Abstract
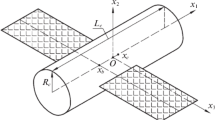
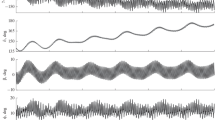
The mode of monoaxial solar orientation of a designed artificial Earth satellite (AES), intended for microgravitational investigations, is studied. In this mode the normal line to the plane of satellite’s solar batteries is permanently directed at the Sun, the absolute angular velocity of a satellite is virtually equal to zero. The mode is implemented by means of an electromechanical system of powered flywheels or gyrodynes. The calculation of the level of microaccelerations arising on board in such a mode, was carried out by mathematical modeling of satellite motion with respect to the center of masses under an effect of gravitational and restoring aerodynamic moments, as well as of the moment produced by the gyrosystem. Two versions of a law for controlling the characteristic angular momentum of a gyrosystem are considered. The first version provides only attenuation of satellite’s perturbed motion in the vicinity of the position of rest with the required velocity. The second version restricts, in addition, the increase in the accumulated angular momentum of a gyrosystem by controlling the angle of rotation of the satellite around the normal to the light-sensitive side of the solar batteries. Both control law versions are shown to maintain the monoaxial orientation mode to a required accuracy and provide a very low level of quasistatic microaccelerations on board the satellite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sazonov, V.V., Komarov, M.M., Polezhaev, V.I., et al., Microaccelerations onboard the Mir orbital station and prompt analysis of gravitational sensitivity of convective processes of heat and mass transfer, Kosm. Issled., 1999, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 86–101. (Cosmic Research, pp. 80–94).
Ignatov, A.I. and Sazonov, V.V., Implementation of satellite attitude motions with low level of microaccelerations using electromechanical executive devices, Kosm. Issled., 2012, vol. 50, no 5, pp. 353–366 (Cosmic Research. P. 380).
Ignatov, A.I. and Sazonov, V.V., Implementation of satellite attitude motions with low level of microaccelerations using electromechanical executive devices, Preprint of Keldysh Inst. of Applied Math., Russ. Acad. Sci., Moscow, 2008, no. 91.
Meeus, J., Astronomical Formulae for Calculators, Richmond: Willmann-Bell, 1988. Translated under the title Astronomicheskie formuly dlya kal’kulyatorov, Moscow: Mir, 1988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.I. Ignatov, V.V. Sazonov, 2013, published in Kosmicheskie Issledovaniya, 2013, Vol. 51, No. 5, pp. 380–388.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ignatov, A.I., Sazonov, V.V. Estimation of residual microaccelerations on board an artificial earth satellite in the monoaxial solar orientation mode. Cosmic Res 51, 342–349 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952513050055
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952513050055