Abstract
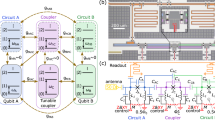
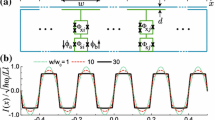
The spectral and temporal characteristics of a fluxonium qubit coupled to a coplanar resonator on a chip have been experimentally studied. The system has been implemented as a planar integral electric circuit, where the fluxonium qubit itself consists of a tunnel Josephson junction with a small area shunted by a high inductance of a series of Josephson junctions with larger areas. To analyze the experimental data, an extended model of the fluxonium qubit capacitively coupled to the resonator has been proposed, and the structure of the energy levels has been obtained by full diagonalization of the Hamiltonian of the system. Numerical predictions of the model allow interpreting the results of two-tone spectroscopy obtained at various external magnetic fluxes in a wide frequency range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. D. Vincenzo, Quantum Information Processing (Forschungszentrum, Julich, 2013), p. A4.
Y. Wang, Y. Li, Z. Yin, and B. Zeng, Quantum Inform. 4, 1 (2018).
W. D. Oliver and P. B. Welander, MRS Bull. 38, 816 (2013).
Z. L. Xiang, S. Ashhab, J.Q. You, and F. Nori, Rev. Mod. Phys. 85, 623 (2013).
A. M. Zagoskin, Quantum Engineering: Theory and Design of Quantum Coherent Structures (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 2011).
C. Muller, J.H. Cole, and J. Lisenfeld, Rep. Prog. Phys. (2019, in press).
A. Dunsworth, A. Megrant, C. Quintana, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 111, 022601 (2017).
C. M. Quintana, A. Megrant, Z. Chen, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 062601 (2014).
I. A. Rodionov, A.S. Baburin, A.R. Gabidullin, S.S. Maklakov, S. Peters, I.A. Ryzhikov, and A.V. Andriyash, Sci. Rep. 9, 12232 (2019).
https://www.ibm.com/blogs/research/2017/11/thefuture-is-quantum/.
R. Barends, A. Shabani, L. Lamata, et al., Nature (London, U.K.) 534, 222 (2016).
A. Nersisyan, S. Poletto, N. Alidoust, R. Manenti, R. Renzas, C.-V. Bui, K. Vu, T. Whyland, Y. Mohan, E.A. Sete, S. Stanwyck, A. Bestwick, and M. Reagor, arXiv:1901.08042 (2019).
V. E. Manucharyan, PhD Thesis (Yale Univ., New Haven, 2012).
N. A. Masluk, PhD Thesis (Yale Univ., New Haven, 2012).
V. E. Manucharyan, J. Koch, L.I. Glazman, and M.H. Devoret, Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 326, 113 (2009).
T. M. Hazard, A. Gyenis, A.D. Paolo, A.T. Asfaw, S.A. Lyon, A. Blais, and A.A. Houck, Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 010504 (2019).
N. Maleeva, L. Grunhaupt, T. Klein, F. Levy-Bertrand, O. Dupre, M. Calvo, F. Valenti, P. Winkel, F. Friedrich, W. Wernsdorfer, A.V. Ustinov, H. Rotzinger, A. Monfardini, M.V. Fistul, and I.M. Pop, Nat. Commun. 9, 3889 (2018).
V. E. Manucharyan, N.A. Masluk, A. Kamal, J. Koch, L.I. Glazman, and M.H. Devoret, Phys. Rev. B 85, 024521 (2012).
I.M. Pop, K. Geerlings, G. Catelani, R.J. Schoelkopf, L.I. Glazman, and M.H. Devoret, Nature (London, U.K.) 508, 369 (2014).
U. Vool and M. Devoret, Int. J. Circ. Theor. Appl. 45, 897 (2017).
Acknowledgments
The samples were fabricated at the Nanofabrication Facility Functional Micro/Nanosystems (ID 74300), Bauman Moscow State Technical University
Funding
The development of a theoretical model to describe the fluxonium qubit coupled to the coplanar resonator, as well as the development of layer-by-layer geometry and fabrication of experimental fluxonium samples, was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 19-42-04137). Experimental studies of the spectral and temporal characteristics of fluxonium qubits were supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (project no. K2A-2018-048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary materials are available for this article at https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364019200074 and are accessible for authorized users.
Russian Text © The Author(s), 2019, published in Pis’ma v Zhurnal Eksperimental’noi i Teoreticheskoi Fiziki, 2019, Vol. 110, No. 8, pp. 569–574.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moskalenko, I.N., Besedin, I.S., Tsitsilin, I.A. et al. Planar Architecture for Studying a Fluxonium Qubit. Jetp Lett. 110, 574–579 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364019200074
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364019200074