Abstract
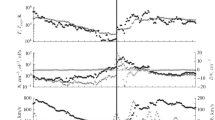
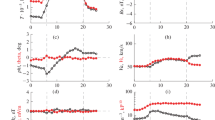
This paper discusses the errors in analyzing solar-terrestrial relationships, which result from either disregarding the types of interplanetary drivers in studying the magnetosphere response on their effect or from the incorrect identification of the type of these drivers. In particular, it has been shown that the absence of selection between the Sheath and ICME (the study of so-called CME-induced storms, i.e., magnetic storms generated by CME) leads to errors in the studies of interplanetary conditions of magnetic storm generation, because the statistical analysis has shown that, in the Sheath + ICME sequences, the largest number of storm onsets fell on the Sheath, and the largest number of storms maxima fell at the end of the Sheath and the beginning of the ICME. That is, the situation is observed most frequently when at least the larger part of the main phase of storm generation falls on the Sheath and, in reality, Sheath-induced storms are observed. In addition, we consider several cases in which magnetic storms were generated by corotating interaction regions, whereas the authors attribute them to CME.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dungey, J.W., Interplanetary magnetic field and the auroral zones, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1961, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 47–48.
Fairfield, D.H. and Cahill, L.J., The transition region magnetic field and polar magnetic disturbances, J. Geophys. Res., 1966, vol. 71, pp. 155–169.
Rostoker, G. and Falthammar, C.-G., Relationship between changes in the interplanetary magnetic field and variations in the magnetic field at the Earth’s surface, J. Geophys. Res., 1967, vol. 72, no. 23, pp. 5853–5863.
Russell, C.T., McPherron, R.L., and Burton, R.K., On the cause of magnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 1974, vol. 79, pp. 1105–1109.
Burton, R.K., McPherron, R.L., and Russell, C.T., An empirical relationship between interplanetary conditions and D st, J. Geophys. Res., 1975, vol. 80, pp. 4204–4214.
Akasofu, S.-I., Energy coupling between the solar wind and the magnetosphere, Space Sci. Rev., 1981, vol. 111, A07S08. doi 10.1029/2005JA011447
Eselevich, V.G. and Fainshtein, V.G., An investigation of the relationship between the magnetic storm Dst indexes and different types of solar wind streams, Ann. Geophys., 1993, vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 678–684.
Huttunen, K.E.J., Koskinen, H.E.J., and Schwenn, R., Variability of magnetospheric storms driven by different solar wind perturbations, J. Geophys. Res., 2002, vol. 107, no. A7. doi 10.1029/2001JA900171
Huttunen, K.E.J. and Koskinen, H.E.J., Importance of post-shock streams and sheath region as drivers of intense magnetospheric storms and high-latitude activity, Ann. Geophys., 2004, vol. 22, pp. 1729–1738.
Huttunen, K.E.J., Koskinen, H.E.J., Karinen, A., and Mursula, K., Asymmetric development of magnetospheric storms during magnetic clouds and sheath regions, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2006, vol. 33, no. 6, L06107. doi 10.1029/2005GL024894
Borovsky, J.E. and Denton, M.H., Differences between CME-driven storms and CIR-driven storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2006, vol. 28, pp. 121–190.
Pulkkinen, T.I., Partamies, N., Huttunen, K.E.J., Reeves, G.D., and Koskinen, H.E.J., Differences in geomagnetic storms driven by magnetic clouds and ICME sheath regions, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2007, vol. 34, L02105. doi 10.1029/2006GL027775
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Yermolaev, M.Yu., Nikolaeva, N.S., and Lodkina, L.G., Interplanetary conditions for CIRinduced and MC induced geomagnetic storms, Bulg. J. Phys., 2007, vol. 34, pp. 128–135.
Plotnikov, I.Y. and Barkova, E.S., Nonlinear dependence of Dst and AE indices on the electric field of magnetic clouds, Adv. Space Res., 2007, vol. 40, pp. 1858–1862.
Longden, N., Denton, M.H., and Honary, F., Particle precipitation during ICME-driven and CIR-driven geomagnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2008, vol. 113, A06205. doi 10.1029/2007JA012752
Turner, N.E., Cramer, W.D., Earles, S.K., and Emery, B.A., Geoefficiency and energy partitioning in CIR-driven and CME-driven storms, J. Atmos. Sol.- Terr. Phys., 2009, vol. 71, pp. 1023–1031.
Guo, J., Feng, X., Emery, B.A., et al., Energy transfer during intense geomagnetic storms driven by interplanetary coronal mass ejections and their sheath regions, J. Geophys. Res., 2011, vol. 116, A05106. doi 10.1029/2011JA016490
Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, Yu.I., and Lodkina, I.G., Modeling the time behavior of the Dst index during the main phase of magnetic storms generated by various types of solar wind, Cosmic Res., 2013, vol. 51, no. 6, pp. 401–412.
Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, Yu.I., and Lodkina, I.G., Dependence of geomagnetic activity during magnetic storms on solar-wind parameters for different types of streams: 4. Simulation for magnetic clouds, Geomagn. Aeron. (Engl. Transl.), 2014, vol. 54, no. 2, pp. 152–161.
Nikolaeva, N., Yermolaev, Y., and Lodkina, I., Predicted dependence of the cross polar cap potential saturation on the type of solar wind stream, Adv. Space Res., 2015, vol. 56, pp. 1366–1373.
Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, Yu.I., and Lodkina, I.G., Modeling of the corrected Dst* index temporal profile on the main phase of the magnetic storms generated by different types of solar wind, Cosmic Res., 2015, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 119–127.
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Nikolaeva, N.S., Lodkina, I.G., and Yermolaev, M.Yu., Relative occurrence rate and geoeffectiveness of large-scale types of the solar wind Cosmic Res., 2010, vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 1–30.
Yermolaev, Y.I., Nikolaeva, N.S., Lodkina, I.G., and Yermolaev, M.Y., Specific interplanetary conditions for CIR-induced, sheath-induced, and ICME-induced geomagnetic storms obtained by double superposed epoch analysis, Ann. Geophys., 2010, vol. 28, pp. 2177–2186.
Yermolaev, Y.I., Nikolaeva, N.S., Lodkina, I.G., and Yermolaev, M.Y., Geoeffectiveness and efficiency of CIR, sheath, and ICME in generation of magnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2012, vol. 117, A00L07. doi 10.1029/2011JA017139
Yermolaev, Y.I., Lodkina, I.G., Nikolaeva, N.S., and Yermolaev, M.Y., Influence of the interplanetary driver type on the durations of the main and recovery phases of magnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2014, vol. 119, no. 10, pp. 8126–8136. doi 10.1002/2014JA019826
Yermolaev, Y.I., Lodkina, I.G., Nikolaeva, N.S., and Yermolaev, M.Y., Dynamics of large-scale solar wind streams obtained by the double superposed epoch analysis, J. Geophys. Res., 2015, vol. 120, no. 9, pp. 7094–7106. doi 10.1002/2015JA021274
Borovsky, J.E., Cayton, T.E., Denton, M.H., Belian, R.D., Christensen, R.A., and Ingraham, J.C., The proton and electron radiation belts at geosynchronous orbit: Statistics and behavior during highspeed stream-driven storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2016, vol. 121, no. 6, pp. 5449–5488. doi 10.1002/2016JA022520
Lockwood, M., Owens, M.J., Barnard, L.A., et al., On the origins and timescales of geoeffective IMF, Space Weather, 2016, vol. 14, pp. 406–432. doi 10.1002/2016SW001375
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Nikolaeva, N.S., Lodkina, I.G., and Yermolaev, M.Yu., Catalog of large-scale solar wind phenomena during 1976–2000, Cosmic Res., 2009, vol. 47, no. 2, pp. 81–94.
King, J.H. and Papitashvili, N.E., Solar wind spatial scales in and comparisons of hourly wind and ACE plasma and magnetic field data, J. Geophys. Res., 2004, vol. 110, no. A2, A02209. doi 10.1029/2004JA010804
Thatcher, L.J. and Muller, H.-R., Statistical investigation of hourly OMNI solar wind data, J. Geophys. Res., 2011, vol. 116, A12107. doi 10.1029/2011JA017027
Mitsakou, E. and Moussas, X., Statistical study of ICMES and their sheaths during solar cycle 23 (1996–2008), Sol. Phys., 2014, vol. 289, pp. 3137–3157. doi 10.1007/s11207-014-0505-y
Richardson, I.G. and Cane, H.V., Near-earth solar wind flows and related geomagnetic activity during more than four solar cycles (1963–2011), J. Space Weather Space Clim., 2012, vol. 2, A02. doi 10.1051/swsc/2012003
Keesee, A.M., Elfritz, J.G., Fok, M.-C., et al., Superposed epoch analyses of ion temperatures during CMEand CIR/HSS-driven storms, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2013, vol. 115, pp. 67–78. doi 10.1016/j.jastp.2013.08.009
Potapov, A.S., ULF wave activity in high-speed streams of the solar wind: Impact on the magnetosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 2013, vol. 118, pp. 6465–6477. doi 10.1002/2013JA019119
Yuan, C.J. and Zong, Q.G., The double-belt outer radiation belt during CME- and CIR-driven geomagnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2013, vol. 118, pp. 6291–6301. 10.1002/jgra.50564
Cramer, W.D., Turner, N.E., Fok, M.-C., and Buzulukova, N.Y., Effects of different geomagnetic storm drivers on the ring current: CRCM results, J. Geophys. Res., 2013, vol. 118, pp. 1062–1073. doi 10.1002/jgra.50138
Kim, K.-C., Lee, D.-Y., and Shprits, Y., Dependence of plasmaspheric hiss on solar wind parameters and geomagnetic activity and modeling of its global distribution, J. Geophys. Res., 2015, vol. 120, pp. 1153–1167. doi 10.1002/2014JA020687
Yermolaev, Y.I., Nikolaeva, N.S., Lodkina, I.G., and Yermolaev, M.Y., Large-scale solar wind structures: Occurrence rate and geoeffectiveness, AIP Conf. Proc., 2010, vol. 1216, pp. 648–651.
Hutchinson, J.A., Wright, D.M., and Milan, S.E., Geomagnetic storms over the last solar cycle: A superposed epoch analysis, J. Geophys. Res., 2011, vol. 116, A09211. doi 10.1029/2011JA016463
Zolotukhina, N., Polekh, N., Kurkin, V., and Romanova, E., Ionospheric effects of solar flares and their associated particle ejections in March 2012, Adv. Space Res., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 2851–2862.
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Lodkina, I.G., Nikolaeva, N.S., and Yermolaev, M.Yu., Dynamics of large-scale solar-wind streams obtained by the double superposed epoch analysis. 2. CIR vs Sheath and MC vs Ejecta comparisons. 2016. http://arxiv.org/abs/1602.08899.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © Y.I. Yermolaev, I.G. Lodkina, N.S. Nikolaeva, M.Y. Yermolaev, M.O. Riazantseva, 2017, published in Kosmicheskie Issledovaniya, 2017, Vol. 55, No. 3, pp. 189–200.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yermolaev, Y.I., Lodkina, I.G., Nikolaeva, N.S. et al. Some problems of identifying types of large-scale solar wind and their role in the physics of the magnetosphere. Cosmic Res 55, 178–189 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952517030029
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952517030029