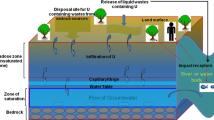
Abstract—The kinetics of Np(VI and V) reduction was studied in model underground water in the presence of bacteria, isolated from from deep-injection disposal of liquid radioactive wastes of Siberian Chemical Plant. Obtained data indicate a chemical instability of Np(VI) in the studied system. The reduction of neptunium (V) depended on its initial concentration and the presence of microorganisms. In microbiome samples, the reduction rate has significantly increased and neptunium-bearing particles more than 200 nm in size were formed. At neptunium concentrations less than 10–7 М, the reduction rate constant did not depend on the radionuclide content (half-reaction period of 36–40 days). An increase of Np concentration to 10–6 М led to a two-fold decrease of the reduction rate constant.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
K. A. Boldyrev, D. V. Kryuchkov, K. V. Martynov, A. S. Nuzhnyi, and V. V. Suskin, Development of Algorithms for Estimating Radionuclide Migration beyond the IBB with Allowance for their Evolution, Preprint IBRAE-2017-11 (IBRAE, Moscow, 2017) [in Russian].
D. L. Clark, S. Siegfried, G. Hecker, D. Jarvinen, and M. P. Neu, “Plutonium,” The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements, Ed. by L. R. Morss, N. M. Edelstein, and J. Fuger, (Springer, Dordrecht, 2006), Vol. 2, 813–1264.
D. Feikhi, Chemistry of Actinides (Mir, Moscow, 1991), Vol. 1, pp. 490–491 [in Russian].
G. A. Icopini, H. Boukhalfa, and M. P. Neu, “Biological reduction of Np(V) and Np(V) citrate by metal-reducing bacteria,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 41 (8), 2764–2769 (2007).
S. A. Ivanova, M. N. Mikheeva, A. P. Novikov, and B. F. Myasoedov, “Preconcentration of neptunium by supported liquid membranes for luminescent analyses of environmental samples,” J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., Lett. 186, 341–345 (1994).
I. M. Kosareva, A. V. Safonov, M. K. Savushkina, B. G. Ershov, S. A. Kabakchi, Yu. A. Revenko, R. R. Khafizov, V. V. Bondin, and T. N. Nazina, “Physicochemical and biological monitoring of deep repositories for liquid radioactive wastes,” Atomic Energy 103 (2), 615–622 (2007).
J. R. Lloyd, J. Chesnes, S. Glasauer, D. J. Bunker, F. R. Livens, and D. R. Lovley, “Reduction of actinides and fission products by Fe(III)-reducing bacteria,” Geomicrobiol. J. 19, 103–120 (2002).
D. R. Lovley and E. J. Phillips, “Reduction of uranium by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans,” Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58 (3), 850–856 (1992).
D. R. Lovley, E. J. P. Phillips, Y. A. Gorby, and E. R. Landa, “Microbial reduction of uranium,” Nature 350, 413–416 (1991).
N. N. Lyalikova and T. V. Khizhnyak, “Reduction of heptavalent technetium by acidophilic bacteria of the genus Thiobacillus,” Microbiology 65 (4), 468–473 (1996).
L. E. Macaskie, “The application of biotechnology to the treatment of wastes produced from the nuclear fuel cycle: biodegradation and bioaccumulation as a means of treating radionuclide-containing streams,” Crit. Rev. Biotechnol.11, 41–112 (1991).
L. E. Macaskie, K. M. Bonthrone, P. Yong, and D. T. Goddard, “Enzymically mediated bioprecipitation of uranium by Citrobacter sp.: a concerted role for exocellular lipopolysaccharide and associated phosphatase in biomineral formation,” Microbiol. 146, 1855–1867 (2000).
B. F. Myasoedov and A. P. Novikov, “Main sources of radioactive contamination in Russia and methods for their determination and speciation,” Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., Art. 229 (1–2), 33–38 (1997).
T. N. Nazina, A. V. Safonov, I. M. Kosareva, V. S. Ivoilov, A. B. Poltaraus, and B. G. Ershov, “Microbiological processes in the Severnyi deep disposal site for liquid radioactive wastes,” Microbiol. 79 (4), 528–537 (2010).
A. P. Novikov, “Migration of radioniclides in the environment,” Geochem. Int. 48 (13), 1285–1398 (2010).
A. P. Novikov, Yu. I. Fabelinsky, E. A. Lavrinovich, T. A. Goryachenkova, and A. A. Grechnikov, “Membrane luminescence determination of technogenic actinides and their speciation in environmental objects,” Geochem. Int. 54 (13), 1196–1209 (2016).
A. P. Novikov, E. V. Zakharova, T. A. Goryachenkova, E. V. Kuzovkina, and A. M. Emel’yanov, “Fractionation of colloidal matter of stratal waters during deep burial of radioactive wastes,” Geochem. Int. 56 (7), 743–749 (2018).
D. L. Parkhurst and C. A. J. Appelo, User’s Guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): A Computer Program for Speciation,Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Rransport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations (1999).
I. Puigdomenech, “INPUT, SED, and PREDOM: Computer programs drawing equilibrium diagrams”, TRITA-OOK-3010 12, Royal Institute of Technology, Dept. Inorg. Chem., S-100 44 Stockholm (1983).
J. C. Renshaw, J. R. Lloyd, and R. L. Francis, “Microbial interaction with actinides and long-lived fission products,” C.R. Chimie 10, 1067–1077 (2007).
B. E. Rittmann, J. E. Banaszak, and D. T. Reed “Reduction of Np(V) and precipitation of Np(IV) by an anaerobic microbial consortium,” Biodegradation 13 (5), 329–342 (2002).
A. I. Rybal’chenko, M. K. Pimenov, and P. P. Kostin, Deep Burial of Liquid Radioactive Wastes (IzdAT, Moscow, 1994) [in Russian].
A. V. Safonov, T. L. Babich, D. S. Sokolova, D. S. Grouzdev, T. P. Tourova, A. B. Poltaraus, E. V. Zakharova, A. Y. Merkel, A. P. Novikov, T. N. Nazina, “Microbial community and in situ bioremediation of groundwater by nitrate removal in the zone of a radioactive waste surface repository,” Front. Microbiol. 1985 (9), 2–17 (2018).
C. L. Thorpe, K. Morris, J. R. Lloyd, M. A. Denecke, K. A. Law, K. Dardenne, C. Boothman, P. Bots, and T. W. Law Gareth, “Neptunium and manganese biocycling in nuclear legacy sediment systems,” Appl. Geochem. 63, 303–309 (2015).
F. Weigel. “Uranium,” The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements, Ed. by L. R. Morss, N. M. Edelstein, and J. Fuger (Springer, Dordrecht, 2006), Vol. 1, pp. 253–698.
A. J. Williamson, “Microbially mediated reduction of Np(V) by a consortium of alkaline tolerant Fe(III)-reducing bacteria,” Mineral. Mag. 79 (6), 1287–1295 (2016).
A. A. Zubkov, O. V. Makarova, V. V. Danilov, E. V. Zakharova, E. P. Kaimin, K. A. Meyailo, and A. I. Rybal’-chenko, “Anthropogenic geochemical processes in reservoir sandstones during disposal of liquid radioactive wastes,” Geoekologiya, No. 2, 133–144 (2002).
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 17-17-01212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by M. Bogina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novikov, A.P., Safonov, A.V., Babich, T.L. et al. Biotransformation of Neptunium in Model Groundwaters. Geochem. Int. 58, 182–188 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702920020081
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702920020081