Abstract
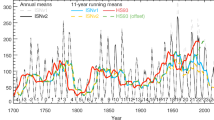
The propagation of cosmic rays in the Earth’s atmosphere is simulated. Calculations of the omnidirectional differential flux of neutrons for different solar activity levels are illustrated. The solar activity effect on the production rate of cosmogenic radiocarbon by the nuclear-interacting and muon components of secondary cosmic radiation in polar ice is studied. It has been obtained that the 14C production rates in ice by the cosmic ray nuclear-interacting component are lower or higher than the average value by 30% during periods of solar activity maxima or minima, respectively. Calculations of the altitudinal dependence of the radiocarbon production rate in ice by the cosmic radiation components are illustrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostinelli, S., Allison, J., Amako, K., et al., Geant4: A Simulation Toolkit, Nuclear Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A, 2003, vol. 506, pp. 250–303.
Boezio, M., Carlson, P., Franke, T., et al., Measurement of the Flux of Atmospheric Muons with the CAPRICE94 Apparatus, Phys. Rev. D, 2000, vol. 62, p. 032007.
Boezio, M., Bonvicini, V., Schiavon, P., et al., Energy Spectra of Atmospheric Muons Measured with the CAPRICE98 Balloon Experiment, Phys. Rev. D, 2003, vol. 67, p. 072003.
Desilets, D. and Zreda, M., Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Secondary Cosmic-Ray Nucleon Intensities and Applications to in Situ Cosmogenic Dating, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2003, vol. 206, pp. 21–42.
Dunai, T.J., Scaling Factors for Production Rates of in Situ Produced Cosmogenic Nuclides: A Critical Reevaluation, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2000, vol. 176, pp. 157–169.
Gleeson, L.J. and Axford, W.I., Solar Modulation of Galactic Cosmic Rays, Astrophys. J., 1968, vol. 154, pp. 1011–1026.
Gordon, M.S., Goldhagen, P., Rodbell, K.P., Zabel, T.H., Tang, H.H.K., Clem, J.M., and Bailey, P., Measurement of the Flux and Energy Spectrum of Cosmic-Ray Induced Neutrons on the Ground, IEEE Trans. Nuclear Sci., 2004, vol. 51, no. 6, pp. 3427–3434.
Heisinger, B., Lal, D., Jull, A.J.T., Kubik, P., Ivy-Ochs, S., Neumaier, S., Knie, K., Lazarev, V., and Nolte, E., Production of Selected Cosmogenic Radionuclides by Muons. 1. Fast Muons, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2002a, vol. 200, pp. 345–355.
Heisinger, B., Lal, D., Jull, A.J.T., Kubik, P., Ivy-Ochs, S., Knie, K., and Nolte, E., Production of Selected Cosmogenic Radionuclides by Muons: 2. Capture of Negative Muons, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2002b, vol. 200, pp. 357–369.
Lal, D., Jull, A.J.T., Pollard, D., and Vacher, L., Evidence for Large Century Time-Scale Changes in Solar Activity in the Past 32 kyr, Based on in Situ Cosmogenic 14C in Ice at Summit, Greenland, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2005, vol. 234, pp. 335–349.
Masarik, J. and Beer, J., An Updated Simulation of Particle Fluxes and Cosmogenic Nuclide Production in the Earth’s Atmosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 2009, vol. 114D, p. D11103.
Nesterenok, A.V. and Naidenov, V.O., Radiocarbon in the Antarctic Ice: The Formation of the Cosmic Ray Muon Component at Large Depths, Geomagn. Aeron., 2010, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 138–144 [Geomagn. Aeron. (Engl. transl.), 2010, vol. 50, p. 134].
Nesterenok, A.V. and Naidenov, V.O., In Situ Formation of Cosmogenic 14C by Cosmic Ray Nucleons in Polar Ice, Nuclear Instrum. Meth. Phys. Res. B, 2012, vol. 270, pp. 12–18.
Panasyuk, M.I., Stranniki Vselennoi Ili Ekho Bol’shogo Vzryva (Wanderers of the Universe or the Echo of Large Explosion), Fryazino: “Vek 2”, 2005.
Raubenheimer, B.C. and Stoker, P.H., Various Aspects of the Attenuation Coefficient of a Neutron Monitor, J. Geophys. Res., 1974, vol. 79, pp. 5069–5076.
Rogers, I.W. and Tristam, M., The Absolute Depth-Intensity Curve for Cosmic-Ray Muons Underwater and the Integral Sea-Level Momentum Spectrum in the Range 1–100 GeV/c, J. Phys. G: Nuclear Phys., 1984, vol. 10, pp. 983–1001.
Sato, T. and Niita, K., Analytical Functions to Predict Cosmic-Ray Neutron Spectra in the Atmosphere, Radiat. Res., 2006, vol. 166, pp. 544–555.
Standard Atmosphere 1976, Committee on Extension to the Standard Atmosphere COESA, US, 1976
Usoskin, I.G., Alanko-Huotari, K., Kovaltsov, G.A., and Mursula, K., Heliospheric Modulation of Cosmic Rays: Monthly Reconstruction for 1951–2004, J. Geophys. Res., 2005, vol. 110A, p. A12108.
Wiebel-Sooth, B., Biermann, P.L., and Meyer, H., Cosmic Rays. VII. Individual Element Spectra: Prediction and Data, Astron. Astrophys., 1998, vol. 330, pp. 389–398.
Ziegler, J.F., Terrestrial Cosmic Ray Intensities, IBM J. Res. Development, 1998, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 117–139.
http://badc.nerc.ac.uk/view/badc.nerc.ac.uk-ATOM-dataent-CIRA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nesterenok, A.V., Naidenov, V.O. Calculation of the solar activity effect on the production rate of cosmogenic radiocarbon in polar ice. Geomagn. Aeron. 52, 992–998 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793212080166
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793212080166