Abstract
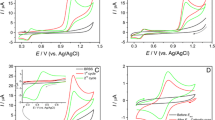
Glutathione (GSH) is one of the most important thiol-containing antioxidants involved in various biochemical processes in the human body. Glutathione determination in biological fluids (saliva, urine, serum) and pharmaceutical preparations is rather important for clinical practice. Various analytical methods such as spectrophotometry, fluorimetry, high-performance liquid chromatography, NMR spectroscopy, capillary electrophoresis, and electrochemical methods are widely used for this purpose. Electrochemical methods are characterized by easy implementation, low cost, and possibility of miniaturization. The electrochemical behavior of reduced (GSH) and oxidized (GSSG) glutathione on a gold-carbon-containing electrode (AuCE) was studied using cathodic voltammetry with different methods of removing oxygen from an electrochemical cell: nitrogen sparging and addition of sodium sulfite (4 mol/dm3). It has been shown that traces of H2O2 that remain in the near-electrode layer on the AuCE even after oxygen removal influence the electrochemical properties of GSH at a cathode sweep of the potential from 0 to –1.8 V: GSH is oxidized by H2O2 to GSSG; the most important product of this reaction is O2. An indirect determination of GSH by the current of oxygen reduction in the Na2SO3 medium in the concentration range from 0.5 × 10–8 to 4.2 × 10–8 mol/dmm3 with a detection limit of 2.5 × 10–9 mol/dm3 is proposed. The developed voltammetric method is approved for the determination of GSH in certain pharmaceutical preparations.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Galli, F., Rossi, R., Floridi, A., and Canestrari, F., Protein thiols and glutathione influence the nitric oxide-dependent regulation of the red blood cell metabolism, Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem., 2002, vol. 6, pp. 186–199.
Dickinson, D.A. and Forman, H.J., Cellular glutathione and thiols metabolism, Biochem. Pharmacol., 2002, vol. 64, pp. 1019–1026.
Hassan, M.Q., Hadi, R.A., Al-Rawi, Z.S., et al., The glutathione defense system in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, J. Appl. Toxicol., 2001, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 69–73.
Watanabe, K. and Guengerich, F.P., Limited reactivity of formyl chloride with glutathione and relevance to metabolism and toxicity of dichloromethane, Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2016, vol. 19, pp. 1091–1096.
Samiec, P., Botsch, C.D., Flagg, E.W., and Kurtz, J.C., Glutathione in human plasma: decline in association with aging, age related macular degeneration, and diabetes, Free Radical Biol. Med., 1998, vol. 24, pp. 699–704.
Weber, G.F., Final common pathways in neurodegenerative diseases: regulatory role of the glutathione cycle, Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 1999, vol. 23, pp. 1079–1086.
Gu, F., Chauhan, V., and Chauhan, A., Glutathione redox imbalance in brain disorders, Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr., 2015, vol. 18, pp. 89–95.
Plotnikov, E., Korotkova, E., Voronova, O., et al., Comparative investigation of antioxidant activity of human serum blood by amperometric, voltammetric and chemiluminescent methods, Arch. Med. Sci., 2016, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 1071–1076.
Korotkova, E., Misini, B., Dorozhko, E., et al., Study of OH radicals in human serum blood of healthy individuals and those with pathological schizophrenia, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2011, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 401–409.
Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R., Seyedhosseini, E., and Robatjazi, H., Spectrophotometric determination of glutathione and cysteine based on aggregation of colloidal gold nanoparticles, Sci. Iran., 2014, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 958–963.
Hepel, M. and Stobiecka, M., Comparative kinetic model of fluorescence enhancement in selective binding of monochlorobimane to glutathione, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2011, vol. 225, no. 1, pp. 72–80.
Markina, M., Lebedeva, E., Neudachina, L., et al., Determination of antioxidants in human skin by capillary zone electrophoresis and potentiometry, Anal. Lett., 2016, vol. 49, no. 12, pp. 1804–1815.
Pastore, A., Massoud, R., Motti, G., et al., Fully automated assay for total homocysteine, cysteine, cysteinylglycine, glutathione, cysteamine, and 2-mercaptopropionylglycine in plasma and urine, Clin. Chem., 1998, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 825–832.
Tsikas, D. and Brunner, G., High-performance liquid chromatography of glutathione conjugates, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 1992, vol. 343, no. 3, pp. 330–334.
Salazar, J.F., Schorr, H., Herrmann, W., et al., Measurement of thiols in human plasma using liquid chromatography with precolumn derivatization and fluorescence detection, J. Chromatogr. Sci., 1999, vol. 37, no. 12, pp. 469–476.
Rae, C.D. and Williams, S.R., Glutathione in the human brain: review of its roles and measurement by magnetic resonance spectroscopy, Anal. Biochem., 2017, vol. 529, pp. 127–143.
Lee, P.T., Goncalves, L.M., and Compton, R.G., Electrochemical determination of free and total glutathione in human saliva samples, Sens. Actuators, B, 2015, vol. 221, pp. 962–968.
Harfield, J.C., Batchelor-McAuley, C., and Compton, R.G., Electrochemical determination of glutathione: a review, Analyst, 2012, vol. 137, pp. 2285–2296.
Hassanvand, Z. and Jalali, F., Electrocatalytic determination of glutathione using transition metal hexacyanoferrates (MHCFs) of copper and cobalt electrode posited on graphene oxide nanosheets, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res., 2018, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 115–129.
Karimi-Maleh, H., Keyvanfard, M., Alizad, K., et al., Electrocatalytic determination of glutathione using multiwall carbon nanotubes paste electrode as a sensor and isoprenaline as a mediator, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2012, vol. 7, pp. 6816–6830.
Taei, M., Hadadzadeh, X., and Hasanpour, F., A voltammetric sensor based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes and a new azoferrocene derivative for determination of glutathione, Sens. J., 2015, vol. 15, no. 8, pp. 4472–4479.
Karimi-Maleh, H., Tahernejad-Javazmi, F., Gupta, V.K., et al., A novel biosensor for liquid phase determination of glutathione and amoxicillin in biological and pharmaceutical samples using a ZnO/CNTs nanocomposite/catechol derivative modified electrode, J. Mol. Liq., 2014, vol. 196, pp. 258–263.
Beitollahi, H., Gholami, A., and Reza Ganjali, M., Preparation, characterization and electrochemical application of Ag-ZnO nanoplates for voltammetric determination of glutathione and tryptophan using modified carbon paste electrode, Mater. Sci. Eng., C, 2015, vol. 57, pp. 107–112.
Karimi-Maleh, H., Tahernejad-Javazmi, F., Ensafi, A.A., et al., A high sensitive biosensor based on FePt/CNTs nanocomposite/N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3,5-dinitrobenzamide modified carbon paste electrode for simultaneous determination of glutathione and piroxicam, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014, vol. 60, pp. 1–7.
Soltani, H., Beitollahi, H., Hatefi-Mehrjardi, A.-H., and Torkzadeh-Mahani, M., Voltammetric determination of glutathione using a modified single walled carbon nanotubes paste electrode, Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem., 2014, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 67–79.
Rezaei, B., Khosropour, H., Asghar Ensafi, A., et al., A differential pulse voltammetric sensor for determination of glutathione in real samples using a trichloro(terpyridine)ruthenium (III)/multiwall carbon nanotubes modified paste electrode, Sens. J., 2015, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 483–490.
Keyvanfard, M. and Alizad, K., A sensitive voltammetric sensor for determination of glutathione based on multiwall carbon nanotubes paste electrode incorporating pyrogallol red, Orient. J. Chem., 2014, vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 593–599.
Liu, B., Ma, C., Li, Y., et al., Voltammetric determination of reduced glutathione using poly(thionine) as a mediator in the presence of Fenton-type reaction, Talanta, 2017, vol. 170, pp. 399–405.
Huang, Y., Yan, H., and Tong, Y., Electrocatalytic determination of reduced glutathione using rutin as a mediator at acetylene black spiked carbon paste electrode, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2015, vol. 743, pp. 25–30.
Noskova, G.N., Zakharova, E.A., Chernov, V.I., et al., Properties and application of gold-carbon composite electrodes in electrochemical analysis methods, Izv. Tomsk. Politekh. Univ., Inzh. Georesur., 2012, vol. 320, no. 3, pp. 109–115.
Zakharova, E.A., Noskova, G.N., Elesova, E.E., and Antonova, S.G., Determination of arsenic (V) in waters by the method of inversion voltammetry against the background of sodium sulfite in the presence of manganese (II) ions, Zavod. Lab., Diagn. Mater., 2012, vol. 79, no. 5, pp. 17–23.
Zakharova, E.A., Antonova, S.G., Noskova, G.N., Skvortsova, L.N., and Te, A.V., Methods of the determination of inorganic arsenic species by stripping voltammetry in weakly alkaline media, J. Anal. Chem., 2016, vol. 71, no. 8, pp. 823–833.
Abedinzadeh, Z., Gardes-Albert, M., and Ferradini, C., Kinetic study of the oxidation mechanism of glutathione by hydrogen peroxide in neutral aqueous medium, Can. J. Chem., 1989, vol. 67, no. 7, pp. 1247–1255.
Shinichi, E., Hoffmann, M.R., and Colussi, A.J., OH-radical specific addition to glutathione S-atom at the air-water interface: relevance to the redox balance of the lung epithelial lining fluid, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2015, vol. 6, no. 19, pp. 3935–3943.
Flohe, L., The fairytale of the GSSG/GSH redox potential, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Gen. Subj., 2013, vol. 1830, no. 5, pp. 3139–3142.
Pisoschi, A.M., Electroanalytical techniques for the determination of sulphite preservative: an editorial, Biochem. Anal. Biochem., 2014, vol. 3, pp. 32–34.
El-Deab, M.S. and Ohsaka, T., Quasi-reversible two-electron reduction of oxygen at gold electrodes modified with a self-assembled submonolayer of cysteine, Electrochem. Commun., 2013, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 214–219.
Skavas, E. and Hemmingsen, T., Kinetics and mechanism of sulphite oxidation on a rotating platinum disc electrode in an alkaline solution, Electrochim. Acta, 2007, vol. 52, pp. 3510–3517.
Senning, A., Sulfur in Organic and Inorganic Chemistry, New York: Marcel Dekker, 1972, vols. 1–3.
Hayon, E., Treinin, A., and Wilf, J., Electronic spectra, photochemistry, and autoxidation mechanism of the sulfite-bisulfite-pyrosulfite systems. SO2–, SO3–, SO4–, and SO5– radicals, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1972, vol. 94, pp. 47–57.
Shi, X., Generation of \({\text{SO}}_{3}^{ - }\) and OH radicals in \({\text{SO}}_{3}^{{2 - }}\) reactions with inorganic environmental pollutants and its implications to \({\text{SO}}_{3}^{{2 - }}\) toxicity, J. Inorg. Biochem., 1994, vol. 56, pp. 155–165.
Oztekin, Y., Ramanaviciene, A., and Ramanavicius, A., Electrochemical glutathione sensor based on electrochemically deposited poly-m-aminophenol, Electroanalysis, 2011, vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 701–709.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
We have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Translated by P. Vlasov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gashevskaya, A.S., Dorozhko, E.V., Korotkova, E.I. et al. Voltammetric Method for Determination of Glutathione on a Gold-Carbon-Containing Electrode. Inorg Mater 56, 1362–1368 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168520140071
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168520140071