Abstract
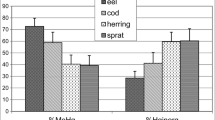
The mercury content is studied in fish from the European Russian lakes and rivers. The results revealed significant accumulation of mercury in fish as the uppermost trophic level of aquatic ecosystems even at extremely low (<10 ng/L) content of this element in water. The maximum accumulation was found in the predatory fishes from Middle and Lower Volga, Severnaya Dvina, and small lakes subjected to anthropogenic air pollution. The influence of temperature and geochemical factors on the penetrative ability of mercury in a fish organism is considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A Guidebook on Hygiene of Water Supply, Ed. By S. N. Cherkinsky (Meditsina, Moscow, 1975) [in Russian].
A Guidebook on the Control of Potable Water (VOZ, Geneva,1994), 2nd Ed., Vol. 1 [in Russian].
A list of Fishery Norms of Maximally Admissible Concentrations (MAC) and Approximate Safe Levels of Exposure (ASLE) of Toxic Matters for Water of Aquatic Objects of Fishery Significance (VNIRO, Moscow, 1999) [in Russian].
A. N. Afonin, K. L. Lipiyainen, and V. Yu. Tsepelev, Maps of the Mean and Multi-Year Air Temperature, (St. Petersburg, Univ., St. Petersburg, 2006) [in Russian]. http://wwwagroatlasru
Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Ed. by R. K. Pachauri and A. Reisinger (IPCC, Geneva, 2008).
T. Crommentuijn, D. Sijm, J. Bruijn, M. Hoop, K. Leeuwen, and E. Plassche, “Maximum permissible and negligible concentrations for metals and metalloids in the Netherlands, taking into account background concentrations,” J. Environ. Manag. 60, 121–143 (2000).
Environmental Quality Objectives for Hazardous Substances in Aquatic Enviroment (UMWELTBUNDESAMT, Berlin, 2001).
A. Farkas, J. Salánki, and A. Specziár “Age- and size-specific patterns of heavy metals in the organs of freshwater fish Abramis brama L. populating a low-contaminated site,” Water Res. 37, 959–964 (2003).
A. S. Friedmann, E. Kimble Costain, L. Deborah, Stansley W. MacLatchy, and E. J. Washuta, “Effect of mercury on general and reproductive health of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) from three lakes in New Jersey,” Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 52, 117–122 (2002).
M. Gochfeld, “Case of mercury exposure, bioavailability and absorption,” Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 56, 174–179 (2003).
T. Gouin, J. M. Armitage, I. T. Cousins, D. C. Muir, C. A. G. Ng, L. Reid, and S. Tao, “Influence of global climate change on chemical fate and bioaccumulation: the role of multimedia models,” Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 32, 20–31 (2013).
A. G. Heath, Water Pollution and Fish Physiology (Lewis Publishers, Amsterdam, 2002).
T. R. Hrabik and C. J. Watras, “Recent declines in mercury concentration in a freshwater fishery: isolating the effects of de-acidification and decreased atmospheric mercury deposition in Little Rock Lake,” Sci. Total Environ. 297, 229–237 (2002).
“Intercomparison 1024: pH, Cond, HCO3, NO3 + NO2, C1, SO4, Ca, Mg, Na, K, Fe, Mn, Cd, Pb, Cu, Ni, and Zn. International Cooperative Programme on Assessment and Monitoring of Acidification of Rivers and Lakes,” iReports of Norwegian Institute of Water Research No. 6029. (Oslo, 2010)
A. P. Losev, Praticum on Agrometeorological Support of Plant Growing (Gidrometeoizdat, St. Petersburg, 1994) [in Russian].
MAFF. Fishery and Food. Aquatic Environment Monitoring Report of Ministry of Agriculture, (Directorate of Fisheries Research, Lowestoft, 1995) 89p.
M. Maily, K. Bishop, L. Bridman, et al. “Critical levels of atmospheric pollution for operation modeling of mercury in forest and lakes ecosystems,” Sci. Tot. Environ. 304, 83–106 (2003).
J. Manio, Responses of Headwater Lakes to Air Pollution Changes in Finland (Helsinki, 2001).
S. J. Moe, K. D. Schamphelaere, W. H. Clements, M. T. Sorensen, P. J. Van den Brink, and M. Liess, “Combined and interactive effects of global climate change and toxicants on populations and communities,” Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 32, 49–61 (2013).
T. I. Moiseenko, “Impact of geochemical factors of aquatic environment on the metal bioaccumulation in fish,” Geochem. Int. 53 (3), 213–223 (2015).
T. I. Moiseenko, L. P. Kudryavtseva, and N. A. Gashkina, Trace Elements in Terrestrial Surface Waters: Technophilic Properties, Bioaccumulation, and Ecotoxicology (Nauka, Moscow, 2006). [in Russian].
T. I. Moiseenko, B. L. Skjelkvale, N. A. Gashkina, et al. “Water chemistry in small lakes along a transect from boreal to arid ecoregions in European Russia: effects of air pollution and climate change,” Appl. Geochem. 28, 69–79 (2013).
J. Moore and S. Ramamurthy, Heavy Metals in Natural Waters (Springer, New York, 1984).
G. Lithner, Quality Criteria for Lakes and Watercourses. Background Report 2—Metals, Swedish EPA Report 3628 (1989).
J. O. Niagu, J. M. Pacyna, J. B. Milford, and C. L. Davidson, Distribution and Characteristic Features of Chromiumin the Atmosphere, Ed. by J. O. Niagu and C. L. Davidson (Wiley Interscience Press, New York, 1988), pp. 125–173.
M. A. Perevoznikova, and E. A. Bogdanova, Heavy Metals in the Fresh-Water Ecosystems (GosNIORKh, St. Petersburg, 1999) [in Russian].
P. A. Popov, Assessment of Ecological State of Basins by Ichthyoindication (NGU, Novosibirsk, 2002) [in Russian].
B. A. Revich, S. L. Fvaliani, and G. I. Tikhonova, Environment and Population Health: Regional Ecological Politics (TsEPR, Moscow, 2003) [in Russian].
D. J. Spry and J. G. Wiener, “Metal bioavailability and toxicity to fish in low-alkalinity lakes: a critical review,” Environ. Pollut. 71, 243–304 (1991).
Z. Svobodová, L. Dušek, M. Hejtmánek, B. Vykusová, and R. Šmid “Bioaccumulation of mercury in various fish species from Orlik and Kamýk water reservoirs in the Czech Republic,” Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 43, 231–240 (1999).
E. B. Swain, D. R. Engstrom, M. E. Brigham, T. A. Henning, and P. L. Brezonic, “Increasing rates of atmospheric mercury deposition in midcontinental North America,” Science 257, 784–787 (1992).
Toxic Chemical Matters. Inorganic Compounds of Groups V–VIII (Khimiya, Leningrad, 1989) [in Russian].
C. J. Watras, R. C. Back, S. Halvorsen, et al. “Bioaccumulation of mercury in pelagic freshwater food webs,” Sci. Tot. Environ 219, 183–208 (1998).
William F. Fitzgerald, Carl H. Lamborg, and Chad R. Hammerschmidt, “Marine biogeochemical cycling of mercury,” Chem. Rev. 107, 641–662 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © T.I. Moiseenko, N.A. Gashkina, 2016, published in Geokhimiya, 2016, No. 6, pp. 495–504.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moiseenko, T.I., Gashkina, N.A. Bioaccumulation of mercury in fish as indicator of water pollution. Geochem. Int. 54, 485–493 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702916060045
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702916060045