Abstract
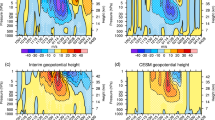
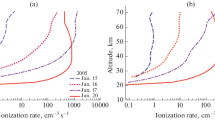
In this paper, we study the effects of solar proton events (SPEs) of January 2005 on the stratosphere circulation in the Southern Hemisphere according to the NCEP-DOE (National Centers for Environmental Prediction-Department of Energy) reanalysis (R-2) data. It was found that in the course of the considered events, in the upper stratosphere (30–10 hPa), where eastern transport of air masses dominates in the whole hemisphere in summer season (December–February), eastern winds noticeably weakened at middle and high latitudes (>40° S), while they strengthened at lower latitudes. In the lower stratosphere (100–50 hPa), where circulation is characterized by a western zonal flow at middle latitudes, a weakening of eastern winds took place only in the polar region (>60° S), with a maximum of the western zonal flow being shifted to higher latitudes. The effects of SPEs of January 2005 observed in the stratosphere circulation of the Northern and Southern Hemispheres were compared. It has been shown that in the Northern (winter) Hemisphere the SPE effects observed in variations of zonal wind velocity are more pronounced than those in the Southern (summer) Hemisphere. It is supposed that the circulation disturbances, which were detected in both hemispheres during the studied SPEs, may be caused by changes in the temperature regime of the polar atmosphere due to variations in its chemical composition (ozone depletion) associated with a considerable increase in the ionization rate.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Brasseur, G.P. and Solomon, S., Aeronomy of the Middle Atmosphere, Dordrecht: Springer, 2005.
Frederick, J.E. and Tinsley, B.A., The response of longwave radiation at the South Pole to electrical and magnetic variations: Links to meteorological generators and the solar wind, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2018, vol. 179, pp. 214–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j/jastp.2018.08.003
Heath, D.F., Krueger, A.J., and Crutzen, P.J., Solar proton event: Influence on stratospheric ozone, Science, 1977, vol. 197, pp. 886–889.
Holzworth, R.H., Norville, K.W., and Williamson, P.R., Solar flare perturbations in stratospheric current systems, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1987, vol. 14, no. 8, pp. 852–855.
Jackman, C.H., McPeters, R.D., Labow, G.J., et al., Northern Hemisphere atmospheric effects due to the July 2000 solar proton event, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2001, vol. 28, no. 15, pp. 2883–2886.
Jackman, C.H., Marsh, D.R., Vitt, F.M., et al., Northern Hemisphere atmospheric influence of the solar proton events and ground level enhancement in January 2005, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 2011, vol. 11, pp. 6153–6166. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-6153-2011
Kanamitsu, M., Ebisuzaki, W., Woollen, J., et al., NCEP-DOE AMIP-II Reanalysis (R-2), Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 2002, vol. 83, no. 11, pp. 1631–1643. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-83-11-1631
Krivolutsky, A.A., Klyuchnikova, A.V., Zakharov, G.R., et al., Dynamical response of the middle atmosphere to solar proton event of July 2000: Three-dimensional model simulations, Adv. Space Res., 2006, vol. 37, pp. 1602–1613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2005.05.115
Logachev, Yu.I., Bazilevskaya, G.A., Vashenyuk, E.V., et al., Catalogue of Solar Proton Events in the 23rd Cycle of Solar Activity (1996–2008), Moscow, 2016. http://www.wdcb.ru/stp/data/SPE/Catalog_SPE_23_ cycle_SA.pdf.
Miroshnichenko, L.I., Solar cosmic rays in the system of solar–terrestrial relations, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2008, vol. 70, pp. 450–466.
Pogosyan, Kh.P., Obshchaya tsirkulyatsiya atmosfery (General Circulation of the Atmosphere), Leningrad: Gidrometeoizdat, 1972.
Rusch, D.W., Gérard, J.-C., Solomon, S., et al., The effect of particle precipitation events on the neutral and ion chemistry of the middle atmosphere. I. Odd nitrogen, Planet. Space Sci., 1981, vol. 29, no. 7, pp. 767–774.
Seppälä, A., Verronen, P.T., Kyrölä, E., et al., Solar proton events of October–November 2003: Ozone depletion in the Northern Hemisphere polar winter as seen by GOMOS/ENVISAT, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2004, vol. 31, L19107. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL021042
Solomon, S., Rusch, D.W., Gérard, J.-C., et al., The effect of particle precipitation events on the neutral and ion chemistry of the middle atmosphere: II. Odd hydrogen, Planet. Space Sci., 1981, vol. 29, no. 8, pp. 885–893.
Tinsley, B.A., The global atmospheric electric circuit and its effects on cloud microphysics, Rep. Prog. Phys., 2008, vol. 71, no. 6, pp. 66801–66900.
Veretenenko, S., Effects of solar proton events of January 2005 on the middle atmosphere dynamics in the Northern Hemisphere, Adv. Space Res., 2021, vol. 68, no. 4, pp. 1814–1824.
Veretenenko, S.V. and Ogurtsov, M.G., Influence of solar–geophysical factors on the state of the stratospheric polar vortex, Geomagn. Aeron. (Engl. Transl.), 2020, vol. 60, no. 7, pp. 974–981.
Veretenenko, S. and Thejll, P., Effects of energetic Solar Proton Events on the cyclone development in the North Atlantic, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2004, vol. 66, no. 5, pp. 393–405.
Weeks, L.H., Cuikay, R.S., and Corbin, J.R., Ozone measurements in the mesosphere during the solar proton event of 2 November 1969, J. Atmos. Sci., 1972, vol. 29, pp. 1138–1142.
Zadorozhny, A.M., Kiktenko, V.N., Kokin, G.A., et al., Middle atmosphere response to the solar proton events of October 1989 using the results of rocket measurements, J. Geophys. Res., 1994, vol. 99, pp. 21059–21069.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The NCEP Reanalysis-2 data were provided by NOAA/OAR/ESLR PSL (Boulder, Colorado, USA) on the web-site https://psl.noaa.gov/. The ionization rates are available on the SOLARIS−HEPPA International Working Group website https://solarisheppa.geomar.de/solarprotonfluxes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author declares that he has no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by E. Petrova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veretenenko, S.V. Effects of Solar Proton Events of January 2005 on the Middle Atmosphere Circulation in the Southern Hemisphere. Geomagn. Aeron. 62, 924–931 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793222070180
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793222070180