNDER PULSED INDUCTION HEATING. J Appl Mech Tech Phy 63, 574–583 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021894422040034
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021894422040034