Abstract
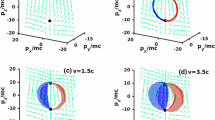
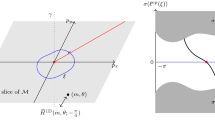
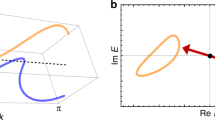
The type-II Weyl and type-II Dirac points emerge in semimetals and in relativistic systems. In particular, the type-II Weyl fermions may emerge behind the event horizon of black holes. The type-II Weyl and Dirac points also emerge as the intermediate states of the topological Lifshitz transitions. In one case, the type-II Weyl point connects the Fermi pockets, and the Lifshitz transition corresponds to the transfer of the Berry flux between the Fermi pockets. In the other case, the type-II Weyl point connects the outer and inner Fermi surfaces. At the Lifshitz transition, the Weyl point is released from both Fermi surfaces. They loose their Berry flux, which guarantees the global stability, and without the topological support, the inner surface disappears after shrinking to a point at the second Lifshitz transition. These examples reveal the complexity and universality of topological Lifshitz transitions, which originate from the ubiquitous interplay of a variety of topological characters of the momentum-space manifolds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Weyl, I. Z. Phys. 56, 330 (1929).
H. B. Nielsen and M. Ninomiya, Nucl. Phys. B 185, 20 (1981), Nucl. Phys. B 193,173 (1981).
G. E. Volovik, The Universe in a Helium Droplet (Clarendon, Oxford, 2003).
J. von Neumann and E. Wigner, Phys. Z. 30, 467 (1929).
S. P. Novikov, Sov. Math. Dokl. 23, 298 (1981).
C. D. Froggatt and H. B. Nielsen, Origin of Symmetry (World Scientific, Singapore, 1991).
P. Horava, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 016405 (2005).
B. Simon, Phys. Rev. Lett. 51, 2167 (1983).
G. E. Volovik, JETP Lett. 46, 98 (1987).
T. D. C. Bevan, A. J. Manninen, J. B. Cook, J. R. Hook, H. E. Hall, T. Vachaspati, and G. E. Volovik, Nature 386, 689 (1997).
M. Krusius, T. Vachaspati, and G. E. Volovik, condmat/9802005.
G. E. Volovik, Physica B 255, 86 (1998); condmat/9802091.
C. Herring, Phys. Rev. 52, 365373 (1937).
A. A. Abrikosov and S. D. Beneslavskii, JETP 32, 699 (1971).
A. A. Abrikosov, J. Low Temp. Phys. 5, 141 (1972).
H. B. Nielsen and M. Ninomiya, Phys. Lett. B 130, 389 (1983).
A. A. Burkov and L. Balents, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 127205 (2011).
A. A. Burkov, M. D. Hook, and L. Balents, Phys. Rev. B 84, 235126 (2011).
H. Weng, Ch. Fang, Zh. Fang, B. A. Bernevig, and X. Dai, Phys. Rev. X 5, 011029 (2015).
Sh.-M. Huang, S.-Y. Xu, I. Belopolski, Ch.-Ch. Lee, G. Chang, B. K. Wang, N. Alidoust, G. Bian, M. Neupane, Ch. Zhang, Sh. Jia, A. Bansil, H. Lin, and M. Z. Hasan, Nat. Commun. 6, 7373 (2015).
B. Q. Lv, H. M. Weng, B. B. Fu, X. P. Wang, H. Miao, J. Ma, P. Richard, X. C. Huang, L. X. Zhao, G. F. Chen, Z. Fang, X. Dai, T. Qian, and H. Ding, Phys. Rev. X 5, 031013 (2015).
S.-Y. Xu, I. Belopolski, N. Alidoust, et al., Science 349, 613 (2015).
L. Lu, Zh. Wang, D. Ye, L. Ran, L. Fu, J. D. Joannopoulos, and M. Soljacic, Science 349, 622 (2015).
M. Z. Hasan, S.-Y. Xu, I. Belopolski, and Sh.-M. Huang, arXiv:1702.07310.
G. E. Volovik and V. A. Konyshev, JETP Lett. 47, 250 (1988).
V. Pardo and W. E. Pickett, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 166803 (2009).
S. Banerjee and W. E. Pickett, Phys. Rev. B 86, 075124 (2012).
A. A. Soluyanov, D. Gresch, Zh. Wang, Q. Sh. Wu, M. Troyer, X. Dai, and B. A. Bernevig, Nature 527, 495 (2015).
Y. Xu, F. Zhang, and Ch. Zhang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 265304 (2015).
T.-R. Chang, S.-Y. Xu, G. Chang, et al., Nat. Commun. 7, 10639 (2016).
G. Autes, D. Gresch, A. A. Soluyanov, M. Troyer, and O. V. Yazyev, arXiv:1603.04624.
S.-Y. Xu, N. Alidoust, G. Chang, et al., arXiv:1603.07318.
J. Jiang, Z. K. Liu, Y. Sun, et al., arXiv:1604.00139.
T. E. O’Brien, M. Diez, and C. W. J. Beenakker, arXiv:1604.01028.
I. M. Lifshitz, Sov. Phys. JETP 11, 1130 (1960).
G. E. Volovik, J. Low Temp. Phys. 43, 47 (2017); arXiv:1606.08318; arXiv:1701.06435.
P. Huhtala and G. E. Volovik, J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 94, 853 (2002); gr-qc/0111055.
G. E. Volovik and M. A. Zubkov, Nucl. Phys. B 881, 514 (2014).
F. R. Klinkhamer and G. E. Volovik, Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 20, 2795 (2005); hep-th/0403037.
G. E. Volovik, Lect. Notes Phys. 718, 31 (2007).
D. Gosalbez-Martinez, I. Souza, and D. Vanderbilt, Phys. Rev. B 92, 085138 (2015); arXiv:1505.07727.
J. W. McClure, Phys. Rev. 108, 612 (1957).
G. P. Mikitik and Yu. V. Sharlai, Phys. Rev. B 73, 235112 (2006).
G. P. Mikitik and Yu. V. Sharlai, Low Temp. Phys. 34, 794 (2008).
T. T. Heikkilä and G. E. Volovik, New J. Phys. 17, 093019 (2015).
J. Nissinen and G. E. Volovik, arXiv:1702.04624.
K. Zhang and G. E. Volovik, arXiv:1604.00849, JETP Lett. 105 (2017, in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Volovik, G.E. Lifshitz transitions via the type-II dirac and type-II Weyl points. Jetp Lett. 105, 519–525 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364017080094
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364017080094