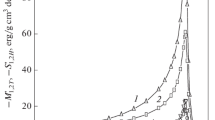
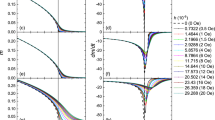
Abstract
The “construction of thermodynamics” of ferromagnet is performed in the spirit of Landau’s phenomenological approach but in view of magnetoelastic interaction (MEI) between magnetic subsystem and crystal lattice, which is not considered in the traditional interpretation of the theory. It is demonstrated that the inclusion of MEI reflected in the magnetization dependence of Debye temperature may be reduced to renormalization of the thermodynamic potential (TDP) and thermodynamic coefficients of Landau. Within the developed model, expressions are obtained for renormalized magnetic components of TDP and its first thermodynamic derivatives, in particular, the variation of molar enthalpy, molar volume, density, specific magnetization, and bulk magnetostriction. Model calculations demonstrating the importance of taking the TDP into account are performed on the real scale of temperatures and observed values of thermophysical functions in the absence of magnetic field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pytte, E., Ann. Phys. N.Y., 1965, vol. 32, no. 3, p. 377.
Tyablikov, S.V., Metody kvantovoi teorii magnetizma (The Methods of Quantum Theory of Magnetism), Moscow: Nauka, 1975.
Shimizu, M., J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1980, vol. 20, no. 1, p. 47.
Shimizu, M., Rep. Prog. Phys., 1981, vol. 44, no. 4, p. 329.
Kim, D.J., Phys. Rev. B, 1982, vol. 25, no. 11, p. 6919.
Turov, E.A. and Shavrov, V.G., Usp. Fiz. Nauk, 1983, vol. 140, no. 3, p. 429.
Zverev, V.M. and Silin, V.P., Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz., 1987, vol. 93, issue 2(8), p. 709.
Podgornykh, S.M. and Zatoplyaev, A.K., Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 1990, no. 12, p. 153.
Valiev, E.Z., Usp. Fiz. Nauk, 1991, vol. 161, no. 8, p. 87.
Zverev, V.M. and Silin, V.P., Pis’ma Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz., 1996, vol. 64, issue 1, p. 33.
Zverev, V.M., Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz., 1997, vol. 112, issue 5(11), p. 1863.
Landau, L.D. and Lifshitz, E.M., Teoreticheskaya fizika, T. 5, Ch. 1: Statisticheskaya fizika (Theoretical Physics, vol. 5, part 1: Statistical Physics), Moscow: Nauka, 1976, part 1.
Belov, K.P., Magnitnye prevrashcheniya (Magnetic Transformations), Moscow: GIFML, 1959.
Vonsovskii, S.V., Magnetizm. Magnitnye svoistva dia-, para-, ferro-, antiferro-i ferrimagnetikov (Magnetism: Magnetic Properties of Dia-, Para-, Ferro-, Antiferro-, and Ferrimagnetics), Moscow: Nauka, 1971.
Bodryakov, V.Yu., Integrated Studies into the Impact Made by Lattice and Magnetic Anharmonism on the Thermodynamic Properties of Solids, Doctoral (Phys.-Math.) Dissertation, Ekaterinburg: UGTU-UPI (Ural State Technical University-UPI), Ekaterinburg, 2005.
Levanyuk, A.P., Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz., 1959, vol. 36, issue 3, p. 810.
Stanley, H., Introduction to Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena, Oxford: Pergamon, 1971. Translated under the title Fazovye perekhody i kriticheskie yavleniya, Moscow: Mir, 1973.
Patashinskii, A.Z. and Pokrovskii, V.L., Fluktuatsionnaya teoriya fazovykh perekhodov (Fluctuation Theory of Phase Transitions), Moscow: Nauka, 1975.
Abrikosov, A.A., Osnovy teorii metallov (Fundamentals of the Theory of Metals), Moscow: Nauka, 1987.
Physics and Applications of Invar Alloys, Tokyo: Maruzen Co, 1978.
Oomi, G., Mori N. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 1981, vol. 50, no. 9, p. 2917.
Zakharov, A.I., Fizika pretsizionnykh splavov s osobymi teplovymi svoistvami (Physics of Precision Alloys of Special Thermal Properties), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1986.
Solontsov, A.Z., Vasil’ev, A.N., and Vagner, D.D., Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 2000, vol. 90, no. 2, p. 113 (Phys. Met. Metallogr. (Engl. transl.), vol. 90, no. 2).
Ruderman, M.A. and Kittel, C., Phys. Rev., 1954, vol. 96, no. 1, p. 99.
Yosida, K., Phys. Rev., 1957, vol. 106, no. 5, p. 893.
Bodryakov, V.Yu. and Povzner, A.A., Zh. Tekh. Fiz., 2004, vol. 74, no. 2, p. 66 (Tech. Phys. (Engl. transl.), vol. 74, no. 2).
Bodryakov, V.Yu. and Povzner, A.A., Fiz. Tverd. Tela, 2004, vol. 46, no. 5, p. 846.
Bodryakov, V.Yu., Povzner, A.A., and Safonov, I.V., Teplofiz. Vys. Temp., 2006, vol. 43, no. 3, p. 396 (High Temp. (Engl. transl.), vol. 43, no. 3, p. 391).
Bashkatov, A.N. and Bodryakov, V.Yu., Metally, 2006, no. 6, p. 75.
Bodryakov, V.Yu. and Povzner, A.A., Zh. Tekh. Fiz., 2007, vol. 77, no. 2, p. 65 (Tech. Phys. (Engl. transl.), vol. 77, no. 2).
Bodryakov, V.Yu. and Bashkatov, A.N., Zh. Tekh. Fiz., 2007, vol. 77, no. 3, p. 23 (Tech. Phys. (Engl. transl.), vol. 77, no. 3).
Bodryakov, V.Yu., Zh. Tekh. Fiz., 2007, vol. 77, no. 8, p. 54 (Tech. Phys. (Engl. transl.), vol. 77, no. 8).
Bodryakov, V.Yu. and Bashkatov, A.N., Zavod. Lab., 2005, vol. 71,no. 5, p. 29.
Bodryakov, V.Yu. and Povzner, A.A., Teplofiz. Vys. Temp., 2004, vol. 42, no. 4, p. 563 (High Temp. (Engl. transl.), vol. 42, no. 4, p. 565).
Bodryakov, V.Yu., Povzner, A.A., and Safonov, I.V., Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 2005, vol. 100, no. 1, p. 4 (Phys. Met. Metallogr. (Engl. transl.), vol. 100, no. 1).
Bodryakov, V.Yu., Povzner, A.A., and Safonov, I.V., Termodinamicheskii podkhod k opisaniyu metallicheskikh tverdykh tel, Teplofiz. Vys. Temp., 2006, vol. 43, no. 3, p. 396 [High Temp. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 43, no. 3, p. ].
Korn, G.A. and Korn, T.M., Mathematical Handbook for Scientists and Engineers, New York: McGraw-Hill, 1961. Translated under the title Spravochnik po matematike dlya nauchnykh rabotnikov i inzhenerov, Moscow: Nauka, 1970.
Novikova, S.I., Teplovoe rasshirenie tverdykh tel (Thermal Expansion of Solids), Moscow: Nauka, 1974.
Tablitsy fizicheskikh velichin. Spravochnik (Tables of Physical Quantities: A Reference Book), Kikoin, I.K., Ed., Moscow: Atomizdat, 1976.
Zinov’ev, V.E., Teplofizicheskie svoistva metallov pri vysokikh temperaturakh. Spravochnik (The Thermophysical Properties of Metals at High Temperatures: A Reference Book), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1989.
Fizicheskie velichiny. Spravochnik (Physical Quantities: A Reference Book), Grigor’ev, I.S. and Meilikhov, E.Z., Eds., Moscow: Energoatomizdat, 1991.
Ledbetter, H.M. and Reed, R.P., J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1973, vol. 2, no. 3, p. 531.
Frantsevich, I.V., Voronov, F.F., and Bakuta, S.A., Uprugie postoyannye i moduli uprugosti metallov i nemetallov (Elastic Constants and Elastic Moduli of Metals and Nonmetals), Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1982.
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.Yu. Bodryakov, 2008, published in Teplofizika Vysokikh Temperatur, Vol. 46, No. 4, 2008, pp. 522–532.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bodryakov, V.Y. The part played by magnetoelastic interaction in the forming of thermodynamic functions of ferromagnets: Thermodynamic potential and its first thermodynamic derivatives. High Temp 46, 474–483 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0018151X08040068
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0018151X08040068