Abstract
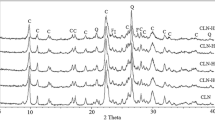
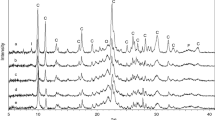
The clinoptilolite rich zeolite from Bigadiç which was formed from alteration of volcanic glass were treated with acidic (HCl, H3BO3, H3PO4), alkaline (KOH, NaOH) solutions. Hydrothermally treated and untreated samples were heat treated at 400, 550 and 700°C. XRD, ICP-MS and N2 gas adsorption were used for physicochemical characterization of zeolites. Considering the Si/Al > 4 and Na+K/Ca+Mg < 1 ratios, zeolite sample is included to earth alkali clinoptilolite class (Heu II) which is also revealed by thermal treatments. Since zeolite structure contains low alkalies it was at collapsed 550°C.
The removal of oxide elements efficiency of acids and alkalies were in the order of HCl > H3PO4 > HBO3 > KOH > NaOH. XRD analysis indicated that the structure of zeolite was not altered with acids and alkali treatments. The structure of zeolite treated with HCl and other acids started to deform at 400 and 550°C respectively. In treatment with HCl, Si/Al ratio increases with significant a decrease in K content which resulted in a decrease in the heat stability of zeolite. No change was observed in the structure and thermal stability of clinoptilolite after alkali treatments. The fact that although significant amount of Na is removed with H3BO3 acid and Na is increased with NaOH but the thermal stability remains the same indicates that Na cation is not an important parameter as much as K. HCl and H3PO4 acid treatments increased the surface area depending on the dissolution of amorphous material and H3PO4 was found to be more effective. However, the total pore size decreased due to formation of new micropores.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. R. Boles, “Composition, Optical Properties, Cell Dimensions and Thermal Stability of Some Heulandite Group Zeolites,” Am. Mineral. 57, 1463–1493 (1972).
A. Alietti, “Polymorphism and Crystal Chemistry of Heulandites and Clinoptilolites,” Am. Mineral. 57, 1448–1462 (1970).
B. Mason and L. B. Sand, “Clinoptilolite from Patagonia. The Relationships between Clinoptilolite and Heulandite,” Am. Mineral. 45, 341–350 (1960).
F. A. Mumton, “Clinoptilolite Redefined,” Am. Mineral. 45, 351–359 (1960).
A. Alietti, G. Gottardi, and L. Poppi, “The Heat Behavior of Cation Exchanged Zeolites with Heulandite Structure,” Tschermarks Min. Pet. Mitt. 21, 291–298 (1972).
H. Minato and M. Utada, “Clinoptilolite from Japan,” Adv. Chem. Series 101, 311–316 (1971).
M. Doula and A. Dimirkou, “Copper Adsorption and Si, Al, Ca and Na Release from Clinoptilolite,” J. Colloid. Inter. Sci. 245, 237–.
C. H. Baerlocher, W. M. Meier, and D. H. Oslon, “Atlas of Zeolite Framework Types,” (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2001).
V. Campos, L. C. Morais, and P. M. Buncler, “Removel of Chromate from Aqueous Solution using Treated Natural Zeolite,” Environ. Geol. 52(8), 1521–1525 (2006).
E. Valcke, B. Engels, and A. Cremers, “The Use of Zeolites as Amendments Radiocaesium- and Radiostrontium-Contaminated Soils, a Soil-Chemical Approach, Cs-K Exchange in Clinoptilolite and Morderite,” Zeolites 18, 205–211 (1997).
M. W. Ackley, S. R. Rege, and H. Saxena, “Application of Natural Zeolites in the Purification and Separation of Gases,” Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 61, 25–42 (2003).
D. Zhao, K. Cleare, C. Oliver, et al., “Characteristics of the Synthetic Heulandite-Clinoptilolite Family of Zeolites,” Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 21, 371–379 (1997).
S. W. Jeong and J. H. Kim, G. Seo, “Liquid-Phase Degradation of HDPE over Alkali-Treated Natural Zeolite Catalysts,” Korean J. Chem. Emg. 18, 848 (2001).
Ch. Panagiotopoulou, E. Kontori, Th. Perraki, et al., “Dissolution of Aluminosilicate Minerals and By-Products in Alkaline Media,” J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 42(9), 2967–2973 (2006).
H. C. Lee, H. C. Woo, R. Ryoo, et al., “Skeletal Isomerization of N-butanes to Isobutene over Acid-Treated Natural Clinoptilolite Zeolites,” Appl. Catal. 196, 135–142 (2000).
G. E. Christidis, S. Kosiari, and E. Petavratzi, “Acid Activation and Bleaching Capacity of Bentonites from the Troodos Ophiolite, Cyprus,” Appl. Clay Sci. 24, 79–91 (2003).
R. G. Gevorkyan, H. H. Sargsyan, G. Karamyan, et al., “Study of Absorption Properties of Modified Zeolites,” Chem. Erde — Geochemistry, 62(3), 237–242 (2002).
C. Helvacı and F. Orti, “Sedimentology and Diagenesis of Miocene Clemanite-Ulexite Deposits (Western Anatolia, Turkey),” J. Sediment. Res. 68(5), 1021–1033, (1998).
H. Yalçın and M. N. Gündoǧdu, “Emet ve Kırka Volkanosedimanter Gölsel Basenlerinde Zeolitlerin Kimyasal Bileşimleri, Kristal Morfolojileri ve ısıil kararlılıkları arasındaki ilişkiler,” Doǧa-Türk Yerbilimleri Dergisi 1, 63–75, (1992). (In Turkish).
Erkül, F., Helvacı, C., Sözbilir, H., “Olivine Basalt and Trachyandesite Peperites formed at the Subsurface/Surface Interface of a Semi-Arid Lake: An Example from the Early Miocene Bigadi-Basin, Western Turkey,” J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 149, 240–262, (2006).
M. N. Gündoǧdu, H. Yalçın, A. Temel, et al., “Geological, Mineralogical and Geochemical Characteristics of Zeolite Deposits Associated with Borates in the Bigadi-, Emet and Kırka Neogene Lacustrine Basins, Western Turkey,” Mineral Deposita 31, 492–451 (1996).
M.N. Gündoǧdu, Neojen Yaşlı Bigadiç Sedimanter Baseninin Jeolojik, Mineralojik ve Jeokimyasal Incelenmesi, PhD. Thesis (Ankara, 1982). (In Turkish).
R. Toprak and I. Girgin, “Aktifle tirilmi Klinoptilolit ile Deri Sanayii atιk Sularιndan Kromun Giderilmesi,” in TUB TAK Ed. by T. J. Engin., Environ. Sci. 24, 343–351 (2000) (In Turkish).
F. Cakicioǧlu-Ozkan and S. Ulku, “The Effect of HCl Treatment on Water Vapor Adsorption Characteristics of Clinoptilolite Rich Natural Zeolite,” Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 77, 47–53, (2005).
S. Brunauer, P. H. Emmet and E. Teller, “Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers,” J. Am. Chem. Soc. 60, 309–319, (1938).
E. P. Barrett, L. G. Joyner, and P. P. Halenda, “The Determination of Pore Volume and Area Distributions in Porous Substances: I. Computations from Nitrogen Isotherms,” J. Am. Chem. Soc., 73, 373–380, (1951).
M. M. Dubinin, “The Potential Theory of Adsorption of Gases and Vapors au]for Adsorbents with Energetically Nonuniform Surfaces,” Chem. Rev. 60, 1–70, (1960).
S. Yamamoto, S. Suriyama, M. Osamu, et al., “Dissolution of Zeolite in Acidic and Alkaline Aqueous Solutions as Revealed by AFM Imaging,” J. Phys. Chem. 100, 474–482, (1996).
K. Okada, N. Arimitsu, Y. Kameshima, et al., “Preparation of Porous Silica from Chlorite by Selective Acid Leaching,” Appl. Clay Sci. 30, 116–124, (2005).
W. P. Gates, M. D. Anderson, M. D. Raven, et al., “Mineralogy of Bentonite from Miles, Quesland, Australia and Characterisation of Acid Activation Products,” Clay Geotechn. Eng., Appl. Clay Sci. 20, 189–197 (2002).
K. Okada, A. Shimail, T. Takei, et al., “Preparation of Microporous Silica from Metakaolinite by Selective Leaching Method,” Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 21, 289–296 (1998).
M. Rozic, S. Cerjan-Stefanovic, and L. Curkovic, “Evaluation of Croation Clinoptilolite and Montmorillonit-Rich Tuffs Ammonium Removal,” Croat. Chem. Acta 75, 255–269, (2002).
X. Cheng, Y. Zhong, J. Wang, et al., “Studies on Modificaton and Structural Ultra-Stabilization of Natural STI Zeolite,” Micropor. Mesop. Mater. 83, 233–243 (2005).
N. C. Brady, The Nature and Properties of Soils, 14th Ed. (New York, 1990).
N. Kantiramis, C. M. Chrissafis, and K. Paraskevopoulos, “Thermal Distinction of HEU-Type Mineral Phases Contained in Greek Zeolite-Rich Volcaniclastic Tuffs,” Eur. J. Miner. 18(4), 509–516, (2006).
Sr. Petrov,, “X-Ray Powder Diffraction Studies of Cation Exchanged Natural Zeolites,” in Mat. 1st. Nat. Symp. Diffr. Methods, 156 (1983).
R. I. Iznaga, A. Gomez, G. Rodriguez-Fuentes, et al., “Natural Clinoptilolite as Exchanger of Ni+ and NH +4 Ions under Hydrothermal Conditions and High Ammonia Concentration,” Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 53, 71–80 (2002).
A. Rivera, G. Rodríguez-Fuentes, and E. Altshuler, “Characterization and Neutralizing Properties of a Natural Zeolite/Na2CO3 Composite Material,” Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 24, 51–58, (1998).
A. Alietti, M. F. Brigatti, and L. Poppi, “Natural Carich Clinoptilolite (Heulandites of Group 3: New Data and Review,” N. Jb. Miner. 11, 493–501 (1977).
P. Misaelides, A. Godelitsas, F. Link, et al., “Application of the Al (pγ)28 Si Nuclear Reaction to the Characterization of the Near Surface Layers of Acid Treated HEU-Type Zeolite Crystals,” Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 6, 37–42, (1996).
A. Alberti, “The Crystal Structure of Two Clinoptilolites,” Tshermarks Min. Pet. Mitt. 19, 176–184, (1975).
A. Langella, M. Pansini, G. Cerr, et al., “Thermal Behavior of Natural and Cation-Exchanged Clinoptilolite from Sardinia (Italy),” Clays Clay Miner. 51(6), 625–633, (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akkoca, D.B., Yιlgιn, M., Ural, M. et al. Hydrothermal and thermal treatment of natural clinoptilolite zeolite from Bigadiç, Turkey: An experimental study. Geochem. Int. 51, 495–504 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702913040022
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702913040022