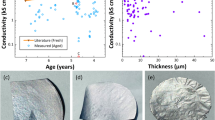
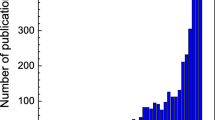
Abstract
The main directions of application and synthesis of lithium niobate (LiNbO3) and the advantages and drawbacks of the synthesis techniques are considered. The results of structural and morphological characteristics appropriate for use in the creation of devices are shown. The tasks for successful implementation of LiNbO3 films into novel devices are formulated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuz’minov, Yu.S., Niobat i tantalat litiya—materialy dlya nelineinoi optiki, Moscow: Nauka, 1975, p. 224.
Matthias, B.T. and Remeika, J.P., Ferroelectricity in the ilmenite structure, Phys. Rev. American Physical Society, 1949, vol. 76, no. 12, pp. 1886–1887.
Ballman, A.A., Growth of piezoelectric and ferroelectric materials by the Czochralski technique, J. Am. Ceramic Soc, 1965, vol. 48, no. 2, p. 112.
Wong, K.K., Properties of lithium niobate, London: INSPEC/Institution of Electrical Engineers, 2002.
Volk, T., and Wöhlecke, M., Lithium niobate: defects, photorefraction and ferroelectric switching, Berlin; Heidelberg: Springer, 2008.
Shcherbina, O., Palatnikov, M., and Kokhanchik, L., Sintez, svoistva kristallov LiNbO3i LiTaO3s mikro-i nanostrukturami, LAP, 2013, p. 168.
Muralt, P. et al., Ferroelectric thin films for microsensors and actuators: a review, J. Micromechanics Microengineering, 2000, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 136–146.
Jayadevan, K.P. and Tseng, T.Y., Review composite and multilayer ferroelectric thin films: processing, properties and applications, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron, 2002, vol. 13, no. 8, pp. 439–459.
Poberaj, G. et al., Lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) for micro-photonic devices, Laser Photon. Rev., 2012, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 488–503.
Buchal, C. and Siegert, M., Ferroelectric thin films for optical applications, Integr. Ferroelectr, 2001, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 1–10.
Pogossian, S.P. and Le Gall H. Modeling planar leaky optical waveguides, J. Appl. Phys., 2003, vol. 93, no. 5, p. 2337.
Fork, D.K., Armani-Leplingard, F., and Kingston, J.J., Application of electroceramic thin films to optical waveguide devices, MRS Bull., 1996, pp. 53–58.
Wohltjen, H., Mechanism of operation and design considerations for surface acoustic wave device vapour sensors, Sen. Actuators, 1984, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 307–325.
Lee, T.C. et al., Surface acoustic wave applications of lithium niobate thin films, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2003, vol. 82, no. 2, pp. 191–193.
Runde, D. et al., Integrated optical electric field sensor based on a Bragg grating in lithium niobate, Appl. Phys. B, 2006, vol. 86, no. 1, pp. 91–95.
Shih, W.-C. et al., Growth of c-axis oriented LiNbO3 film on sapphire by pulsed laser deposition for surface acoustic wave applications, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2008, vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 4056–4059.
Kadota, M. et al., High-frequency lamb wave device composed of MEMS structure using LiNbO3 thin film and air gap, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control, 2010, vol. 57, no. 11, pp. 2564–2571.
Dogheche, E. et al., Growth process and surface acoustic wave characteristics of LiNbO3 /diamond/silicon multilayered structures, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2003, vol. 42, pp. 572–574.
Tan, T. et al. Sputter deposited c-oriented LiNbO3 thin films on SiO2, J. Appl. Phys., 1996, vol. 79, no. 7, pp. 3548–3553.
Moon, S. et al. Characteristics of metal-LiNbO3-Si for a single transistor FRAM, Conference: Applications of Ferroelectrics, 2000.
Gupta, V. et al., Growth and characterization of c-axis oriented LiNbO3 film on a transparent conducting Al:ZnO inter-layer on Si, J. Mater. Res., 2004, vol. 19, no. 8, pp. 2235–2239.
Hao, L. et al., Epitaxial fabrication and memory effect of ferroelectric LiNbO3 film/ AlGaN/GaN heterostructure, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, vol. 95, p. 232907.
You, P. et al., Growth of highly near-c-axis oriented ferroelectric LiNbO3 thin films on Si with a ZnO buffer layer, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, vol. 102, p. 051914.
Zaitsev, I., Chto, zhe stalo s FRAM pamyat’yu?, Komponenty i tekhnologii, 2007, no. 8, pp. 60–64.
Takiev, A.S., Budushchie tekhnologii pamyati: FeRAM iznutri, 2003, https://3dnews.ru/172104, p. 172104.
Czabaj, B.M., Patent US8658435 B2, 2014.
Lee, S-Y., Patent US6605835 B2, 2003.
Scott, J.F., and Paz de Araujo, C.A. Ferroelectric memories, Science, 1989, vol. 246, pp. 1400–1405.
Shu, W. et al. Experimental study of LiNbO3 memristors for use in neuromorphic computing, Microelectronic Engineering, 2017, V. 168, pp. 37–40.
Haitao, L. et al., Memristive behaviors of LiNbO3 ferroelectric diodes, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2010, vol. 97, p. 012902.
Greenlee, J.D., Petersburg, C.F., et al. In-situ oxygen X-ray absorption spectroscopy investigation of the resistance modulation mechanism in LiNbO2 memristors, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, vol. 100, p. 182106.
Pan, X. et al., Rectifying filamentary resistive switching in ion-exfoliated LiNbO3 thin films, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2016, vol. 108, p. 032904.
Strukov, D.B. et al., The missing memristor found, Nature, 2008, vol. 453, pp. 80–83.
Yang, J.J. et al., Memristive switching mechanism for metal/oxide/metal nanodevices, Nature Nanotechnol., 2008, vol. 3, pp. 429–433.
Driscoll, T. et al., Phase-transition driven memristive system, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, vol. 95, p. 043503.
Di Ventra, M. et al., Elements with memory: memristors, memcapacitors, and meminductors, IEEE, 2009, vol. 97, no. 10, pp. 1717–1724.
Lu, W., Patent US 20130134379 A1, 2013.
Sheng, P. et al., Structure and ferromagnetism in vanadium-doped LiNbO3, J. Appl. Phys., 2012, vol. 112, no. 3, pp. 1–7.
Song, C. et al., Room temperature ferromagnetism and ferroelectricity in cobalt-doped LiNbO3 film, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, vol. 92, no. 26, pp. 2901–262901.
Díaz-Moreno, C. et al., Multiferroic response of nanocrystalline lithium niobate, J. Appl. Phys., 2012, vol. 111, no. 7, pp. 5–8.
Ishii, M. et al., Ferromagnetism of nano-LiNbO3 with vacancies, Trans. Mater. Res. Soc. Japan, 2012, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 443–446.
Vasconcelos, N.S.L.S. et al., Epitaxial growth of LiNbO3 thin films in a microwave oven, Thin Solid Films, 2003, vol. 436, no. 2, pp. 213–219.
Postnikov, V.S., Ievlev, V.M., Zolotukhin, I.V., and Rodin, G.S., Vyrashchivanie epitaksial’nykh plenok LiNbO3, Izv. AN SSSR. Neorganicheskie Materialy, 1973, vol. 9, no. 8, pp. 1455–1456.
Ballman, A.A. et al., The growth of LiNbO3 thin films by liquid phase epitaxial techniques, Journal of Crystal Growth, 1975, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 289–295.
Kondo, S. et al., Liquid-phase-epitaxial growth of single- crystal LiNbO3 thin film, Applied Physics Letters, 1975, vol. 26, no. 9, pp. 489–491.
Miyazawa, S., Fushimi, S., and Kondo, S., Optical waveguide of LiNbO3 thin film grown by liquid phase epitaxy, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1975, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 8–10.
Ballman, A.A. and Tien, P.K., Patent US 3998687 A, 1976.
Dubs, C. et al., Rib waveguides based on Zn-substituted LiNbO3 films grown by liquid phase epitaxy, Opt. Mater. (Amst), 2009, vol. 31, no. 11, pp. 1650–1657.
Lu, Y., Dekker, P., and Dawes, J.M., Growth and characterization of lithium niobate planar waveguides by liquid phase epitaxy, J. Cryst. Growth, 2009, vol. 311, no. 5, pp. 1441–1445.
Margueron, S. et al., Effect of deposition conditions on the stoichiometry and structural properties of LiNbO3 thin films deposited by MOCVD, Proc. SPIE—Int. Soc. Opt. Eng., p. 8626.
Dislich, H., New routes to multicomponent oxide glasses, Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. English, 1971, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 363–370.
Hirano, S. and Kato, K., Formation of LiNbO3 films by hydrolysis of metal alkoxides, J. Non. Cryst. Solids, 1988, vol. 100, no. 1, pp. 538–541.
Nashimoto, K. and Cima, M.J., Epitaxial LiNbO3 thin films prepared by a sol-gel process, Mater. Lett., 1991, vol. 10, no. 7–8, pp. 348–354.
Simões, A.Z. et al., Potassium niobate thin films prepared through polymeric precursor method, Mater. Lett., 2004, vol. 58, no. 20, pp. 2537–2540.
Fakhri, M.A. et al., Optical investigation of nanophotonic lithium niobate-based optical waveguide, Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt., 2015, vol. 121, no. 1, pp. 107–116.
Schwartz, H. and Tourtellotte, H.A., Vacuum deposition by high-energy laser with emphasis on barium titanate films, Vac. Sci. Technol., 1969, vol. 6, p. 3763.
Baumann, R.C., Rost, T.A., and Rabson, T.A., Deposition and physical characterization of thin films of lithium niobate on silicon substrates, J. Appl. Phys., 1990, vol. 68, p. 2989.
Shibata, Y., Kaya, K., and Akashi, K., Epitaxial growth of LiNbO3 thin films by excimer laser ablation method and their surface acoustic wave properties, J. Appl. Phys., 1992, vol. 61, p. 1000.
Ogale, S.B. et al., Pulsed laser deposition of stoichiometric LiNbO3 thin films by using O2 and Ar gas mixtures as ambients, J. Appl. Phys., 1992, vol. 11, p. 5718.
Lee, S.H. et al., Low-temperature growth of epitaxial LiNbO3 films on sapphire (0001) substrates using pulsed laser deposition, J. Appl. Phys., 1995, vol. 67, p. 43.
Gonzalo, J. et al., Li deficiencies in LiNbO3 films prepared by pulsed laser deposition in a buffer gas, J. Appl. Phys., 1997, vol. 82, p. 3129.
Balestrino, G. et al., Epitaxial LiNbO3 thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition for optical waveguides, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2001, vol. 78, p. 1204.
Jelínek, M. et al., Composition, XRD and morphology study of laser prepared LiNbO3 films, Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process, 2013, vol. 110, no. 4, pp. 883–888.
Wang, X. et al., Oxygen pressure dependent growth of pulsed laser deposited LiNbO3 films on diamond for surface acoustic wave device application, J. Cryst. Growth, 2013, vol. 375, pp. 73–77.
Wang, X. et al., Influence of substrate temperature on the growth and optical waveguide properties of oriented LiNbO3 thin films, J. Cryst. Growth, 2007, vol. 306, pp. 62–67.
Foster, N.F. The deposition and piezoelectric characteristics of sputtered lithium niobate films, J. Appl. Phys., 1969, vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 420–421.
Russo, D.P.G. and Kumar, C.S., Sputtered ferroelectric thin-film electro-optic modulator, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1973, vol. 23, no. 5, pp. 229–231.
Takada, S. et al., Optical waveguides of single-crystal LiNbO3 film deposited by rf sputtering, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1974, vol. 24, no. 10, p. 490.
Hewig, G.M. et al., R.F. sputtering of LiNbO3 thin films, Thin Solid Films, 1982, vol. 88, no. 1, pp. 67–74.
Rabson, T.A., Baumann, R.C., and Timothy, A., Thin film lithium niobate on silicon, Ferroelectrics, 1990, vol. 112, pp. 265–271.
Kanata, T., Kobayashi, Y., and Kubota, K., Epitaxial growth of LiNbO3–LiTaO3 thin films on Al2O3, J. Appl. Phys., 1987, vol. 62, no. 7, pp. 2989–2993.
Sumets, M. et al., Sputtering condition effect on structure and properties of LiNbO3 films, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron, 2015, vol. 26, no. 6, pp. 4250–4256.
Iyevlev, V. et al., Electrical and structural properties of LiNbO3 films, grown by RF magnetron sputtering, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron, 2011, vol. 22, no. 9, pp. 1258–1263.
Ievlev, V.M. et al., Struktura i svoistva plenok LiNbO3, poluchennykh metodom vysokochastotnogo magnetronnogo raspyleniya, Perspektivnye Materialy, 2010, vol. 3, pp. 26–33.
Sidorov, N.V. and Kalinnikov, V.T., Protsessy razuporyadocheniya v segnetoelektricheskikh kristallakh i ikh proyavlenie v spektrakh kombinatsionnogo rasseyaniya sveta (Processes of disordering in ferroelectric crystals and their manifestation in Raman spectra), Apatity: izd. Kol’skogo nauchnogo tsentra RAN, 2001.
Sumets, M. et al., Electrical properties of Si-LiNbO3 heterostructures grown by radio-frequency magnetron sputtering in an Ar + O2 environment, Thin Solid Films, 2014, vol. 552, pp. 32–38.
Akazawa, H. and Shimada, M., Factors driving c-axis orientation and disorientation of LiNbO3 thin films deposited on TiN and indium tin oxide by electron cyclotron resonance plasma sputtering, J. Appl. Phys., 2006, vol. 99, no. 12, p. 124103.
Ievlev, V.M. and Rodin, G.S., Rost i struktura kondensirovannykh plenok BaTiO3 i LiNbO3, in Sb. Voprosy fiziki tverdogo tela. (Issues of solid state physics), Voronezh: VPI, 1973, pp. 136–141.
Rodin, G.S., Poluchenie, substruktura, orientatsiya i fazovyi sostav plenok niobat litiya, Cand. Sci. (Physmath) Dissertation, Voronezh, 1986.
Park, S.K. et al., Properties of LiNbO3 thin film prepared from ceramic Li–Nb–K–O target, Solid State Commun., 1999, vol. 111, no. 6, pp. 347–352.
Simões, A.Z. et al., Influence of oxygen atmosphere on crystallization and properties of LiNbO3 thin films, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2004, vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 1607–1613.
Kiselev, D.A. et al. Effect of annealing on the structure and phase composition of thin electro-optical lithium niobate films, Inorganic Materials, 2014, vol. 50, no. 4, pp. 419–422.
Bornand, V. et al. LiNbO3 thin films deposited on Si substrates: a morphological development study, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2002, vol. 77, pp. 571–577.
Akazawa, H. and Shimada, M., Correlation between interfacial structure and c-axis-orientation of LiNbO3 films grown on Si and SiO2 by electron cyclotron resonance plasma sputtering, Journal of Crystal Growth, 2004, vol. 270, pp. 560–567.
Akazawa, H. et al., Mechanism for LiNb3O8 phase formation during thermal annealing of crystalline and amorphous LiNbO3 thin films, J. Mater. Res., 2007, vol. 22, pp. 1726–1736.
Veignant, F. et al., Structural evolution of lithium niobate deposited on sapphire (0001): from early islands to continuous films, J. Cryst. Growth, 1999, vol. 196, no. 1, pp. 141–150.
Ievlev, V.M., Tonkie plenki neorganicheskikh materialov: mekhanizm rosta i struktura: uch. posobie, (Thin films of inorganic minerals: growth mechanism and structure), Voronezh: VGU, 2008, p. 496.
Lee, G.H., Yoshimoto, M., and Koinuma, H., Selfassembled island formation of LiNbO3 by pulsed laser deposition on α-Al2O3 substrate, Appl. Surf. Sci., 1998, vol. 127, pp. 393–397.
Feigelson, R.S., Epitaxial growth of lithium niobate thin films by the solid source MOCVD method, J. Cryst. Growth, 1996, vol. 166, no. 1, pp. 1–16.
Shtansky, D.V. et al. Crystallography and structural evolution of LiNbO3 and LiNb1–xTaxO3 films on sapphire prepared by high-rate thermal plasma spray chemical vapor deposition, J. Mater. Res., 2001, vol. 16, no. 8, pp. 2271–2279.
He, J. and Ye, Z., Highly c-axis oriented LiNbO3 thin film on amorphous SiO2 buffer layer and its growth mechanism, Chinese Sci. Bull., 2003, vol. 48, no. 21, p. 2290.
Akazawa, H., Nucleation and crystallization of Li2O–Nb2O5 ternary compound thin films co-sputtered from LiNbO3 and Li2O targets, Thin Solid Films, 2014, vol. 556, pp. 74–80.
Mercante, A.J. et al., 110 GHz CMOS compatible thin film LiNbO3 modulator on silicon, Opt. Express, 2016, vol. 24, no. 14, p. 15590.
Iyevlev, V., Kostyuchenko, A., and Sumets, M., Fabrication, substructure and properties of LiNbO3 films, Proceedings of SPIE, The International Society for Optical Engineering. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2011, vol. 7747, p. 77471.
Bornand, V. and Papet, P., LiNbO3-based ferroelectric heterostructures, Journal de Physique IV, 2005, vol. 126, pp. 89–92.
Akazawa, H. and Fukuda, H., Epitaxial ZnO/LiNbO3/ZnO stacked layer waveguide for application to thin-film Pockels sensors, AIP Adv., 2015, vol. 5, no. 5, p. 57163.
Kao, M.C. et al., Pyroelectric Ta-modified LiNbO3 thin films and devices for thermal infrared detection, Thin Solid Films, 2008, vol. 516, no. 16, pp. 5518–5522.
Lee, C.-T. et al., GaN-based enhancement-mode metal-oxide-semiconductor high-electron mobility transistors using LiNbO3 ferroelectric insulator on gate-recessed structure, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, 2015, vol. 62, no. 8, pp. 2481–2487.
Sumets, M. et al., Influence sputtering conditions on electrical characteristics of Si-LiNbO3 heterostructures formed by radio-frequency magnetron sputtering, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., 2014, vol. 603, no. 1, pp. 202–215.
Kiselev, D.A. et al., The effect of silicon-substrate orientation on the local piezoelectric characteristics of LiNbO3 films, J. Surf. Investig. X-ray. Synchrotron Neutron Tech., 2016, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 742–747.
Ievlev, V. et al., Band diagram of the Si-LiNbO3 heterostructures grown by radio-frequency magnetron sputtering, Thin Solid Films, 2013, vol. 542, pp. 289–294.
Sumets, M., Charge transport in LiNbO3-based heterostructures, J. Nonlinear Opt. Phys. Mater., 2017, vol. 26, no. 1, p. 1750011.
Ievlev, V., Sumets, M., and Kostyuchenko, A., Conduction mechanisms in Si-LiNbO3 heterostructures grown by ion-beam sputtering method, J. Mater. Sci., 2013, vol. 48, no. 4, pp. 1562–1570.
Hao, L.Z. et al., Electron trap memory characteristics of LiNbO3 film/AlGaN/GaN heterostructure, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2010, vol. 96, no. 3, p. 32103.
Sumets, M. et al., Temperature transition of p- to ntype conduction in the LiNbO3/Nb2O5 polycrystalline films, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2017, vol. 191, pp. 35–44.
Lim, D. et al., Characteristics of LiNbO3 memory capacitors fabricated using a low thermal budget process, Solid. State. Electron., 2001, vol. 45, no. 7, pp. 1159–1163.
Tsirlin, M., Influence of gas phase composition on the defects formation in lithium niobate, J. Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 39, no. 9, pp. 3187–3189.
Gordillo-Vázquez, F.J. and Afonso, C.N., Influence of Ar and O2 atmospheres on the Li atom concentration in the plasma produced by laser ablation of LiNbO3, J. Appl. Phys., 2002, vol. 92, no. 12, p. 7651.
Simões, A.Z. et al., Influence of oxygen flow on crystallization and morphology of LiNbO3 thin films, Ferroelectrics, 2002, vol. 271, no. 1, pp. 33–38.
Sumets, M. et al., Influence of thermal annealing on structural properties and oxide charge of LiNbO3 films, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., 2015, vol. 26, no. 10, pp. 7853–7859.
Iyevlev, V., Sumets, M., and Kostyuchenko, A., Current- voltage characteristics and impedance spectroscopy of LiNbO3 films grown by RF magnetron sputtering, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron, 2012, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 913–920.
Lanfredi, S. and Rodrigues, A.C.M., Impedance spectroscopy study of the electrical conductivity and dielectric constant of polycrystalline LiNbO3, J. Appl. Phys., 1999.
Ievlev, V. et al., Dielectric losses and ac conductivity of Si-LiNbO3 heterostructures grown by the RF magnetron sputtering method, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., 2013, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 1651–1657.
Joshi, V., Roy, D., and Mecartney, M.L., Nonlinear conduction in textured and non textured lithium niobate thin films, Integr. Ferroelectr., 1995, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 321–327.
Gorbenko, O.Yu., Struktura i svoistva perovskitnykh i perovskitopodobnykh tonkoplenochnykh materialov, poluchennykh khimicheskim osazhdeniem iz para: dis. d. khim. nauk (Structure and properties of perovskite-like thin film material, obtained by chemical vapor depositions: PhD dissertation), Moscow, 2003.
Nakamura, A. et al., Dislocation structure at a \(\left\{ {\bar 12\bar 10} \right\}/\left\{ {10\bar 10} \right\}\) low-angle tilt grain boundary in LiNbO3, J. Mater. Sci., 2012, vol. 47, no. 13, pp. 5086–5096.
Furushima, Y. et al., Dislocation structures and electrical conduction properties of low angle tilt grain boundaries in LiNbO3, J. Appl. Phys., 2016, vol. 120, no. 14.
Veignant, F., Epitaxial growth of LiNbO3 on αAl2O3(0001), Thin Solid Films, 1998, vol. 336, nos. 1–2, pp. 163–167.
Abrahams, S.C., Reddy, J.M., and Bernstein, J.L., Ferroelectric lithium niobate. 3. Single crystal x-ray diffraction study at 24°C, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1966, vol. 27, no. 6, pp. 997–1012.
Shandilya, S., Tomar, M., and Gupta, V., Deposition of stress free c-axis oriented LiNbO3 thin film grown on (002) ZnO coated Si substrate, J. Appl. Phys., 2012, vol. 111, no. 10, pp. 10–16.
Shandilya, S. et al., Purely hopping conduction in caxis oriented LiNbO3 thin films, J. Appl. Phys., 2009, vol. 105, no. 9, p. 94105.
Mansingh, A. and Dhar, A., The AC conductivity and dielectric constant of lithium niobate single crystals, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 1985, vol. 18, no. 10, pp. 2059–2071.
Shandilya, S. et al., Optical properties of the c-axis oriented LiNbO3 thin film, Thin Solid Films, 2012, vol. 520, no. 6, pp. 2142–2146.
Satapathy, S. et al., Blue shift of optical band-gap in LiNbO3 thin films deposited by sol-gel technique, Thin Solid Films, 2012, vol. 520, no. 21, pp. 6510–6514.
Ching, W.Y., Gu, Z.-Q., and Xu, Y.-N., First-principles calculation of the electronic and optical properties of LiNbO3, Phys. Rev. B, 1994, vol. 50, no. 3, pp. 1992–1995.
Bhatt, R. et al., Urbach tail and bandgap analysis in near stoichiometric LiNbO3 crystals, Phys. Status Solidi, 2012, vol. 209, no. 1, pp. 176–180.
Schmidt, W.G. et al., LiNbO3 ground- and excitedstate properties from first-principles calculations, Phys. Rev. B, 2008, vol. 77, no. 3, p. 35106.
Schulz, M.B. and Matsinger, J.H., Rayleigh-wave electromechanical coupling constants, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1972, vol. 20, no. 9, pp. 367–369.
Nelson, D.F. and Mikulyak, R.M., Refractive indices of congruently melting lithium niobate, J. Appl. Phys., 1974, vol. 45, no. 8, pp. 3688–3689.
Choi, S.-W. et al., Effect of RTA treatment on LiNbO3 MFS memory capacitors, Korean J. Ceram, 2000, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 138–142.
Simões, A.Z. et al., LiNbO3 thin films prepared through polymeric precursor method, Mater. Lett., 2003, vol. 57, no. 15, pp. 2333–2339.
Easwaran, N. et al., Dielectric and AC conduction properties of thermally evaporated lithium niobate thin films, Phys. Status Solidi, 1992, vol. 129, no. 2, pp. 443–451.
Edon, V., Rèmiens, D., and Saada, S., Structural, electrical and piezoelectric properties of LiNbO3 thin films for surface acoustic wave resonators applications, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2009, vol. 256, no. 5, pp. 1455–1460.
Yamada, T., Niizeki, N., and Toyoda, H., Piezoelectric and elastic properties of lithium niobate single crystals, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 1967, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 151–155.
Kwang-Ho, Kim. et al., Properties of lithium niobate thin films by RF magnetron sputtering with wafer target, J. Korean Phys. Soc., 1998, vol. 32, pp. 1508–1512.
Wemple, S.H. et al., Relationship between linear and quadratic electro-optic coefficiens in LiNbO3, LiTaO3, and other oxygen-octahedra ferroelectrics based on direct measurement of spontaneous polarization, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1968, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 209–211.
Zhao, J.P., Liu, X.R., and Qiang, L.S., Preparation and characterization of LiNbO3 thin films derived from metal carboxylate gels, Key Eng. Mater., 2007, vol. 336–338, pp. 213–216.
Kim, Y.-S. et al., Properties of LiNbO3 thin films fabricated by CSD (chemical solution decomposition) method (AWAD2003: Asia-Pacific workshop on fundamental and application of advanced semiconductor devices), Technical report of IEICE. SDM, 2003, vol. 103, no. 162, pp. 33–36.
Lee, T.-H. et al., Investigation of LiNbO3 thin films grown on Si substrate using magnetron sputter, Mater. Sci. Eng. B., 2007, vol. 136, no. 1, pp. 92–95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sumets, M.P., Dybov, V.A. & Ievlev, V.M. LiNbO3 films: Potential application, synthesis techniques, structure, properties. Inorg Mater 53, 1361–1377 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168517130015
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168517130015