Abstract
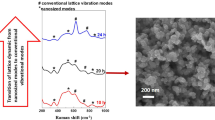
Three-dimensional flower-like SnO2-based structures have been produced by the alkaline hydrothermal treatment of t-SnO2 powder with no additive and in the presence of aminoterephthalic acid (ATPA). The synthesis products have been characterized by a variety of physicochemical techniques (scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, Raman and IR spectroscopies, X-ray diffraction, and others). The results demonstrate that raising the ATPA concentration in the reaction mixture changes the morphology of the materials and leads to the SnO2 → SnO2/Sn3O4 → Sn3O4 phase transformation in the structures through the formation of SnO x nonstoichiometric tin oxide phases with 1 < x < 2. Hydrothermal treatment of the starting reagents in the presence of ≤75 wt % ATPA leads to the formation of hierarchical structures dominated by a nonstoichiometric tin oxide, which is thermally unstable at t ≥ 500°C. The morphology and phase composition of the synthesized structures have been shown to have a significant effect on the electronic conductivity of the material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, H. and Rogach, A.L., Hierarchical SnO2 nanostructures: recent advances in design, synthesis, and applications, Chem. Mater., 2014, vol. 26, pp. 123–133.
Das, S. and Jayaraman, V., SnO2: a comprehensive review on structures and gas sensors, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2014, vol. 66, pp. 112–255.
Zeng, W., Zhang, H., Li, Y., Chen, W., and Wang, Z., Hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchical flower-like SnO2 nanostructures with enhanced ethanol gas sensing properties, Mater. Res. Bull., 2014, vol. 57, pp. 91–96.
Stefik, M., Cornuz, M., Mathews, N., et al., Transparent, conducting Nb:SnO2 for host–guest photoelectrochemistry, Nano Lett., 2012, vol. 12, no. 10, pp. 5431–5435.
Wan, N., Zhao, T., Suna, S., Wu, Q., and Bai, Y., Nickel and nitrogen co-doped tin dioxide nanocomposite as a potential anode material for lithium-ion batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, vol. 143, pp. 257–264.
Hou, L.R., Lian, L., Zhou, L., Zhang, L.H., and Yuan, C.Z., Interfacial hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2 nanorods towards photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange, Mater. Res. Bull., 2014, vol. 60, pp. 1–4.
Cheng, L., Ma, S., Wang, T., et al., Highly sensitive acetic acid gas sensor based on coral-like and Y-doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by electrospinning, Mater. Lett., 2014, vol. 137, pp. 265–268.
Chen, Y., Ma, S.Y., et al., Facile synthesis of SnO2 mesoporous tubular nanostructure with high sensitivity to ethanol, Mater. Lett., 2015, vol. 143, pp. 55–59.
Wang, Y., Su, T., et al., Synthesis of hollow SnO2 microspheres and its enhanced photocatalytic properties, Mater. Let., 2014, vol. 137, pp. 241–244.
Zhang, H., Zeng, W., et al., Hydrothermal synthesis of flower-like SnO2 architectures with superior gas sensing properties, Mater. Lett., 2015, vol. 145, pp. 133–136.
Tao, T., He, L., Li, J., and Zhang, Y., A new way for synthesizing SnO2 nanosheets, Mater. Lett., 2015, vol. 138, pp. 45–47.
Cheary, R.W. and Coelho, A.A., A fundamental parameters approach of X-ray line-profile fitting, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 1992, vol. 25, pp. 109–121.
Balzar, D. and Ledbetter, H., Accurate modeling of size and strain broadening in the Rietveld refinement: the “double-Voigt” approach, Adv. X-ray Anal., 1995, vol. 38, pp. 397–404.
Guo, Y.Q., Tan, R.Q., et al., Shape-controlled growth and single-crystal XRD study of submillimeter-sized single crystals of SnO, CrystEngComm, 2011, vol. 13, pp. 5677–5680.
Wang, F., Zhou, X., et al., Observation of single tin dioxide nanoribbons by confocal Raman microspectroscopy, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, vol. 111, pp. 18839–18843.
Sarker, P. and Huda, M.N., Understanding the thermodynamic pathways of SnO-to-SnOx phase transition, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2016, vol. 111, pp. 359–365.
Mcquire, K., Pan, Z., et al., Raman studies of semiconducting oxide nanobelts, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2002, vol. 2, no. 5, pp. 1–4.
Zheng, M.J., Ma, L., et al., Preparation and structural characterization of nanocrystalline SnO2 powders, Appl. Phys. A, 2005, vol. 81, pp. 721–723.
Sun, S.H., Meng, G.W., et al., Raman scattering study of rutile SnO2 nanobelts synthesized by thermal evaporation of Sn powders, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2003, vol. 376, pp. 103–107.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © T.M. Zima, I.A. Bataev, 2017, published in Neorganicheskie Materialy, 2017, Vol. 53, No. 12, pp. 1311–1317.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zima, T.M., Bataev, I.A. Synthesis and characterization of three-dimensional flower-like tin dioxide-based structures. Inorg Mater 53, 1279–1285 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168517120196
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168517120196