Abstract
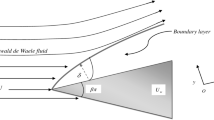
The paper presents a global stability analysis of the two-dimensional incompressible boundary layer with the effect of streamwise pressure gradient. A symmetric wedge flow is considered at different values of the dimensionless pressure gradient parameter βH. The pressure gradient dp/dx in the flow direction is zero, when βH = 0, favorable (negative) for βH > 0, and adverse (positive) for βH < 0. The base flow is computed by numerical solution of Falkner—Skan equation. The Reynolds number is based on the displacement thickness δ* at the inflow boundary. The stability equations governing the flow are derived in body-fitted coordinates. The stability equations are discretized using the Chebyshev spectral collocation method. The discretized equations, together with boundary conditions, form a general eigenvalue problem and are solved using Arnoldi’s algorithm. The temporal global modes are computed for βH = 0.022, 0.044, and 0.066, for favorable and adverse pressure gradients. The temporal growth rate ωi is found to be negative for all the global modes. The ωi value is smaller for the favorable pressure gradient (FPG) than for the adverse pressure gradient (APG) at the same Reynolds number (Re = 340). Thus, the FPG has a stabilizing effect on the boundary layer. The comparison of the spatial eigenmodes and spatial amplification rates for FPG and APG show that FPG has a stabilizing effect, whereas APG has a destabilizing effect on the disturbances.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. J. Obremski, M. V. Morkovin, and M. Landahl, “A portfolio of stability characteristics of incompressible boundary layer,” AGARDograph 134 (1969).
E. R. Van Driest and C. B. Blumer, “Boundary layer transition: freestream turbulence and pressure gradient effect,” AIAA J. 1, 1303–1306 (1963).
S. K. Saxena and T. K. Bose, “Numerical study of effect of pressure gradient on stability of an incompressible boundary layer,” Phys. Fluids 17, 1910–1912 (1974).
T. C. Corke and S. Gruber, “Resonant growth of three-dimensional modes in Falkner-Skan boundary layers with adverse pressure gradient,” J. Fluid Mech. 320, 211–233 (1996).
C. Liu and S. A. Maslowe, “A numerical investigation of resonant interactions in adverse pressure gradient boundary layers,” J. Fluid Mech. 378, 269–289 (1999).
B. J. Abu-Ghannam and R. Shaw, “Natural transition of boundary layers- the effects of turbulence, pressure gradient, and flow history,” J. Mech. Engng. Sci. 22, 213–228 (1980).
J. P. Gostelow, A. R. Blunden, and G. J. Walker, “Effect of free-stream turbulence and adverse pressure gradients on boundary layer transition,” J. Turbomach. 116, 392–404 (1994).
N. Vinod and R. Govindarajan, “Pattern of breakdown of laminar flow into turbulent spots,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 114501 (2004).
N. Vinod and R. Govindarajan, “The signature of laminar instabilities in the zone of transition to turbulence,” J. Turbulence 8(2), (2007).
R. Narasimha, “The laminar-turbulent transition zone in the boundary layer,” Progr. Aero. Sci. 22, 29–80 (1985).
A. Seifert and H.P. Hodson, “Periodic turbulent strips and calmed regions in a transitional boundary layer,” AIAA J. 37, 1127–1129 (1999).
S. A. Maslowe and R. J. Spiteri, “The continuous spectrum for a boundary layer in a streamwise pressure gradient,” Phys. Fluids 13, 1294 (2001).
Y. H. Zurigat, A. H. Nayfeh, and J. A. Masad, “Effect of pressure gradient on the stability of compressible boundary layers,” AIAA J. 30, 2204–2211 (1992).
K. J. Franko and S. Lele, “Effect of adverse pressure gradient on high speed boundary layer transition,” Phys. Fluids 26, 24106 (2014).
W. Zhang, H. Yang, D. Hua-Shu, and Z. Zuchao, “Flow unsteadiness and stability characterstics of low-Re flow past an inclined triangular cylinder,” J. Fluids Eng. 139, 121203 (2017).
R. L. Kimmel, “The effect of pressure gradients on transition zone length in hypersonic boundary layer,” Flight Dynamics Directorate (1993).
N. Itoh, “Effect of pressure gradients on the stability of three-dimensional boundary layers,” Fluid Dynamic Research 7, 37–50 (1991).
M. W. Johnson and A. Pinarbasi, “The effect of pressure gradients on boundary layer receptivity,” Flow, Turbulence and Combustion 93, 1–24 (2014).
J. A. Masad and Y. H. Zurigat, “The effect of pressure gradients on first mode of instability in compressible boundary layer,” Phys. Fluids 6, 3945 (1994).
A. Tumin and D. E. Ashpis, “Optimal dsturbances in boundary layers subject to streamwise pressure gradient,” 33rd AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conf. (2003).
J. P. Gostelow and A. R. Blunden, “Investigation of boundary layer transition in an adverse pressure gradient,” ASME J. Turbomachinery 111, 366–374 (1989).
S. Igarashi, H. Sasaki, and M. Honda, “Influence of pressure gradient upon boundary layer stability and transition,” Acta Mechanica 73, 187–198 (1988).
R. Govindarajan and R. Narasimha, “Stability of spatially developing boundary layers in pressure gradients,” J. Fluid Mech. 300, 117–147 (1995).
G.J. Walker and J. P. Gostelow, “Effect of adverse pressure gradients on the nature and length of boundary layer transtion,” Gas Turbines and Aeroengine Congress and Exposition (1989).
L. Chonghui, “A numercal investigation of instability and transition in adverse pressure gradient boundary layers,” Ph.D. Thesis, McGill University, Montreal (1997).
P Corbett and A. Bottaro, “Optimal perturbations for boundary layers subject to streamwise pressure gradient,” Phys. Fluids 12, 120–131 (2000).
F. Alizard and J. C. Robinet, “Spatially convective global modes in a boundary layer,” Phys. Fluids 19, 114105 (2007).
U. Ehrenstein and F. Gallaire, “On two-dimensional temporal modes in spatially evolving open flow: the flat-plate boundary layer,” J. Fluid Mech. 536, 209–218 (2005).
E. Akervik, U. Ehrenstein, F. Gallaire, and D. S. Henningson, “Global two-dimensional stability measure of the flat plate boundary-layer flow,” Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 27, 501–513 (2008).
R. Bhoraniya and N. Vinod, “Global stability analysis of axisymmetric boundary layer over a circualr cylinder,” Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 32, 425–449 (2018).
R. Bhoraniya and N. Vinod, “Global stability analysis of axisymmetric boundary layer over a circular cone,” J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 822, 012018 (2017).
R. Bhoraniya and N. Vinod, “Global stability analysis of axisymmetric boundary layer over a circular cone,” Phys. Rev. Fluids 02, 063901 (2017).
V. Theofilis, “Advances in global linear instability analysis of nonparallel and three-dimensional flows,” Progr. Aerospace Sci. 39, 249–315 (2003).
H. Fasel, U. Rist, and U. Konzelmann, “Numerical investigation of the three-dimensional development in boundary layer transition,” AIAA J 28, 29–37 (1990).
G. Swaminathan, Kirti. Shahu, A. Sameen, and R. Govindarajan, “Global instabilities in diverging channel flows,” Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 25, 53–64 (2011).
M. R. Malik, “Numerical methods for hypersonic boundary layer stability,” J. Comput. Phys. 86(2), 376–412 (1990).
B. Costa, W. S. Don, and A. Simas, “Spatial resolution properties of mapped spectral Chebyshev methods,” Proceedings of SCPDE, 179–188 (2007).
L. M. Mach, “A numerical study of temporal eigenvalue spectrum of the Blasius boundary layer.” J. Fluid Mech. 73, 497–520 (1976).
D. Sipp and D. Lebedev, “Global stability of base and mean flows: a general approach to its applications to cylinder and open cavity flow,” J. Fluid Mech. 593, 333–358 (2007).
O. Marquet, D. Sipp, and D. Lebedev, “Sensitivity analysis and passive control of cylinder flow,” J. Fluid Mech. 615, 221–252 (2008).
J. W. Nichols and S. K. Lele, “Global modes and transient response of a cold supersonic jet,” J. Fluid Mech. 669, 225–241 (2011).
X. Garnaud, L. Lesshafft, P. J. Schimd, and P. Huerre, “Modal and transient dynamics of jet flows,” Phys. Fluids. 25, 044103 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The Author declares no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Russian Text © The Author(s), 2019, published in Izvestiya RAN. Mekhanika Zhidkosti i Gaza, 2019, No. 6, pp. 84–97.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhoraniya, R., Narayanan, V. Global Stability Analysis of Spatially Developing Boundary Layer: Effect of Streamwise Pressure Gradients. Fluid Dyn 54, 821–834 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0015462819060028
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0015462819060028