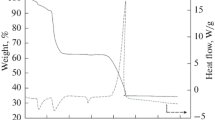
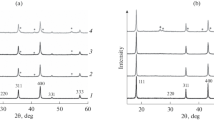
Abstract—
Carbon-coated composites based on LiFePO4 with the olivine structure have been prepared by the Pechini method. The materials have been characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, and Raman spectroscopy. Optimizing the LiFePO4 precursor heat treatment conditions, we have obtained LiFePO4 with the olivine structure and a primary particle size of ~30 nm. On the addition of 0.2 wt % silver to the composite, a cathode material with improved electrochemical performance has been obtained. The discharge capacity of the resultant material at cycling current densities of 20 (C/8), 1600 (10C), and 3200 mA/g (20 C) is 166, 85, and 53 mAh/g, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Padhi, A.K., Nanjundaswamy, K.S., and Goodenough, J.B., Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1997, vol. 144, no. 4, pp. 1188–1194. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1837571
Amin, R., Maier, J., Balaya, P., Chen, D.P., and Lin, C.T., Ionic and electronic transport in single crystalline LiFePO4 grown by optical floating zone technique, Solid State Ionics, 2008, vol. 179, nos. 27–32, pp. 1683–1687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2008.01.079
Zhang, S.M., Zhang, J.X., Xu, S.J., Yuan, X.J., and He, B.C., Li ion diffusivity and electrochemical properties of FePO4 nanoparticles acted directly as cathode materials in lithium ion rechargeable batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, vol. 88, pp. 287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.10.029
Xu, X.L., Zhao, X.X., Hui, K.S., Dinh, D.A., and Hui, K.N., Rechargeable batteries: regulating electronic and ionic transports for high electrochemical performance, Adv. Mater. Technol., 2021. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202101107
Eftekhari, A., LiFePO4/C nanocomposites for lithium-ion batteries, J. Power Sources, 2017, vol. 343, pp. 395–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.01.080
Zaghib, K., Guerfi, A., Hovington, P., Vijh, A., Trudeau, M., Mauger, A., Goodenough, J.B., and Julien, C.M., Review and analysis of nanostructured olivine-based lithium rechargeable batteries: status and trends, J. Power Sources, 2013, vol. 232, pp. 357–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.12.095
Novikova, S.A. and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Cathode materials based on olivine lithium iron phosphates for lithium-ion batteries, Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci., 2017, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 129–139.
Tian, X.N., Chen, W.H., Jiang, Z.Q., and Jiang, Z.J., Porous carbon-coated LiFePO4 nanocrystals prepared by in situ plasma-assisted pyrolysis as superior cathode materials for lithium ion batteries, Ionics, 2020, vol. 26, no. 6, pp. 2715–2726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-03422-6
El-Shinawi, H., Cussen, E.J., and Corr, S.A., Morphology-directed synthesis of LiFePO4 and LiCoPO4 from nanostructured Li1 + 2xPO3 + x , Inorg. Chem., 2019, vol. 58, no. 10, pp. 6946–6949. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b00517
Stenina, I.A. and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Nanomaterials for lithium-ion batteries and hydrogen energy, Pure Appl. Chem., 2017, vol. 89, no. 8, pp. 1185–1194. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2016-1204
Chen, Z.Y., Zhang, Z., Zhao, Q.F., Duan, J.F., and Zhu, H.L., Understanding the impact of k-doping on the structure and performance of LiFePO4/C cathode materials, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2019, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 119–124. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2019.16449
Wang, H.Q., Lai, A.J., Huang, D.Q., Chu, Y.Q., Hu, S.J., Pan, Q.C., Liu, Z.H., Zheng, F.H., Huang, Y.G., and Li, Q.Y., Y–F co-doping behavior of LiFePO4/C nanocomposites for high-rate lithium-ion batteries, New J. Chem., 2021, vol. 45, no. 12, pp. 5695–5703. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nj06081j
Wang, L., Wei, R., Zhang, H., Zhang, K., Liang, F., Yao, Y., and Li, Y., B–Mg co-doping behavior of LiFePO4 cathode material: balance of oxygen vacancy and enhancement of electrochemical performance, Ionics, 2022, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 593–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04349-7
Novikova, S., Yaroslavtsev, S., Rusakov, V., Kulova, T., Skundin, A., and Yaroslavtsev, A., (LiFe1 – x \({\text{M}}_{x}^{{{\text{II}}}}\)PO4)/ C (MII = Co, Ni, Mg) as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, vol. 122, pp. 180–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.08.11810.1016/j.electacta.2013.08.118
Liu, W.M., Huang, Q.Z., and Hu, G.R., A novel preparation route for multi-doped LiFePO4/C from spent electroless nickel plating solution, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, vol. 632, pp. 185–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.01.110
Drozhzhin, O.A., Sumanov, V.D., Karakulina, O.M., Abakumov, A.M., Hadermann, J., Baranov, A.N., Stevenson, K.J., and Antipov, E.V., Switching between solid solution and two-phase regimes in the Li1 – xFe1 – y-MnyPO4 cathode materials during lithium (de)insertion: combined PITT, in situ XRPD and electron diffraction tomography study, Electrochim. Acta, 2016, vol. 191, pp. 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.01.018
Yaroslavtsev, S., Novikova, S., Rusakov, V., Vost-rov, N., Kulova, T., Skundin, A., and Yaroslavtsev, A., LiFe1 – xMgxPO4/C as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries, Solid State Ionics, 2018, vol. 317, pp. 149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2018.01.011
Huang, Y.H. and Goodenough, J.B., High-rate LiFePO4 lithium rechargeable battery promoted by electrochemically active polymers, Chem. Mater., 2008, vol. 20, no. 23, pp. 7237–7241. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm8012304
Li, H.Q. and Zhou, H.S., Enhancing the performances of Li-ion batteries by carbon-coating: present and future, Chem. Commun., 2012, vol. 48, no. 9, pp. 1201–1217. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cc14764a
Kucinskis, G., Bajars, G., and Kleperis, J., Graphene in lithium ion battery cathode materials: a review, J. Power Sources, 2013, vol. 240, pp. 66–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.03.160
Gryzlov, D., Novikova, S., Kulova, T., Skundin, A., and Yaroslavtsev, A., Behavior of LiFePO4/CPVDF/Ag-based cathode materials obtained using polyvinylidene fluoride as the carbon source, Mater. Des., 2016, vol. 104, pp. 95–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.05.040
Li, L., Wu, L., Wu, F., Song, S.P., Zhang, X.Q., Fu, C., Yuan, D.D., and Xiang, Y., Review—recent research progress in surface modification of LiFePO4 cathode materials, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2017, vol. 164, no. 9, pp. A2138–A2150. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.1571709jes
Kapaev, R.R., Novikova, S.A., Chekannikov, A.A., Gryzlov, D.Y., Kulova, T.L., Skundin, A.M., and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Effect of carbon sources and synthesis conditions on the LiFePO4/C cathode properties, Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci., 2018, vol. 57, no. 2, pp. 183–192. https://doi.org/10.1515/rams-2018-0063
Stenina, I.A., Minakova, P.V., Kulova, T.L., Desyatov, A.V., and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., LiFePO4/carbon nanomaterial composites for cathodes of high-power lithium ion batteries, Inorg. Mater., 2021, vol. 57, no. 6, pp. 620–628. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0020168521060108
Yaroslavtsev, A.B. and Stenina, I.A., Carbon coating of electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries, Surf. Innov., 2021, vol. 9, no. 2–3, pp. 92–110. https://doi.org/10.1680/jsuin.20.00044
Meng, F.B., Xiong, X.Y., Tan, L., Yuan, B., and Hu, R.Z., Strategies for improving electrochemical reaction kinetics of cathode materials for subzero-temperature Li-ion batteries: a review, Energy Stor. Mater., 2022, vol. 44, pp. 390–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.10.032
He, L.P., Zha, W.K., and Chen, D.C., Fabrication and electrochemical properties of 3D nano-network LiFePO4@multiwalled carbon nanotube composite using risedronic acid as the phosphorus source, Prog. Nat. Sci.–Mater. Int., 2019, vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 156–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2019.02.005
Khan, S., Raj, R.P., Mohan, T.V.R., and Selvam, P., Electrochemical performance of nano-sized LiFePO4-embedded 3D-cubic ordered mesoporous carbon and nitrogenous carbon composites, RSC Adv., 2020, vol. 10, no. 51, pp. 30406–30414. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra04754f
Mwizerwa, J.P., Liu, C., Xu, K., Zhao, N., Chen, Z., and Shen, J., In-situ solution phase synthesis of LiFePO4@VSe2 composite as highly active cathode for Li-ion batteries, J. Alloys Compd., 2022, vol. 901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.163639
Christmann, K., Introduction to Surface Physical Chemistry, New York: Steinkopff, 1991.
Peng, J.M., Chen, Z.Q., Li, Y., Hu, S.J., Pan, Q.C., Zheng, F.H., Wang, H.Q., and Li, Q.Y., Conducting network interface modulated rate performance in LiFePO4/C cathode materials, Rare Met., 2022, vol. 41, no. 3, pp. 951–959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01838-6
Wang, K.-X., Li, X.-H., and Chen, J.-S., Surface and interface engineering of electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries, Adv. Mater., 2015, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 527–545. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201402962
Stenina, I.A., Sobolev, A.N., Kuz’mina, A.A., Kulova, T.L., Skundin, A.M., Tabachkova, N.Yu., and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Electrochemical properties of Li4Ti5O12/C and Li4Ti5O12/C/Ag nanomaterials, Inorg. Mater., 2017, vol. 53, no. 10, pp. 1039–1045. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0020168517100144
Gao, Y., Xiong, K., Xu, H., and Zhu, B.F., Enhanced high-rate and low-temperature electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/polypyrrole cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2019, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 3408–3417. https://doi.org/10.20964/2019.04.01
Fedorkova, A., Orinakova, R., Orinak, A., Talian, I., Heile, A., Wiemhofer, H.D., Kaniansky, D., and Arlinghaus, H.F., PPy doped PEG conducting polymer films synthesized on LiFePO4 particles, J. Power Sources, 2010, vol. 195, no. 12, pp. 3907–3912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2010.01.003
Vicente, N., Haro, M., Cintora-Juarez, D., Perez-Vicente, C., Tirado, J.L., Ahmad, S., and Garcia-Belmonte, G., LiFePO4 particle conductive composite strategies for improving cathode rate capability, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 163, pp. 323–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.02.148
Ozerova V.V., Stenina I.A., Kuz’mina A.A., Kulova T.L., and Yaroslavtsev A.B., Cathode materials based on lithium iron phosphate/PEDOT composites for lithium-ion batteries, Inorg. Mater., 2020, vol. 56, no. 6, pp. 648–656. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0020168520050106
Wang, S.Y., Cao, K.W., Xu, L.H., Zhao, D.L., and Tong, Y.J., Carbon nanotubes/reduced graphene oxide composites as electrode materials for supercapacitors, Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process., 2022, vol. 128, no. 1, paper 81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05231-z
Dong, J., Lin, Y., Zong, H., Yang, H., Wang, L., and Dai, Z., Three-dimensional architecture reduced graphene oxide–LiFePO4 composite: preparation and excellent microwave absorption performance, Inorg. Chem., 2019, vol. 58, no. 3, pp. 2031–2041. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b03043
Cao, H., Wen, L., Guo, Z.-q., Piao, N., Hu, G.-j., Wu, M.-J., and Li, F., Application and prospects for using carbon materials to modify lithium iron phosphate materials used at low temperatures, New Carbon Mater., 2022, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1872-5805(22)60584-5
Cao, J., Liu, R., Guo, H., Tian, S., Zhang, K., Ren, X., Wang, Y., and Liang, G., High-temperature solid-phase synthesis of lithium iron phosphate using polyethylene glycol grafted carbon nanotubes as the carbon source for rate-type lithium-ion batteries, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2022, vol. 907, paper 116049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2022.116049
Liang, G.C., Wang, L., Ou, X.Q., Zhao, X., and Xu, S.Z., Lithium iron phosphate with high-rate capability synthesized through hydrothermal reaction in glucose solution, J. Power Sources, 2008, vol. 184, no. 2, pp. 538–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.02.056
Wang, J., Shao, Z.B., and Ru, H.Q., Influence of carbon sources on LiFePO4/C composites synthesized by the high-temperature high-energy ball milling method, Ceram. Int., 2014, vol. 40, no. 5, pp. 6979–6985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.12.025
Fey, G.T.K. and Lu, T.L., Morphological characterization of LiFePO4/C composite cathode materials synthesized via a carboxylic acid route, J. Power Sources, 2008, vol. 178, no. 2, pp. 807–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.09.039
Kuzmanovic, M., Jugovic, D., Mitric, M., Jokic, B., Cvjeticanin, N., and Uskokovic, D., The use of various dicarboxylic acids as a carbon source for the preparation of LiFePO4/C composite, Ceram. Int., 2015, vol. 41, no. 5, pp. 6753–6758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.01.121
Ornek, A., Bulut, E., and Ozacar, M., The chemical, physical and electrochemical effects of carbon sources on the nano-scale LiFePO4 cathode surface, Ceram. Int., 2014, vol. 40, no. 10, pp. 15727–15736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.07.096
Wang, X.F., Feng, Z.J., Hou, X.L., Liu, L.L., He, M., He, X.S., Huang, J.T., and Wen, Z.H., Fluorine doped carbon coating of LiFePO4 as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries, Chem. Eng. J., 2020, vol. 379, paper 122371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122371
Avci, E., Mazman, M., Uzun, D., Bicer, E., and Sener, T., High performance LiFePO4/CN cathode material promoted by polyaniline as carbon–nitrogen precursor, J. Power Sources, 2013, vol. 240, pp. 328–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.04.030
Du, J., Kong, L.B., Liu, H., Liu, J.B., Liu, M.C., Zhang, P., Luo, Y.C., and Kang, L., Template-free synthesis of LiFePO4/C nanocomposite for high power lithium-ion batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, vol. 123, pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.12.157
Yan, X., Yang, Y., Li, C., Liu, J., Wang, J., Xi, F., Wang, T., and He, W., The synthesis of LiFePO4/C with polyaniline as coated carbon source and sucrose as reducing carbon source, Ionics, 2022, vol. 28, pp. 1559–1571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04430-1
Chen, Z.Y., Du, B.L., Xu, M., Zhu, H.L., Li, L.J., and Wang, W.H., Polyacene coated carbon/LiFePO4 cathode for Li ion batteries: understanding the stabilized double coating structure and enhanced lithium ion diffusion kinetics, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, vol. 109, pp. 262–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.07.159
Mo, Y.D., Liu, J.C., Meng, C., Xiao, M., Ren, S., Sun, L.Y., Wang, S.J., and Meng, Y.Z., Stable and ultrafast lithium storage for LiFePO4/C nanocomposites enabled by instantaneously carbonized acetylenic carbon-rich polymer, Carbon, 2019, vol. 147, pp. 19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.02.049
Shi, M., Li, R.W., and Liu, Y.L., In situ preparation of LiFePO4/C with unique copolymer carbon resource for superior performance lithium-ion batteries, J. Alloys Compd., 2021, vol. 854, paper 157162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157162
Chen, Z.Y., Zhu, H.L., Ji, S., Fakir, R., and Linkov, V., Influence of carbon sources on electrochemical performances of LiFePO4/C composites, Solid State Ionics, 2008, vol. 179, nos. 27–32, pp. 1810–1815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2008.04.018
Dimesso, L., Spanheimer, C., Jacke, S., and Jaegermann, W., Synthesis and characterization of three-dimensional carbon foams–LiFePO4 composites, J. Power Sources, 2011, vol. 196, no. 16, pp. 6729–6734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2010.11.015
Stenina, I.A., Kulova, T.L., Skundin, A.M., and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., High grain boundary density Li4Ti5O12/anatase-TiO2 nanocomposites as anode material for Li-ion batteries, Mater. Res. Bull., 2016, vol. 75, pp. 178–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2015.11.050
Chekannikov, A., Kapaev, R., Novikova, S., Tabachkova, N., Kulova, T., Skundin, A., and Yaroslavtsev, A., Na3V2(PO4)3/C/Ag nanocomposite materials for Na-ion batteries obtained by the modified Pechini method, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2017, vol. 21, no. 6, pp. 1615–1624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3524-4
Pechini, M.P., Method of preparing lead and alkaline earth titanates and niobates and coating method using the same to form a capacitor, US Patent 3330697, 1967.
Svitan’ko, A., Scopets, V., Novikova, S., and Yaroslavtsev, A., The effect of composite formation with oxides on the ion conductivity of NASICON-type LiTi2(PO4)3 and olivine-type LiFePO4, Solid State Ionics, 2015, vol. 271, pp. 42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2014.10.022
Wilcox, J.D., Doeff, M.M., Marcinek, M., and Kostecki, R., Factors influencing the quality of carbon coatings on LiFePO4, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2007, vol. 154, no. 5, pp. A389–A395. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2667591
Vidano, R.P., Fischbach, D.B., Willis, L.J., and Loehr, T.M., Observation of Raman band shifting with excitation wavelength for carbons and graphites, Solid State Commun., 1981, vol. 39, no. 2, pp. 341–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-1098(81)90686-4
Stenina, I.A., Bukalov, S.S., Kulova, T.L., Skundin, A.M., Tabachkova, N.Yu., and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Influence of a carbon coating on the electrochemical properties of lithium-titanate-based nanosized materials, Nanotechnol. Russ., 2015, vol. 10, nos. 11–12, pp. 865–871. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1995078015060130
Doeff, M.M., Hu, Y.Q., McLarnon, F., and Kostecki, R., Effect of surface carbon structure on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4, Electrochem. Solid State Lett., 2003, vol. 6, no. 10, pp. A207–A209. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1601372
Song, J., Sun, B., Liu, H., Ma, Z., Chen, Z., Shao, G., and Wang, G., Enhancement of the rate capability of LiFePO4 by a new highly graphitic carbon-coating method, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, vol. 8, no. 24, pp. 15225–15231. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b02567
Sharikov, F.Y., Drozhzhin, O.A., Sumanov, V.D., Baranov, A.N., Abakumov, A.M., and Antipov, E.V., Exploring the peculiarities of LiFePO4 hydrothermal synthesis using in situ Calvet calorimetry, Cryst. Growth Des., 2018, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 879–882. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.7b01366
Yen, H., Rohan, R., Chiou, C.-Y., Hsieh, C.-J., Bolloju, S., Li, C.-C., Yang, Y.-F., Ong, C.-W., and Lee, J.-T., Hierarchy concomitant in situ stable iron(II)–carbon source manipulation using ferrocenecarboxylic acid for hydrothermal synthesis of LiFePO4 as high-capacity battery cathode, Electrochim. Acta, 2017, vol. 253, pp. 227–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.09.065
Kosova, N.V., Podgornova, O.A., and Gutakovskii, A.K., Different electrochemical responses of LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 prepared by mechanochemical and solvothermal methods, J. Alloys Compd., 2018, vol. 742, pp. 454–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.242
Safronov, D.V., Novikova, S.A., Skundin, A.M., and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Lithium intercalation and deintercalation processes in Li4Ti5O12 and LiFePO4, Inorg. Mater., 2012, vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 57–61. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0020168512010141
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Federation Ministry of Science and Higher Education as part of the state research target for the Kurnakov Institute of General and Inorganic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novikova, S.A., Il’in, A.B., Gryzlov, D.Y. et al. LiFePO4/C/Ag Cathode Materials Prepared by the Pechini Method. Inorg Mater 58, 822–830 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168522070111
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168522070111