Abstract
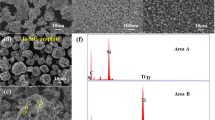
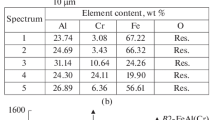
Changes in the phase composition of the 20 vol % Ti3SiC2-Cu composite during detonation spraying as well as corresponding microstructure formation processes in the sprayed coatings have been studied. It was demonstrated that when the amount of the explosive acetylene+oxygen mixture is kept constant (under the constant filled volume fraction of the barrel of the detonation gun of a CCDS2000 facility), the phase composition of the coating depends on the composition of the explosive mixture. The Ti3SiC2-Cu system is prone to interfacial interaction; therefore, in order to produce a dense coating preserving the phase composition, oxygen-depleted explosive mixtures should be used and small filled fractions of the barrel. As the temperature of the sprayed particles increases with increasing oxygen content in the explosive mixture, titanium silicon carbide reacts with copper, which results in the formation of the titanium carbide phase and dissolution of the de-intercalated silicon in the copper matrix leading to the formation of TiC x -Cu〈Si〉 coatings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ulianitsky, V., Shtertser, V., Zlobin, Z., and Smurov, I., Computer-controlled detonation spraying: From process fundamentals toward advanced applications, J. Thermal Spray Technol., 2011, vol 20, no. 4, p. 791.
Dudina, D.V., Zlobin, S.B., Bulina, N.V., et al., Detonation spraying of TiO2-2.5 vol. % Ag powders in a reducing atmosphere, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2012, vol. 32, no. 4, p. 815.
Dudina, D.V., Korchagin, M.A., Zlobin, S.B., et al., Compositional variations in the coatings formed by detonation spraying of Ti3Al at different O2/C2H2 ratios, Intermetallics, 2012, vol. 29, p. 140.
Dudina, D.V., Zlobin, S.B., Ulianitsky, V.Yu., et al., Detonation spraying of TiO2-Ag: Controlling the phase composition and microstructure of the coatings, Ceram. Trans., 2012, vol. 237, p. 161.
Barsoum, M.W., The MN + 1AXN phases: A new class of solids; thermodynamically stable nanolaminates, Prog. Solid State Chem., 2000, vol. 28, nos. 1–4, p. 201.
Zhou, Y. and Gu, W., Chemical reaction and stability of Ti3SiC2 in Cu during high-temperature processing of Cu/Ti3SiC2 composites, Z. Metallkd., 2004, vol. 95, no. 1, p. 50.
Wu, J.Y., Zhou, W.C., and Wang, J.Y., Tribological behavior of Ti2SnC particulate reinforced copper matrix composites, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2006, vol. 422, nos. 1–2, p. 266.
Peng, L., Fabricatikon and properties of Ti3AlC2 particulated reinfirced copper composites, Scr. Mater., 2007, vol. 56, no. 9, p. 729.
Zhang, J. and Zhou, Y.C., Microstructure, mechanical and electrical properties of Cu-Ti3AlC2 and in situ TiCx composites, J. Mater. Res., 2008, vol. 23, no. 4, p. 924.
Ngai, T.L., Zheng, W., and Li, Y., Effect of sintering temperature on the preparation of Cu-Ti3SiC2 metal matrix composites, Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater. Int., 2013, vol. 23, no. 1, p. 70.
Sonestedt, M., Frodelius, J., Palmquist, J.-P., et al., Microstructure of high velocity oxy-fuel sprayed Ti2AlC coatings, J. Mater. Sci., 2010, vol. 45, no. 10, p. 2760.
Eklund, P., Bekers, M., Jansson, U., The M n + 1AXn phases: Materials science and thin-film processing, Thin Solid Films, 2010, vol. 518, no. 8, p. 1851.
Smithells Metals Reference Book, Brandes, E.A. and Brook, G.B., Eds., Reed Educational and Professional Publishing, 1992, 7th ed.
Lomovsky, O.L., Dudina, D.V., Ulianitsky, V.Yu., Cold and detonation spraying of TiB2-Cu nanocomposites, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, vols. 534–536, p. 1373.
Barsoum, M.W., El-Raghy, T., Rawn, C.J., Thermal properties of Ti3SiC2, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1999, vol. 60, no. 4, p. 429.
Dudina, D.V., Mali, V.I., Anisimov, A.G., et al., Ti3SiC2-Cu composites by mechanical milling and spark plasma sintering: Possible microstructure formation scenarios, Met. Mater. Int., 2013 (in press).
Kim, J.-S., Kwon, Y.-S., Dudina, D.V., Nanocomposites TiB2-Cu: Consolidation and erosion behavior, J. Mater. Sci., 2005, vol. 40, no. 13, p. 3491.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.V. Dudina, I.S. Batraev, V.Yu. Ulianitsky, M.A. Korchagin, G.V. Golubkova, S.Yu. Abramov, O.I. Lomovsky, 2014, published in Neorganicheskie Materialy, 2014, Vol. 50, No. 1, pp. 41–45.
The article was translated by the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dudina, D.V., Batraev, I.S., Ulianitsky, V.Y. et al. Control of interfacial interaction during detonation spraying of Ti3SiC2-Cu composites. Inorg Mater 50, 35–39 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168514010038
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168514010038