Abstract
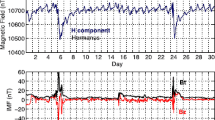
Results of modeling the time behavior of the D st index at the main phase of 93 geomagnetic storms (−250 < D st ≤ −50 nT) caused by different types of solar wind (SW) streams: magnetic clouds (MC, 10 storms), corotating interaction regions (CIR, 31 storms), the compression region before interplanetary coronal ejections (Sheath before ICME, 21 storms), and “pistons” (Ejecta, 31 storms) are presented. The “Catalog of Large-Scale Solar Wind Phenomena during 1976–2000” (ftp://ftp.iki.rssi.ru/pub/omni/) created on the basis of the OMNI database was the initial data for the analysis. The main phase of magnetic storms is approximated by a linear dependence on the main parameters of the solar wind: integral electric field sumEy, dynamic pressure P d , and fluctuation level sB in IMF. For all types of SW, the main phase of magnetic storms is better modeled by individual values of the approximation coefficients: the correlation coefficient is high and the standard deviation between the modeled and measured values of D st is low. The accuracy of the model in question is higher for storms from MC and is lower by a factor of ∼2 for the storms from other types of SW. The version of the model with the approximation coefficients averaged over SW type describes worse variations of the measured D st index: the correlation coefficient is the lowest for the storms caused by MC and the highest for the Sheath- and CIR-induced storms. The model accuracy is the highest for the storms caused by Ejecta and, for the storms caused by Sheath, is a factor of ∼1.42 lower. Addition of corrections for the prehistory of the development of the beginning of the main phase of the magnetic storm improves modeling parameters for all types of interplanetary sources of storms: the correlation coefficient varies within the range from r = 0.81 for the storms caused by Ejecta to r = 0.85 for the storms caused by Sheath. The highest accuracy is for the storms caused by MC. It is, by a factor of ∼1.5, lower for the Sheath-induced storms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Lodkina, I.G., Nikolaeva, N.S., and Yermolaev, M.Yu., Statistical study of interplanetary condition effect on geomagnetic storms, Kosm. Issled., 2010, vol. 48, no. 6, pp. 499–515. [Cosmic Research, pp. 485–500].
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Lodkina, I.G., Nikolaeva, N.S., and Yermolaev, M.Yu., Statistical study of interplanetary condition effect on geomagnetic storms: 2. Variations of parameters, Kosm. Issled., 2011, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 24–37. [Cosmic Research, pp. 21–34].
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Nikolaeva, N.S., Lodkina, I.G., and Yermolaev, M.Yu., Specific interplanetary conditions for CIR-, Sheath-, and ICME-induced geomagnetic storms obtained by double superposed epoch analysis, Ann. Geophys., 2010, vol. 28, pp. 2177–2186.
Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, Yu.I., and Lodkina, I.G., Dependence of geomagnetic activity during magnetic storms on the solar wind parameters for different types of streams, Geomagn. Aeron., 2011, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 49–65.
Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, Yu.I., and Lodkina, I.G., Dependence of geomagnetic activity during magnetic storms on the solar wind parameters for different types of streams: 2. Main phase of storm, Geomagn. Aeron., 2012, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 28–36.
Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, Yu.I., and Lodkina, I.G., Geomagnetic activity during magnetic storms as a function of solar wind parameters for different types of flows: 3. Development of storm, Geomagn. Aeron., 2012, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 37–48.
Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, Yu.I., and Lodkina, I.G., Geomagnetic activity during magnetic storms as a function of solar wind parameters for different types of flows: 4. Modeling for magnetic clouds, Geomagn. Aeron., 2013, no. 6. (in press).
Burton, R.K., McPherron, R.L., and Russell, C.T., An empirical relationship between interplanetary conditions and D st, J. Geophys. Res., 1975, vol. 80, pp. 4204–4214.
Kane, R.P., Severe geomagnetic storms and Forbush decreases: interplanetary relationships reexamined, Ann. Geophys., 2010, vol. 28, pp. 479–489.
Ontiveros, V., Geomagnetic storms caused by shocks and ICMEs, J. Geophys. Res., 2010, vol. 115, A10244. doi: 10.1029/2010JA015471.
Weigel, R.S., Solar wind density influence on geomagnetic storm intensity, J. Geophys. Res., 2010, vol. 115, A09201. doi: 10.1029/2009JA015062.
Feldstein, Y.I., Modelling of the magnetic field of magnetospheric ring current as a function of interplanetary parameters, Space Sci. Rev., 1992, vol. 59, pp. 83–165.
Fenrich, F.R. and Luhmann, J.G., Geomagnetic response to magnetic clouds of different polarity, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1998, vol. 25, pp. 2999–3002.
O’Brien, T.P. and McPherron, R.L., An empirical phase space analysis of ring current dynamics: Solar wind control of injection and decay, J. Geophys. Res., 2000, vol. 105, pp. 7707–7720.
O’Brien, T.P. and McPherron, R.L., Forecasting the ring current index D st in real time, J. of Atmosph. and Sol.-Terrestr. Phys., 2000, vol. 62, pp. 1295–1299.
Wang, C.B., Chao, J.K., and Lin, C.-H., Influence of the solar wind dynamic pressure on the decay and injection of the ring current, J. Geophys. Res., 2003, vol. 108, no. A9, p. 1341. doi: 10.1029/2003JA009851.
Maltsev, Y.P., Points of controversy in the study of magnetic storms, Space Sci. Rev., 2004, vol. 110, pp. 227–267.
Siscoe, G., McPherron, R.L., Liemohn, M.W., Ridley, A.J., and Lu, G., Reconciling prediction algorithms for D st, J. Geophys. Res., 2005, vol. 110, A02215. doi: 10.1029/2004JA010465.
Podladchikova, T.V. and Petrukovich, A.A., Extended geomagnetic storm forecast ahead of available solar wind measurements, Space Weather, 2012, vol. 10, S07001. doi: 10.1029/2012SW000786.
Vassiliadis, D., Klimas, A.J., Baker, D.N., and Roberts, D.A., A description of solar wind-magnetosphere coupling based on nonlinear filters, J. Geophys. Res., 1995, vol. 100, no. A3, pp. 3495–3512.
Vassiliadis, D., Klimas, A.J., and Baker, D.N., Models of D st geomagnetic activity and of its coupling to solar wind parameters, Phys. Chem. Earth (C), 1999, vol. 24, nos. 1–3, pp. 107–112.
Vassiliadis, D., Klimas, A.J., Valdivia, J.A., and Baker, D.N., The D st geomagnetic response as a function of storm phase and amplitude and the solar wind electric field, J. Geophys. Res., 1999, vol. 104, no. A11, pp. 24957–24976.
Klimas, A.J., Vassiliadis, D., Baker, D.N., and Roberts, D.A., The organized nonlinear dynamics of the magnetosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 1996, vol. 101, pp. 13089–13113.
Klimas, A.J., Vassiliadis, D., and Baker, D.N., D st index prediction using data-derived analogues of the magnetospheric dynamics, J. Geophys. Res., 1998, vol. 103, pp. 20435–20447.
Wu, J.-G. and Lundstedt, H., Neural network modeling of solar wind-magnetosphere interaction, J. Geophys. Res., 1997, vol. 102, no. A7, pp. 14457–14466.
McPherron, R.L. and O’Brien, T.P., Predicting geomagnetic activity: the D st index, in Space Weather, vol. 125 of Geophys. Monogr. ser., Song, P., Singer, H.J., and Siscoe G.L., Eds., Washington, DC: AGU, 2001.
Temerin, M. and Li, X., A new model for the prediction of dst on the basis of the solar wind, J. Geophys. Res., 2002, vol. 107, no. A12, p. 1472.
Temerin, M. and Li, X., D st model for 1995–2002, J. Geophys. Res., 2006, vol. 111, A04221. doi: 10.1029/2005JA011257.
Sharifi, J., Araabi, B.N., and Lucas, C., Multi-step prediction of D st index using singular spectrum analysis and locally linear neurofuzzy modeling, Earth Planets Space, 2006, vol. 58, pp. 331–341.
Amata, E., Pallocchia, G., Consolini, G., Marcucci, M.F., and Bertello, I., Comparison between three algorithms for D st predictions over the 2003–2005 period, J. of Atmosph. and Sol.-Terrest. Phys., 2008, vol. 70, pp. 496–502.
Boynton, R.J., Balikhin, M.A., Billings, S.A., Sharma, A.S., and Amariutei, O.A., Data derived NARMAX D st model, Ann. Geophys., 2011, vol. 29, pp. 965–971.
Ji, E.-Y., Moon, Y.-J., Gopalswamy, N., and Lee, D.H., Comparison of D st forecast models for intense geomagnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2012, vol. 117, A03209. doi: 10.1029/2011JA016872.
Borovsky, J.E. and Denton, M.H., Differences between CME-driven storms and CIR-driven storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2006, vol. 111, A07808. doi: 10.1029/2005JA011447.
Denton, M.H., Borovsky, J.E., Skoug, et al., Geomagnetic storms driven by ICME and CIR-dominated solar wind, J. Geophys. Res., 2006, vol. 111, A07S07. doi: 10.1029/2005JA011436.
Huttunen, K.E.J., Koskinen, H.E.J., Karinen, A., and Mursula, K., Asymmetric development of magnetospheric storms during magnetic clouds and sheath regions, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2006, vol. 33, p. L06107. doi: 10.1029/2005GL027775.
Pulkkinen, T.I., Partamies, N., Huttunen, K.E.J., Reeves, G.D., and Koskinen, H.E.J., Differences in geomagnetic storms driven by magnetic clouds and ICME sheath regions, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2007, vol. 34, L02105. doi: 10.1029/2006GL027775.
Plotnikov, I.Ya. and Barkova, E.S., Nonlinear dependence of D st and A e indices on the electric field of magnetic clouds, Adv. Space Res., 2007, vol. 40, pp. 1858–1862.
Longden, N., Denton, M.H., and Honary, F., Particle precipitation during ICME-driven and CIR-driven geomagnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2008, vol. 113, p. A06205. doi: 10.1029/2007JA012752.
Turner, N.E., Cramer, W.D., Earles, S.K., and Emery, B.A., Geoefficiency and energy partitioning in CIR-driven and CME-driven storms, J. of Atmosph. and Sol.-Terrest. Phys., 2009, vol. 71, pp. 1023–1031.
Despirak, I.V., Lubchich, A.A., and Guineva, V., Development of substorm bulges during storms of different interplanetary origins, J. of Atmosph. and Sol.-Terrest. Phys., 2011, vol. 73, pp. 1460–1464.
Guo, J., Feng, X., Emery, B.A., et al., Energy transfer during intense geomagnetic storms driven by interplanetary coronal mass ejections and their sheath regions, J. Geophys. Res., 2011, vol. 116, A05106. doi: 10.1029/2011JA016490.
Tsurutani, B.T., Lakhina, G.S., Pickett, J.S., Guarnieri, F.L., Lin, N., and Goldstein, B.E., Nonlinear Alfven’s waves, discontinuities, proton perpendicular acceleration, and magnetic holes/decreases in interplanetary space and the magnetosphere: Intermediate shocks?, Nonlinear Proc. Geophys., 2005, vol. 12, p. 321.
Jordanova, V.K., Modeling the behavior of corotating interaction region driven storms in comparison with coronal mass ejection driven storms, in Recurrent Magnetic Storms: Corotating Solar Wind Streams, Tsurutani, B.T., McPherron, R.L., Gonzalez, W.D., Lu, G., Sobral, J.H.A., and Gopalswamy, N., Eds., vol. 167 of Geophysical Monograph Series, Washington, DC: AGU, 2006.
Liemohn, M.W. and Jazowski, M., Ring current simulations of the 90 intense storms during solar cycle 23, J. Geophys. Res., 2008, vol. 113, p. A00A17. doi: 10.1029/2008JA013466.
Liemohn, M.W., Jazowski, M., Kozyra, J.U., Ganushkina, N., Thomsen, M.F., and Borovsky, J.E., CIR versus CME drivers of the ring current during intense magnetic storms, Proc. R. Soc. A, 2010, vol. 466, pp. 3305–3328. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2010.0075.
Cerrato, Y., Saiz, E., Cid, C., Gonzalez, W.D., and Palacios, J., Solar and interplanetary triggers of the largest D st variations of the solar cycle 23, J. of Atmosph. and Sol.-Terrest. Phys., 2012, vol. 80, pp. 111–123.
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Nikolaeva, N.S., Lodkina, I.G., and Yermolaev, M.I., Geoeffectiveness and efficiency of CIR, Sheath, and ICME in generation of magnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2012, vol. 117, p. A00L07. doi: 10.1029/2011JA017139.
Tsyganenko, N.A. and Sitnov, M.I., Modeling the dynamics of the inner magnetosphere during strong geomagnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2005, vol. 110, p. A03208. doi: 10.1029/2004JA010798.
Levitin, A.E., Dremukhina, L.A., Gromova, L.I., and Ptitsyna, N.G., Modeling giant disturbances in geomagnetic field, Physics of Auroral Phenomena, Proc. XXXIV Annual Seminar, Apatity, 2011, pp. 29–32.
King, J.H. and Papitashvili, N.E., Solar wind spatial scales in and comparisons of hourly wind and ace plasma and magnetic field data, J. Geophys. Res., 2004, vol. 110, no. A2, p. A02209. doi: 10.1029/2004JA010804.
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Nikolaeva, N.S., Lodkina, I.G., and Yermolaev, M.Yu., Catalog of Large-Scale Solar Wind Phenomena during 1976–2000, Kosm. Issled., 2009, vol. 47, no. 2, pp. 99–113. [Cosmic Research, pp. 81–94].
Garcia, H.A. and Dryer, M., The solar flares on February 1986 and the ensuing intense geomagnetic storm, Solar Phys., 1987, vol. 109, pp. 119–137.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Tang, F., and Lee, E.T., Great magnetic storms, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1992, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 73–76.
Eselevich, V.G. and Fainshtein, V.G., An investigation of the relationship between the magnetic storm D st-index and different types of solar wind streams, Ann. Geophys., 1993, vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 678–684.
Huttunen, K.E.J. and Koskinen, H.E.J., Importance of post-shock streams and sheath region as drivers of intense magnetospheric storms and high-latitude activity, Ann. Geophys., 2004, vol. 22, pp. 1729–1738.
Yermolaev, Y.I., Yermolaev, M.Y., Lodkina, I.G., and Nikolaeva, N.S., Statistic investigation of heliospheric conditions resulting in magnetic storms, Kosm. Issled., 2007, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 3–11. [Cosmic Research, pp. 1–8].
Yermolaev, Y.I., Yermolaev, M.Y., Lodkina, I.G., and Nikolaeva, N.S., Statistic investigation of heliospheric conditions resulting in magnetic storms: 2, Kosm. Issled., 2007, vol. 45, no. 6, pp. 489–498. [Cosmic Research, pp. 461–470].
Yermolaev, Y.I., Yermolaev, M.Y., Nikolaeva, N.S., and Lodkina, L.G., Interplanetary conditions for CIR-induced and MC-induced geomagnetic storms, Bulg. J. Phys., 2007, vol. 34, pp. 128–135.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.S. Nikolaeva, Yu.I. Yermolaev, I.G. Lodkina, 2013, published in Kosmicheskie Issledovaniya, 2013, Vol. 51, No. 6, pp. 443–454.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, Y.I. & Lodkina, I.G. Modeling the time behavior of the D st index during the main phase of magnetic storms generated by various types of solar wind. Cosmic Res 51, 401–412 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952513060038
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952513060038