Abstract
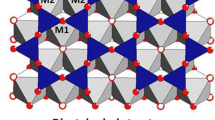
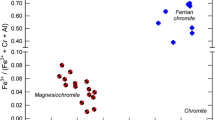
The paper proposes pioneering data on the polarized optical absorption spectra of Li-Fe micas: intermediate members of the siderophyllite-zinnwaldite-polylithionite and annite-protolithionite-zinnwaldite-trilithionite series with variable Fe and Li proportions and Li- and Fe-bearing muscovite (phengite). Based on the analysis of structural data, the complicated structure of the Fe2+ → Fe3+ charge transfer band in the mica structures is explained, and arguments are presented to justify the ascribing of its shortwave component (CTB-1, ν = 17200-14900 cm−1) to charge transfer in the pair Fe2+(M2) → Fe3+(M2) and the longwave component (CTB-2, ν = 14200-13600 cm−1) to charge transfer in the pair Fe2+(M1) Fe3+(M2). It is demonstrated that the anomalous shift of the superposition of two-component CTB toward the shortwave region, to 17000 cm−1, results from a decrease in the length of oxygen edges between adjacent M2M2 and M1M2 tetrahedrons when Li is accommodated in the mica structure. The first data are presented on the spectrum of Fe2+ ions in large distorted M3(M1) tetrahedrons (OAC Fe2+ II) in hetero-octahedral Li micas (zinnwaldite), and the behavior of the corresponding absorption bands at 11400 and 8000 cm−1 is determined. It is proved that characteristics of the optical spectra of Fe2+ ions can be used as an indicator of the structure of the octahedral layer in the mica structures. Results of the comparative analyses of spectral parameters of the Fe2+ → Fe3+ charge transfer, crystal field spectra of Fe2+ ions, and the crystal-chemical characteristics controlling them in micas of the polylithionite-siderophyllite series are completely consistent with the character of cation ordering in the crystal structures of these micas determined by X-ray diffraction analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. K. Lazarenko, V. I. Pavlishin, V. T. Latysh, and Yu. G. Sorokin, Mineralogy and Genesis of Miarolic Pegmatites from Volhynia (L’vovskii Univ., Lvov, 1973) [in Russian].
N. I. Ponomareva, V. V. Gordienko, and V. V. Butorin, “Physicochemical Conditions of the Formation of Lithium-Iron Micas in Granite Pegmatites,” Zap. Vsesoyuz. Mineral. Ob-va 122, 102–106 (1993).
T. N. Shuriga, A. P. Zhukhlistov, B. B. Zvyagin, et al., “Typomorphism of Lithium Micas and Its Applications,” in New Data on Typomorphic Minerals (Nauka, Moscow, 1980), pp. 228–243 [in Russian].
M. F. Brigatti, C. Lugli, L. Poppi, et al., “Crystal Chemical Variation in Li- and Fe-Rich Micas from Pikes Peak Batholith, Central Colorado,” Am. Mineral. 85, pp. 1275–1286 (2000).
P. Černý and D. M. Burt, “Paragenesis, Crystallochemical Characteristics and Geochemical Evolution of Micas in Granite Pegmatites,” in Micas, Ed. by S. W. Bailey, Rev. Mineral. 13, 257–356 (1984).
E. E. Foord, P. Cerny, L. L. Jackson, et al., “Mineralogical and Geochemical Evolution of Micas from Miarolitic Pegmatites of Anorogenic Pikes-Peak Batholith, Colorado,” Mineral. Petrol. 55, 1–26 (1995).
E. Roda-Robles, A. Pesquera, P. Gil-Crespo, et al., “Mineralogy and Geochemistry of Micas from the Pinilla de Fermoselle Pegmatite (Zamora, Spain),” Eur. J. Mineral. 18, 369–377 (2006).
V. I. Pavlishin, “Infrared Spectra of Micas of the Lithium-Iron Series,” Zap. Vsesoyuz. Mineral. Ob-va 104, 70–74 (1975).
A. M. Kalinichenko, V. I. Pavlishin, and I. V. Matyash, “On the Allocation of Iron Ions in the Structure of Lithium-Iron Micas: Data of Proton Magnetic Resonance,” Konstitutsiya Svoistva Mineralov, No. 9, 48–52 (1975).
C. Levillain, P. Maurel, and F. Menil, “Mossbauer Studies of Synthetic and Natural Micas of the Polylithionite-Siderophyllite Join,” Phys. Chem. Minerals 7, 71–76 (1981).
A. I. Bakhtin, Rock-Forming Silicates: Optical Spectra, Crystal Chemistry, Relations to Color, and Typomorphism (Kazanskii Univ., Kazan, 1985) [in Russian].
A. N. Platonov and T. N. Shuriga, “Optical Spectra and Coloration of Muscovites from Rare-Metal Deposits,” Mineral. Zh. 27(2), 73–80 (2005).
V. M. Khomenko, V. F. Grinchenko, A. N. Platonov, and O. V. Zinchenko, “Nature and Typomorphic Significance of Biotite Color in Granitoid Complexes with Reference to the Northwestern Ukrainian Shield,” Mineral. Zh. 10(4), 23–31 (1988).
V. M. Khomenko, A. N. Platonov, and N. I. Krasnova, “Optical Properties of Phlogopites from the Kovdor Massif,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Geol., No. 12, 94–105 (1991).
G. H. Faye, “The Optical Absorption Spectra of Certain Transition Metal in Muscovite, Lepidolite, and Fuchsite,” Can. J. Earth Sci. 5, 31–38 (1968).
G. H. Faye, “The Optical Absorption Spectra of Iron in Six-Coordinate Sites in Chlorite, Biotite, Phlogopite and Vivianite. Some Aspects of Pleochroism in the Sheet Silicates,” Can. Mineral. 9, 403–425 (1968).
D. W. Robbins and R. G. Strens, “Charge Transfer in Ferromagnesian Silicates: The Polarized Electronic Spectra of Trioctahedral Micas,” Mineral. Mag. 38, 551–563 (1972).
G. R. Rossman, “Spectroscopy of Micas,” in Micas, Ed. by S. W. Bailey, Rev. Mineral. 13, 145–181 (1984).
G. Smith, “Low Temperature Optical Study of Metal-Metal Charge Transfer Transitions in Various Minerals,” Phys. Chem. Minerals 3, 375–383 (1978).
V. I. Pavlishin, T. F. Semenova, and I. V. Rozhdestvenskaya, “Protolithionite-3T: Structure, Typochemistry, and Significance,” Mineral. Zh. 3(1), 47–60 (1981).
S. Guggenheim, “Cation Ordering in Lepidolite,” Am. Mineral. 66, 1221–1232 (1981).
S. Guggenheim and S. W. Bailey, “The Refinement of Zinnwaldite-1M in Subgroup Symmetry,” Am. Mineral. 62, 1158–1167 (1977).
M. Rieder, J. Hybler, L. Smrcok, and Z. Weiss, “Refinement of the Crystal Structure of Zinnwaldite 2M1,” Eur. J. Mineral. 8, 1241–1248 (1996).
Z. Weiss, M. Rieder, L. Smrčok, et al., “Refinement of the Crystal Structures of Two “Protolithionites”, Eur. J. Mineral. 5, 493–502 (1993).
F. Sartori, M. Franzini, and S. Merlino, “Crystal Structure of 2M2 Lepidolite,” Acta Crystallogr. 29, 573–578 (1973).
H. Takeda and C. W. Burnham, “Fluor-Polilithionite: A Lithium Mica with Nearly Hexagonal (Si2O5)−2 Ring,” Mineral. J. (Japan) 6, 102–109 (1969).
M. N. Taran, K. Langer, I. Abs-Wurmbach, et al., “Local Relaxation Around [6]Cr3+ in Synthetic Pyrope-Knorringite Garnets, [8]Mg [6]3 (Al1 − x Cr [4]x ) [4]2 Si3O12, from Electronic Absorption Spectra,” Phys. Chem. Minerals 31, 650–657 (2004).
M. D. Foster, “Interpretation of the Composition of Trioctahedral Micas,” U.S. Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 354B, 1–49 (1960).
M. F. Brigatti, D. E. Kile, and L. C. Poppi, “Crystal Structure and Crystal Chemistry of Lithium-Bearing Muscovite 2M1,” Can. Mineral. 39, 1171–1180 (2001).
R. G. Burns, Mineralogical Application of Crystal Field Theory (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1993).
R. G. Burns, “Intervalence Transitions in Mixed-Valence Minerals of Iron and Titanium,” Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 9, 345–383 (1981).
V. M. Khomenko, M. A. Litvin, and A. N. Platonov, “Charge Transfer Bands of Fe2+ → Fe3+ in the Optical Spectra of Amphiboles: Crystal Chemical Controlling Factors,” Mineral. Zh. 8(6), 3–11 (1986).
D. M. Sherman, “Molecular Orbital (SCF-Xα-SW) Theory of Metal-Metal Charge Transfer Processes in Minerals. I. Application to Fe2+-Fe3+ Charge Transfer and Electron Delocalization in Mixed Valence Iron Oxides and Silicates,” Phys. Chem. Minerals 14, 355–363 (1987).
K. O. Backhaus, “Structure Refinement of a 1M-Lepidolite,” Crystal. Res. Tech. 18, 1253–1260 (1983).
B. E. Brown, “The Crystal Structure of a 3T Lepidolite,” Am. Mineral. 63, 332–336 (1978).
M. F. Brigatti, P. Frigieri, and L. C. Poppi, “Crystal Chemistry of Mg-, Fe-Bearing Muscovites 2M1,” Am. Mineral. 83, 775–785 (1998).
R. M. Hazen and C. W. Burnham, “The Crystal Structures of One-Layer Phlogopite and Annite,” Am. Mineral. 58, 884–900 (1978).
S. W. Bailey, “Classification and Structures of the Micas,” in Micas, Ed. by S. W. Bailey, Rev. Mineral. 13, 1–60 (1984).
“Nomenclature of the Micas,” Mineral. Mag. 63, 267–279 (1999).
A. I. Ginzburg and L. G. Fel’dman, “Tantalum and Niobium Deposits,” in Ore Deposits of the USSR (Nedra, Moscow, 1978), Vol. 3, pp. 292–341 [in Russian].
K. Langer and V. M. Khomenko, “The Influence of Crystal Field Stabilization Energy on Fe2+ Partitioning in Paragenetic Minerals,” Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 137, 220–231 (1999).
G. Smith, D. Howes, and Z. Hasan, “Mossbauer and Optical Spectra of Biotite: A Case for Fe2+-Fe3+ Interaction,” Phys. Stat. Solidi. A57, K187–K192 (1980).
M. D. Dyar, “Mossbauer Spectra of Biotite from Metapelites,” Am. Mineral. 75, 656–666 (1990).
G. J. Redhammer, E. Dachs, and G. Amthauer, “Mossbauer Spectroscopic and X-Ray Powder Diffraction Studies of Synthetic Micas on the Join Annite KFe3AlSi3O10(OH)2-Phlogopite KMg3AlSi3O10(OH)2,” Phys. Chem. Minerals 22, 282–294 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.N. Platonov, V.M. Khomenko, T.N. Shuriga, 2009, published in Geokhimiya, 2009, No. 2, pp. 184–196.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Platonov, A.N., Khomenko, V.M. & Shuriga, T.N. Optical absorption spectra and Fe distribution in the structures of Li-Fe micas. Geochem. Int. 47, 174–185 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702909020050
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702909020050