Abstract
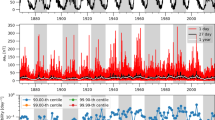
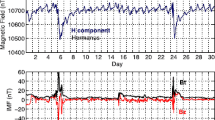
The paper suggests that spacecraft equipment failures in the near-Earth environment may be caused by one of the following types of streams coming to the Earth’s orbit: (a) slow solar wind in the streamer belt or chains; (b) sporadic solar wind; (c) proton flux with an energy of E > 60 MeV. The laws of solar-terrestrial physics derived to date allow sufficiently reliable determination of the sources of these streams on the Sun as well as fairly precise calculation of their parameters and time of arrival at the Earth’s orbit. We have concluded that spacecraft maintenance and extension of their service life require timely and fairly accurate information regarding the onset of an adverse environmental effect on spacecraft. A successful solution to the problem depends mainly on the current state of the art of research and development in solar-terrestrial, ionospheric, and magnetospheric physics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belov, A.V., Villorezi, Dzh., Dorman, L.I., et al., The Influence of the Cosmic Medium on the Functioning of Artificial Earth Satellites, Geomagn. Aeron., 2004, vol. 44, no. 4, p. 502.
Eselevich, M.V. and Eselevich, V.G., sporadic plasma fluxes and their sources in a period of extreme solar activity from October 26 through November 5, 2003, Kosm. Issl., 2004, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 595–607.
Eselevich, V.G., Physical Bases of the Relationship of Disturbances in the near-Earth Medium with Phenomena on the Sun, Int. Conf. “Solar-Terrestrial Physics,” 2005, no. 8, pp. 13–18.
Eselevich, M.V., Eselevich, V.G., and Fukiki, K., Streamer Belt and Chains As the Main Sources of Quasi-Stationary Slow Solar Wind, Sol. Phys., 2007, vol. 240, pp. 135–151.
Eselevich, V.G., Fainshtein, V.G., and Rudenko, G.V., Study of the Structure of Streamer Belts and Chains in the Solar Corona, Sol. Phys., 1998, vol. 188, no. 2, pp. 277–297.
Eselevich, V.G., Fainshtein, V.G., Rudenko, G.V., et al., Forecast of the Velocity of the Quasi-Stationary Solar Wind and the Intensity of Geomagnetic Disturbances Caused by It, Kosm. Issl., 2009, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 1–20.
Koshiishi, H., Matsumoto, H., and Goka, T., Single-Event Upset in Geostationary Transfer Orbit during Solar-Activity Maximum Period Measured by the Tsubasa Satellite, Adv. Space Res., 2008, vol. 42, pp. 1500–1503.
Popov, G.V. and Zherebtsov, G.A., The Role of Groundbased Geophysical Measurements in Studying the Electrification of Geostationary Satellites, in: Issledovaniya po geomagnetizmu, aeronomii i fizike Solntsa (Studies of the Geomagnetism, Aeronomy, and Physics of the Sun), Moscow: Nauka, 1989, no. 86, pp. 3–43.
Popov, G.V., Babkin, G.V., Degtarev, V.I, et al., Geophysical Forecasting of the Level of Radiative Electrification of Spacecraft in Orbital Conditions, in: Rukovodstvo dlya konstruktorov (Guidelines for Designers), Popova, G.V. and Babkin, G.V., Eds., Kaliningrad: TsNIImash., 1993.
Spacecraft Anomaly Database, National Geophysical Data Center, July 10, 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.G. Eselevich, A.I. Efimov, I.D. Tserenin, 2011, published in Solnechno-Zemnaya Fizika, 2011, Vol. 17, pp. 137–141.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eselevich, V.G., Efimov, A.I. & Tserenin, I.D. A study of the effect of different solar wind streams on spacecraft functioning. Geomagn. Aeron. 51, 1095–1100 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793211080172
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793211080172