Abstract
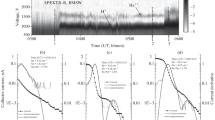
Characteristics of polar wind fluxes at a height of ∼20000 km measured by the Hyperboloid mass-spectrometer installed onboard the Interball-2 satellite are presented in the paper. The characteristics are presented for the upwelling flows of ionospheric ions H+, He+, and O+ from the sunlit polar cap in the period of solar activity minimum. Orbit segments with minimal precipitation of magnetospheric ions and electrons were preliminarily selected, and the measurements where the fluxes of ions coming from the cusp/cleft were excluded as carefully as possible. Thus, the densities, field-aligned velocities, and temperatures of ions in the regions where fluxes of polar wind could be detected with the maximal probability degree are presented in the paper. It is found that cases when only H+ ions are reaching the detector are with high probability the polar wind outflows. Their characteristics agree well with the Tube-7 hydrodynamic model and are as follows: n ≈ 1.5 cm−3, V ∥ ∼ 21 km/s; T ∥ = 3500 K, and T ⊥ = 2000 K. In cases when He+ and O+ ions are also detected, the temperatures are substantially higher than the model ones, and the measured field-aligned velocities of O+ fluxes are several times higher than the model ones. Moreover, it was revealed that the polar wind outflows are predominantly observed in the polar cap regions where the polar rain fluxes are very small.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dessler, A.J. and Michel, F.C., Plasma in the Geomagnetic Tail, J. Geophys. Res., 1966, vol. 71, pp. 1421–1426.
Banks, P.M. and Holzer, E.N., The Polar Wind, J. Geophys. Res., 1968, vol.73, pp. 6846–6854.
Grigoriev, S.A., Zinin, L.V., Vasilenko, I.Yu., and Lynovsky, V.E., Multi-Ion One-Dimensional MHD Models of Upper Ionospjere Dynamics: 1. A Mathematical Ionospheric Model with Seven Positive ion Species,, Kosm. Issled., 1999, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 451–462. [Cosmic Research, pp. 425–436.]
Demars, H.G. and Schunk, R.W., Seasonal and Solar Cycle Variations of the Polar Wind, J. Geophys. Res., 2001, vol. 106, pp. 8157–8168.
Tam, S.W.Y., Yasseen, F, Chang, T., and Ganguli, S.B., Self-Consistent Kinetic Photoelectron Effects on the Polar Wind, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1995, vol. 22, pp. 2107–2110.
Su, Y.-J., Horwitz, J.L., Wilson, G.R., et al., Self-Consistent Simulation of the Photoelectron-Driven Polar Wind from 120 km to 9Re Altitude, J. Geophys. Res., 1998, vol. 103, pp. 2279–2296.
Barakat, A.R., Demars, H.G., and Schunk, R.W., Dynamic Features of the Polar Wind in the Presence of Hot Magnetospheric Electrons, J. Geophys. Res., 1998, vol. 103, pp. 29289–29303.
Yau, A.W., Whalen, B.A., Peterson, W.K., and Shelley, E.G., Distribution of Upflowing Ionospheric Ions in the High-Altitude Polar Cap and Auroral Ionosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 1984, vol. 89, pp. 5507–5522.
Abe, T., Whalen, B.A., Yau, A.W., et al., EXOS D (Akebono) Suprathermal Mass Spectrometer Observations of the Polar Wind, J. Geophys. Res., 1993, vol. 98, pp. 11191–11203.
Abe, T., Watanabe, S., Whalen, B.A., et al., Observation of Polar Wind and Thermal Ion Outflow by Akebono/SMS, J. Geomagn. Geoelectr., 1996, vol. 48, pp. 319–325.
Abe, T., Yau, A.W., Watanabe, S., et al., Long-Term Variation of the Polar Wind Velocity, J. Geophys. Res., 2004, vol. 109. doi: 10.1029/2003JA010223.
Burch, J.L., Mende, S.B., Mitchell, D.G., et al., Views of the Earth’s Magnetosphere with the IMAGE Satellite, Science, 2001, vol. 291, pp. 619–624.
Reinisch, B.W., Haines, D.M., Bibl, K., et al., The Radio Plasma Imager Investigation on the IMAGE Spacecraft, Space Sci. Rev., 2000, vol. 91, pp. 319–359.
Reinisch, B.W., Huang, X., Song, P., et al., Plasma Density Distribution along the Magnetospheric Field: RPI Observations from IMAGE, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2001, vol.28, pp. 4521–4524.
Huang, X., Reinisch, B.W., Song, P., et al., Developing an Empirical Density Model of the Plasmasphere Using IMAGE/RPI Observations, Adv. Space Res., 2004, vol. 33, pp. 829–832.
Nsumei, P.A., Huang, X., Reinisch, B.W., et al., Electron Density Distribution over the Northern Polar Region Deduced from IMAGE/Radio Plasma Imager Sounding, J. Geophys. Res., 2003, vol. 108. doi: 1029/2002JA009616.
Chugunin, D.V., Zinin, L.V., Galperin, Yu.I., et al., Polar Wind Observations on the Nightside of the Polar Cap at Altitudes of 2–3 R E: Results of the Interball-2 Satellite, Kosm. Issled., 2002, vol. 40, no. 4, pp. 416–433. [Cosmic Research, pp. 387–403.]
Nsumei, P.A., Reinisch, B.W., Song, P., et al., Polar Cap Electron Density Distribution from IMAGE Radio Plasma Imager Measurements: Empirical Model with the Effects of Solar Illumination and Geomagnetic Activity, J. Geophys. Res., 2008, vol. 113. doi: 10.1029/2007JA012566.
Su, Y.-J., Horwitz, J.L., Moore, T.E., et al., Polar Wind Survey with the Thermal Ion Dynamics Experiment/Plasma Source Instrument Suite aboard POLAR, J. Geophys. Res., 1998, vol. 103, pp. 29 305–29 337.
Elliott, H.A., Comfort, R.H., Craven, P.D., et al., Solar Wind Influence on the Oxygen Content of Ion Outflow in the High-Altitude Polar Cap during Solar Minimum Conditions, J. Geophys. Res., 2001, vol. 106, pp. 6067–6084.
Carbary, J.F., A Kp-Based Model of Auroral Boundaries, Space Weather, 2005, vol. 3. doi: 10.1029/2005SW000162.
Horita, R.E., Yau, A.W., Whalen, B.A., et al., Ion Depletion Zones in the Polar Wind: EXOS D Suprathermal Ion Mass Spectrometer Observations in the Polar Cap, J. Geophys. Res., 1993, vol. 98, pp. 11 439–11 448.
Dubouloz, N., Berthelier, J.-J., Malingre, M., et al., Thermal Ion Measurements on Board INTERBALL Auroral Probe by the HYPERBOLOID Experiment, Ann. Geophys., 1998, vol. 16, pp. 1070–1085.
Perraut, S., Roux, A., Darrouzet, F., et al., ULF Wave Measurements onboard the Interball Auroral Probe, Ann. Geophys., 1998, vol. 16, p. 1105.
Pedersen, A., Solar Wind and Magnetosphere Plasma Diagnostics by Spacecraft Electrostatic Potential Measurements, Ann. Geophys., 1995, vol. 13, pp. 118–129.
Escoubet, C.P., Pedersen, A., Schmidt, R., and Lindqvist, P.A., Density in the Magnetosphere Inferred from ISEE 1 Spacecraft Potential, J. Geophys. Res., 1997, vol. 102, pp. 17 595–17 610.
Torkar, K., Jeszenszky, H., Veselov, M.V., et al., Spacecraft Potential Measurements on Board INTERBALL-2 Satellite and Derived Plasma Densities, Kosm. Issled., 1999, vol. 37, pp. 644–653. [Cosmic Research, pp. 606–614.]
Bouhram, M., Dubouloz, N., Hamelin, M., et al., Electrostatic Interaction between Interball-2 and the Ambient Plasma. 1. Determination of the Spacecraft Potential from Current Calculations, Ann. Geophys., 2002, vol. 20, pp. 365–376.
Zinin, L.V., Galperin, Yu.I., Gladyshev, V.A., et al., Modeling of the Anisotropic Thermal Plasma Measurements of the Energy-Mass-Angle Ion Spectrometers Onboard a Charged Satellite, Kosm. Issled., 1995, vol. 33, no. 6, pp. 563–571. [Cosmic Research, pp. 511–518.]
Winningham J.D. and Heikkila, W.J., Polar Cap Auroral Electron Fluxes Observed with Isis 1, J. Geophys. Res., 1974, vol. 79, p. 949.
Sauvaud, J.A., Barthe, H., Aousti, C., et al., The ION Experiment Energetic Ion Composition and Electron Energy Spectrometers for the Auroral Probe, in Interball Mission and Payload, RSA-IKI-CNES, 1995, pp. 268–283.
Newell, P.T., Greenwald, R.A., and Ruohoniemi, J.M., The Role of the Ionosphere in Aurora and Space Weather, Rev. Geophys., 2001, vol. 39, pp. 137–149.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.V. Chugunin, 2009, published in Kosmicheskie Issledovaniya, 2009, Vol. 47, No. 6, pp. 483–494.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chugunin, D.V. Characteristics of thermal ion outflows in the polar cap according to data of the Interball-2 satellite. Cosmic Res 47, 449–459 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S001095250906001X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S001095250906001X