Abstract—
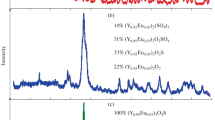
We have perfected processes for the synthesis of lanthanum, gadolinium, and yttrium oxyselenides by heating oxides in flowing hydrogen and selenium vapor. The optimal selenidation temperature is 700°C for lanthanum, 850°C for gadolinium, and 900°C for yttrium. Subsequent annealing of the materials in flowing hydrogen at 1000°C makes it possible to remove trace levels of amorphous selenium and impurity phases containing diselenide groups.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ropp, R.C., The chemistry of artificial lighting devices: lamps, phosphors and cathode ray tubes, in Studies in Inorganic Chemistry, New York: Elsevier, 1993.
Shionoya, S., Yen, W.M., and Yamamoto, H., Phosphor Handbook, Laser and Optical Science and Technology, vol. 21, Weber, M.J., Ed., Boca Raton: CRC, 2006.
Bugby, S.L., Jambi, L.K., and Lees, J.E., A comparison of CsI:Tl and GOS in a scintillator–CCD detector for nuclear medicine imaging, J. Instrum., 2016, vol. 11, p. P09009. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-0221/11/09/p09009
Hussey, D.S., LaManna, J.M., Baltic, E., and Jacobson, D.L., Neutron imaging detector with 2 μm spatial resolution based on event reconstruction of neutron capture in gadolinium oxysulfide scintillators, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A, 2017, vol. 866, pp. 9–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2017.05.035
Jiang, X.F., Xiu, Q.L., Zhou, J.R., Yang, J.Q., Tan, J.H., Yang, W.Q., Zhang, L.J., Xia, Y.G., Zhou, X.J., Zhou, J.J., Zhu, L., Teng, H.Y., Yang, G.A., Song, Y.S., Sun, Z.J., and Chen, Y.B., Study on the neutron imaging detector with high spatial resolution at China Spallation Neutron Source, Nucl. Eng. Technol., 2021, vol. 53, no. 6, pp. 1942–1946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2020.12.009
Kertzscher, G. and Beddar, S., Inorganic scintillation detectors based on Eu-activated phosphors for Ir-192 brachytherapy, Phys. Med. Biol., 2017, vol. 62, no. 12, pp. 5046–5075. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/aa716e
Tisseur, D., Eck, D., Estre, N., Kistler, M., Payan, E., and Tamagno, L., Detector upgrade for fast MeV X-ray imaging for severe accidents experiments, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2020, vol. 67, no. 7, pp. 1715–1721. https://doi.org/10.1109/tns.2020.2995969
Yoneyama, A., Baba, R., and Kawamoto, M., Quantitative analysis of the physical properties of CsI, GAGG, LuAG, CWO, YAG, BGO, and GOS scintillators using 10-, 20- and 34-keV monochromated synchrotron radiation, Opt. Mater. Express, 2021, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 398–411. https://doi.org/10.1364/ome.409161
Santelli, J., Lechevallier, S., Baaziz, H., Vincent, M., Martinez, C., Mauricot, R., Parini, A., Verelst, M., and Cussac, D., Multimodal gadolinium oxysulfide nanoparticles: a versatile contrast agent for mesenchymal stem cell labeling, Nanoscale, 2018, vol. 10, no. 35, pp. 16775–16786. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr03263g
Jiao, J.X., Liu, Y.W., Wang, H., Yin, X.M., Xing, M.M., Luo, X.X., and Tian, Y., Enhancing upconversion luminescence and thermal sensing properties of Er/Yb co-doped oxysulfide core–shell nanocrystals, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2021, vol. 104, no. 2, pp. 985–994. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.17509
Larquet, C., Klein, Y., Hrabovsky, D., Gauzzi, A., Sanchez, C., and Carenco, S., Tunable magnetic properties of (Gd,Ce)2O2S oxysulfide nanoparticles, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2019, no. 6, pp. 762–765. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.201801466
Huang, J., Tang, Z.Y., Guo, M., Wang, Y., Wang, Z.L., Wu, Z., and Zhang, P.B., Incorporation of gadolinium oxide and gadolinium oxysulfide microspheres: MRI/CT monitoring and promotion of osteogenic/chondrogenic differentiation for bone implants, Chemnanomat, 2020, vol. 6, no. 12, pp. 1819–1832. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.202000476
Belaya, S.V., Bakovets, V.V., Rakhmanova, M.I., Maksimovskii, E.A., Yushina, I.V., Shayapov, V.R., and Korolkov, I.V., Films of (Gd1–xTbx)2O2S solid solutions produced by oxide sulfidation in NH4SCN vapor and their optical properties, Inorg. Mater., 2020, vol. 56, no. 8, pp. 836–846. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168520080038
Knoll, G.F., Radiation Detection and Measurement, New York: Wiley, 2010, 4th ed.
Tarasenko, M.S., Ryadun, A.A., Orazov, Zh.K., Pomelova, T.A., Zalesskii, V.B., Malyutina-Bronskaya, V.V., Fedorov, V.E., Wang, H.-Ch., and Naumov, N.G., The concentration quenching of photoluminescence and the quantum yield in (Y1–xPrx)2O2Se solid solutions, Inorg. Mater., 2021, vol. 57, no. 8, pp. 830–834. https://doi.org/10.1134/S002016852108015x
Tarasenko, M.S., Kiryakov, A.S., Ryadun, A., Kuratieva, N.V., Plyusnin, P.E., and Naumov, N.G., Y2O2Se as a potential matrix for optical materials: a novel preparation method and optical properties, Mater. Today Commun., 2019, vol. 21, p. 100665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2019.100665
Tarasenko, M.S., Kiryakov, A.S., Ryadun, A.A., Kuratieva, N.V., Malyutina-Bronskaya, V.V., Fedorov, V.E., Wang, H.-C., and Naumov, N.G., Facile synthesis, structure, and properties of Gd2O2Se, J. Solid State Chem., 2022, vol. 312, p. 123224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2022.123224
Suponitskii, Yu.L., Kuz’micheva, G.M., and Eliseev, A.A., Rare-earth oxysulfides, Usp. Khim., 1988, vol. 57, no. 3, pp. 367–384. https://doi.org/10.1070/RC1988v057n03ABEH003345
Larquet, C. and Carenco, S., Metal oxysulfides: from bulk compounds to nanomaterials, Front. Chem., 2020, vol. 8, p. 179. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00179
Eick, H.A., The crystal structure and lattice parameters of some rare earth mono-seleno oxides, Acta Crystallogr., 1960, vol. 13, no. 2, p. 161. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0365110X60000339
Guittard, M., Flahaut, J., and Domange, L., The complete series of oxyselenides of the rare-earths and Y, Acta Crystallogr., 1966, vol. 21, no. 5, p. 832. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0365110X66003967
Dernier, P.D., Bucher, E., and Longinotti, L.D., Temperature induced symmetry transformation in the Th3P4 type compounds La3S4, La3Se4, Pr3S4 and Pr3Se4, J. Solid State Chem., 1975, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 203–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4596(75)90247-9
Dugue, J., Adolphe, C., and Khodadad, P., Structure cristalline de l’oxyséléniure de lanthane La4O4Se3, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem., 1970, no. 26, pp. 1627–1628. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567740870004582
Strobel, S., Choudhury, A., Dorhout, P.K., Lipp, C., and Schleid, T., Rare-earth metal(III) oxide selenides M4O4Se[Se2] (M = La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm) with discrete diselenide units: crystal structures, magnetic frustration, and other properties, Inorg. Chem., 2008, vol. 47, no. 11, pp. 4936–4944. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic800233c
Mehta, S.K., Chaudhary, S., Kumar, S., Bhasin, K.K., Torigoe, K., Sakai, H., and Abe, M., Surfactant assisted synthesis and spectroscopic characterization of selenium nanoparticles in ambient conditions, Nanotechnology, 2008, vol. 19, no. 29, p. 295601. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/29/295601
Van Overschelde, O., Guisbiers, G., and Snyders, R., Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles by excimer pulsed laser ablation in water, APL Mater., 2013, vol. 1, no. 4, p. 042114. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4824148
Kubelka, P., New contributions to the optics of intensely light-scattering materials: Part I, J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1948, vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 448–457. https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSA.38.000448
Yannopoulos, S.N. and Andrikopoulos, K.S., Raman scattering study on structural and dynamical features of noncrystalline selenium, J. Chem. Phys., 2004, vol. 121, no. 10, pp. 4747–4758. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1780151
Patterson, A.L., The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination, Phys. Rev., 1939, vol. 56, pp. 978–982. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.56.978
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, grant no. 20-53-00036 Bel_a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pomelova, T.A., Tarasenko, M.S., Yushina, I.V. et al. Optimization of R2O2Se (R = La, Gd, Y) Synthesis for the Preparation of Optical Materials. Inorg Mater 59, 12–20 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168523010168
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168523010168